Fx Yx2 Graph
Step 3 The function h (x) = (x 3)2 is of the form y = f (x c), so we know the graph of h (x) will be the same as that of f (x), but shifted left 3 units Thus, we can obtain points on the graph of h (x) by taking our points from the graph of f (x) = x2 and subtracting 3 from each of the xvalues.
Fx yx2 graph. To start, let’s consider the quadratic function y=x 2 Its basic shape is the redcoloured graph as shown Furthermore, notice that there are three similar graphs (bluecoloured) that are transformations of the original g(x)=(x5) 2 Horizontal translation by 5 units to the right;. When I type "S x^2 y^2 z^2 = 1" into the input bar, this works perfectly;. This occurs when a constant is added to any function If we add a positive constant to each ycoordinate, the graph will shift up If we add a negative constant, the graph will shift down For example, consider the functions g (x) = x 2 − 3 and h (x) = x 2 3 Begin by evaluating for some values of the independent variable x.
Algebra Graph f (x)=2 f (x) = 2 f ( x) = 2 Rewrite the function as an equation y = 2 y = 2 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b. Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;. Compared to the graph of \(y = x^2\text{,}\) the graph of \(f (x) = 2x^2\) is expanded, or stretched, vertically by a factor of \(2\text{}\) The \(y\)coordinate of each point on the graph has been doubled, as you can see in the table of values, so each point on the graph of \(f\) is twice as far from the \(x\)axis as its counterpart on the basic graph \(y = x^2\text{}\).
Use a graph of f(x) to determine the value of f(n), where n is a specific xvalueTable of Contents0000 Finding the value of f(2) from a graph of f(x)002. I've since realised that 'y' can b. The graph of a function f(x,y) with domain D is a collection of points (x,y,z) in space such that z = f(x,y), (x,y) ∈ D The domain D is a set of points in the xy plane The graph is then obtained by moving each point of D parallel to the z axis by an amount.
Translations The graph of a function can be moved up, down, left, or right by adding to or subtracting from the output or the input Adding to the output of a function moves the graph up Subtracting from the output of a function moves the graph down Here are the graphs of y = f (x), y = f (x) 2, and y = f (x) 2. The parameter a can be added to or subtracted from the input x before the rule f is applied y = f(x) becomes y = f(x ± a) These transformations are called horizontal shifts or translationsThey move the graph of the given function left (adding positive a) or right (subtracting positive a). Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with 0 0 in the expression f ( 0) = ( 0) 2 − 2 ⋅ 0 − 2 f ( 0) = ( 0) 2 2 ⋅ 0 2 Simplify the result.
The graph of a function on its own doesn't determine the codomain It is common to use both terms function and graph of a function since even if considered the same object, they indicate viewing it from a different perspective Graph of the function f ( x ) = x 4 − 4 x {\displaystyle f (x)=x^ {4}4x}. Y=f(x) and y 2 =f(x) intersect where y=0 or 1 As long as y>0, the gradients of y=f(x) and y 2 =f(x) have the same sign for a certain x value, and they have stationary points located at the same x values y 2 =f(x) is symmetrical about the xaxis At the x values where y=f(x) passes through the xaxis, provided f'(x)≠0, y 2 =f(x) passes vertically through the xaxis. In this video I try to explain what a function in maths is I once asked myself, why keep writing y=f(x) and not just y!??.
Thus, the xaxis is a horizontal asymptoteThe equation = means that the slope of the tangent to the graph at each point is equal to its ycoordinate at that point Relation to more general exponential functions. Function F(x;y) = x 2y2 at height 1" That is, we mean the set f(x;y) 2R2 jx y2 = 1g Note Every graph is a level set (why?) But not every level set is a graph Graphs must pass the vertical line test (Level sets may or may not) Surfaces in R3 Graphs vs Level Sets Graphs (z= f(x;y)) The graph of f R2!R is f(x;y;z) 2R3 jz= f(x;y)g. A (xd)² c < Basic Form Example (x3)² 3 Since there's no a, you don't have to worry about flipping on the x axis and compressing or stretchign the function Now we look at d d = 3 In order to find the zeros of the function, x must equal 3.
Graph The graph of = is upwardsloping, and increases faster as x increases The graph always lies above the xaxis, but becomes arbitrarily close to it for large negative x;. Open Middle PointSlope Exercise (2). The graph of y = f (x) is the graph of y = f (x) reflected about the yaxis Here is a picture of the graph of g(x) =(05x)31 It is obtained from the graph of f(x) = 05x31 by reflecting it in the yaxis Summary of Transformations To graph Draw the graph of f and Changes in the equation of y = f(x) Vertical Shifts y = f (x) c.
This equation into two functions, f(x,y) = p 4− x2 −y2 and f(x,y) = − p 4− x2 −y2, representing the upper and lower hemispheres Each of these is an example of a function with a restricted domain only certain values of x and y make sense (namely, those for which x2 y2 ≤ 4) and the graphs of these functions are limited to a small. The level curves of f(x,y) = x 2 y 2 are curves of the form x 2 y 2 =c for different choices of c These are circles of radius square root of c Several of them are shown below One can think of the level curve f(x,y)=c as the horizontal crosssection of the graph at height z=c When each level curve f(x,y)=c is plotted at a height of c units above the xyplane, we get the figure. Graph of z = f(x,y) New Resources SSS Triangle Exploration;.
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music. A B O c X y х X 1 Match the Question Sketch the graph of f (x,y)=x² y?. • The graph of f(x)=x2 is a graph that we know how to draw It’s drawn on page 59 We can use this graph that we know and the chart above to draw f(x)2, f(x) 2, 2f(x), 1 2f(x), and f(x) Or to write the previous five functions without the name of the function f,.
Steps for Solving Linear Equation y = f ( x ) = 2 ( x 1 ) y = f ( x) = 2 ( x 1) Use the distributive property to multiply 2 by x1 Use the distributive property to multiply 2 by x 1 y=2x2 y = 2 x 2 Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side. Description Function Grapher is a full featured Graphing Utility that supports graphing up to 5 functions together You can also save your work as a URL (website link) Usage To plot a function just type it into the function box. I have to graph a problem in Nebulous Logic with Matlab I am rusty on my commands (never used Matlab before, so i'm not sure which one command to use I am trying to make a function f(x,y)=(x10)^2(y10)^2 I need consideer a interval of 10,10 and construct five fuzzy sets (C1,C2,C3,C4,C5) for eachone.
The graphs in the pictures are correct You have to interpret y = f ( x) and y = f ( x) as relations between real numbers These relations can be graphed in the plane They are different relations, as the pictures show When f ( x) < 0, there are no points ( x, y) such that. Answer (1 of 3) y=xx y=x if x∈0,1) y=x1 if x∈1,2) y=x2 if x∈2,3) all are straight lines which bounded in certain domain so, i hope u can draw it now. I took a Matlab course over the summer, and now have to graph a problem in calculus I am rusty on my commands, so I'm not sure which one to use I am trying to make a 3d plot of a function f(x,y)=(x^21)^2(x^2yx1)^2 Do I have to open a function, or can I just use a command with a script?.
The graph of f(x) in this example is the graph of y = x 2 3 It is easy to generate points on the graph Choose a value for the first coordinate, then evaluate f at that number to find the second coordinate The following table shows several values for x and the function f evaluated at those numbers x 2 1 0 1 2 f(x) 1. The graphs of \(y = f (x)\) and \(y = g(x)\) are said to be translations (or shifts) of the graph of \(y = x^2\text{}\) They are shifted to a different location in the plane but retain the same size and shape as the original graph In general, we have the following principles Vertical Shifts. A function may be thought of as a rule which takes each member x of a set and assigns, or maps it to the same value y known at its image x → Function → y A letter such as f, g or h is often used to stand for a functionThe Function which squares a number and adds on a 3, can be written as f(x) = x 2 5The same notion may also be used to show how a function affects particular values.
Beyond simple math and grouping (like "(x2)(x4)"), there are some functions you can use as well Look below to see them all They are mostly standard functions written as you might expect You can also use "pi" and "e" as their respective constants Please. Sketch the graph of the quadratic function f(x) = −x 2 2x − 1 Indicate the coordinates of the vertex, the yintercept and the xintercepts (if any) (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE If there are multiple xintercepts, enter your answers as a commaseparated list) vertex(x, y)=. Similarly, the graph of y = x 2 3 is 3 units below the graph of y = x 2 The constant term "c" has the same effect for any value of a and b Parabolas in the vertexform or the ahk form, y = a(x h) 2 k To understand the vertexform of the quadratic equation, let's go back our orginal equation, f(x) = x 2 In this equation, remember.
A quadratic ftlnction,f, is defined on R, the set of real numbers Diagram 1 shows part of the with equation y = f (x) The turning point is (2, 3) Diagram 2 shows part of the with equation y = h(x) The turning point is (7, 6) Y Diagram 2 o (a) (2,3) Diagram 1 Given that h (x) = f a) 4 b Write down the values of a and b. Answer (1 of 15) x^2y^2=0 x^2=y^2 x=\sqrt{y^2} x=\sqrt{y^2} This is the equation of a straight line x=y and x=y Or the equivalent form y=x and y=x. Now, let's find the vertex There are several ways to do this, including using the formula b/(2a) for the xvalue ((4))/(2*1) = 4/2 = 2 Substitute x = 2 and find the yvalue (2)^24(2) = 4 8 = 4 The vertex is found at (2, 4) Here is the graph Also, I would suggest factoring the equation to find xintercepts x(x 4) = 0 so x = 0 and x = 4.
If x = 5, y = 2(5) 6 = 4 We then note that the graph of (5, 4) also lies on the line To find solutions to an equation, as we have noted it is often easiest to first solve explicitly for y in terms of x Example 2 Graph x 2y = 4 Solution We first solve for y in terms of x to get We now select any two values of x to find the associated. C < 0 moves it down We can move it left or right by adding a. Combine all terms containing F \left (x2\right)F=y ( x 2) F = y Divide both sides by x2 Divide both sides by x 2 \frac {\left (x2\right)F} {x2}=\frac {y} {x2} x 2 ( x 2) F = x 2 y Dividing by x2 undoes the multiplication by x2 Dividing by.
H(x)=x 2 5 Vertical translation by 5 units upwards;. Thus, "x 2 y 2" is written "x*x y*y" or "x^2 y^2" 2 For example, f(x,y) = x 2 y 2 will be graphed as in the image below 3 You may wish to save the graph image as a file on your PC it will use about 35 KB. The tangent plane at the graph of f ( x, y) = x 2 y 2 at ( 0, 0) is z = f ( 0, 0) ∂ f ∂ x ( 0, 0) ( x − 0) ∂ f ∂ y ( 0, 0) ( y − 0) The partial derivatives are ∂ f ∂ x = 2 x and ∂ f ∂ y = 2 y We have that f ( 0, 0) = 0 ∂ f ∂ x ( 0, 0) = 0 ∂ f ∂ y ( 0, 0) = 0.
O A OB O C X X f Sketch the graph of F (x,y) = V1 x2 y2 State the domain and range of the function. S is defined as a sphere However, when I type "S f(x,y,z) = 1" into the input bar, nothing is graphed and the algebra window shows S as an undefined Implicit Curve I need to keep the function f, so that it can be modified by the user using an input box I'd like. In order to graph a function, you have to have it in vertex form;.
I(x)=(x) 2 Reflection along the origin. We are given the quadratic function y = f (x) = (x 2)2 For the family of quadratic functions, the parent function is of the form y = f (x) = x2 When graphing quadratic functions, there is a useful form called the vertex form y = f (x) = a(x −h)2 k, where (h,k) is the vertex Data table is given below (both for the parent function and the given function). Get the free "Surface plot of f(x, y)" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Engineering widgets in WolframAlpha.
State the domain and range of the function Which of the following surface graphs represents f (x,y) = x² y2?. This tool graphs z = f (x,y) mathematical functions in 3D It is more of a tour than a tool All functions can be set different boundaries for x, y, and z, to maximize your viewing enjoyment This tool looks really great with a very high detail level, but you may find it more comfortable to use less detail if you want to spin the model.
Level Sets Math Insight
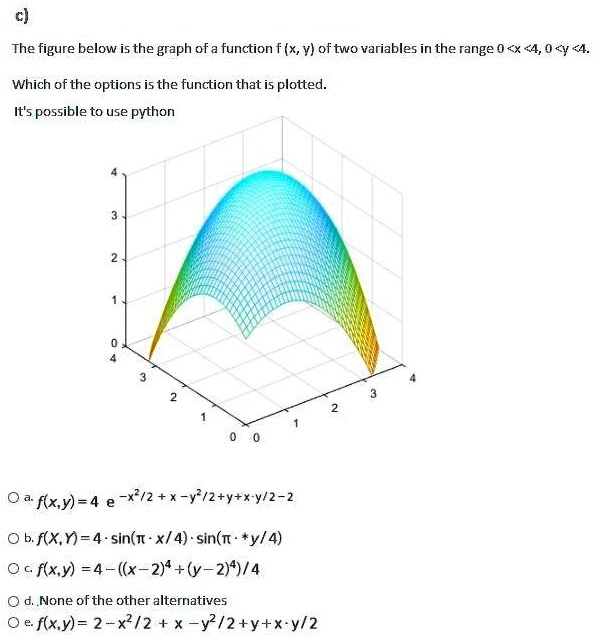
Solved The Figure Below Is The Graph Of A Function X Vl Oftwo Variables In The Range X 4 0 V 4 Which Ofthe Options Is The Function That Is Plotted It S Possible To Use Python Flx Y

Matlab Tutorial
Fx Yx2 Graph のギャラリー
Math Ntu Edu Tw
How Do You Graph F X Y Sqrt X 2 Y 2 1 Ln 4 X 2 Y 2 Socratic

Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y 16 X 2 Y 2 1 2 In The X Y Plane Study Com

Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Frac Ln X 2 Y 2 4 Sqrt 4 X 2 Sqrt 4 Y 2 Study Com
Canvas Instructure Com

Functions Of 2 Variables

Compute The Function Z F X Y 9 X 2 9y 2 Identify The Graph Of Z F X Y Study Com
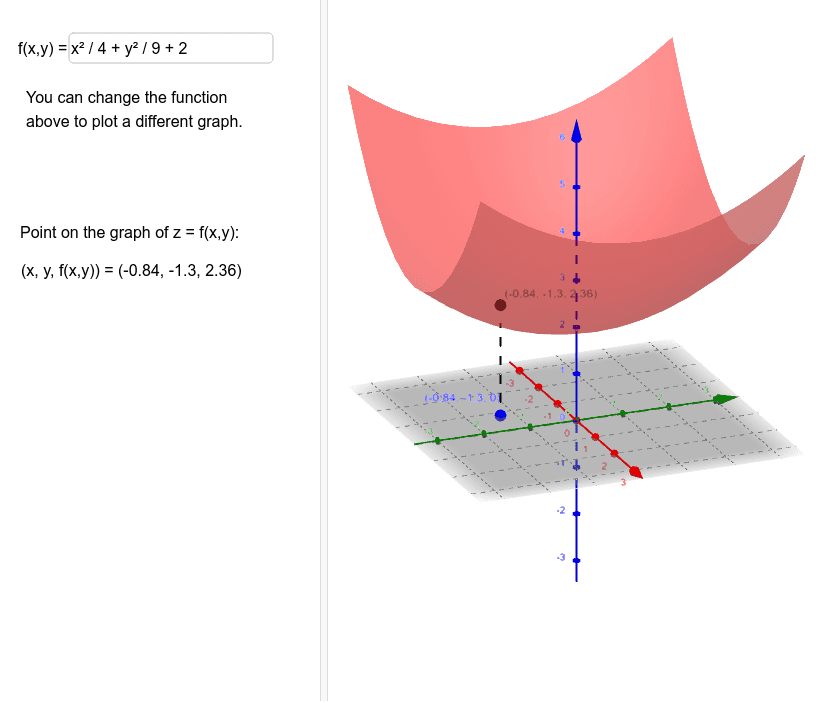
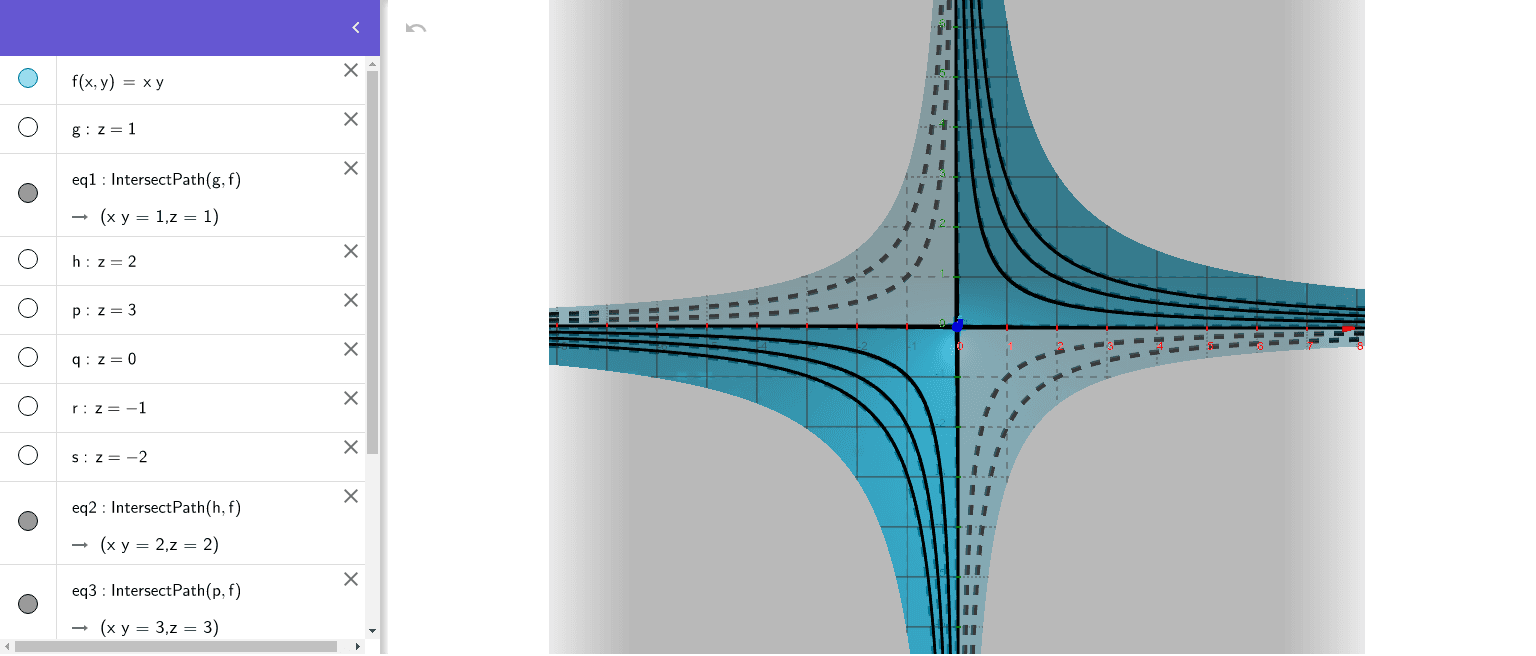
Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra
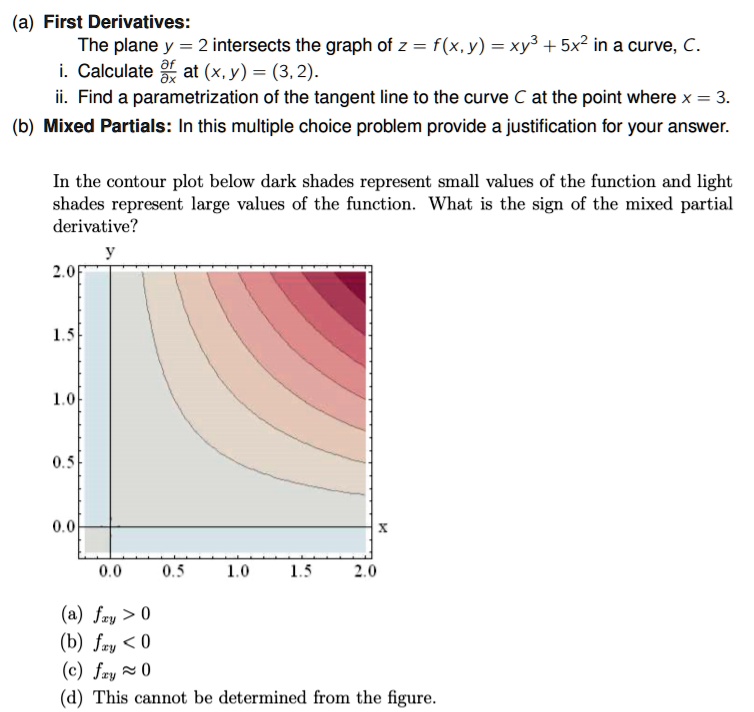
Solved A First Derivatives The Plane Y 2 Intersects The Graph Of 2 F X Y Xy3 5x2 In A Curve A Calculate 3 At X Y 3 2 Find A Parametrization
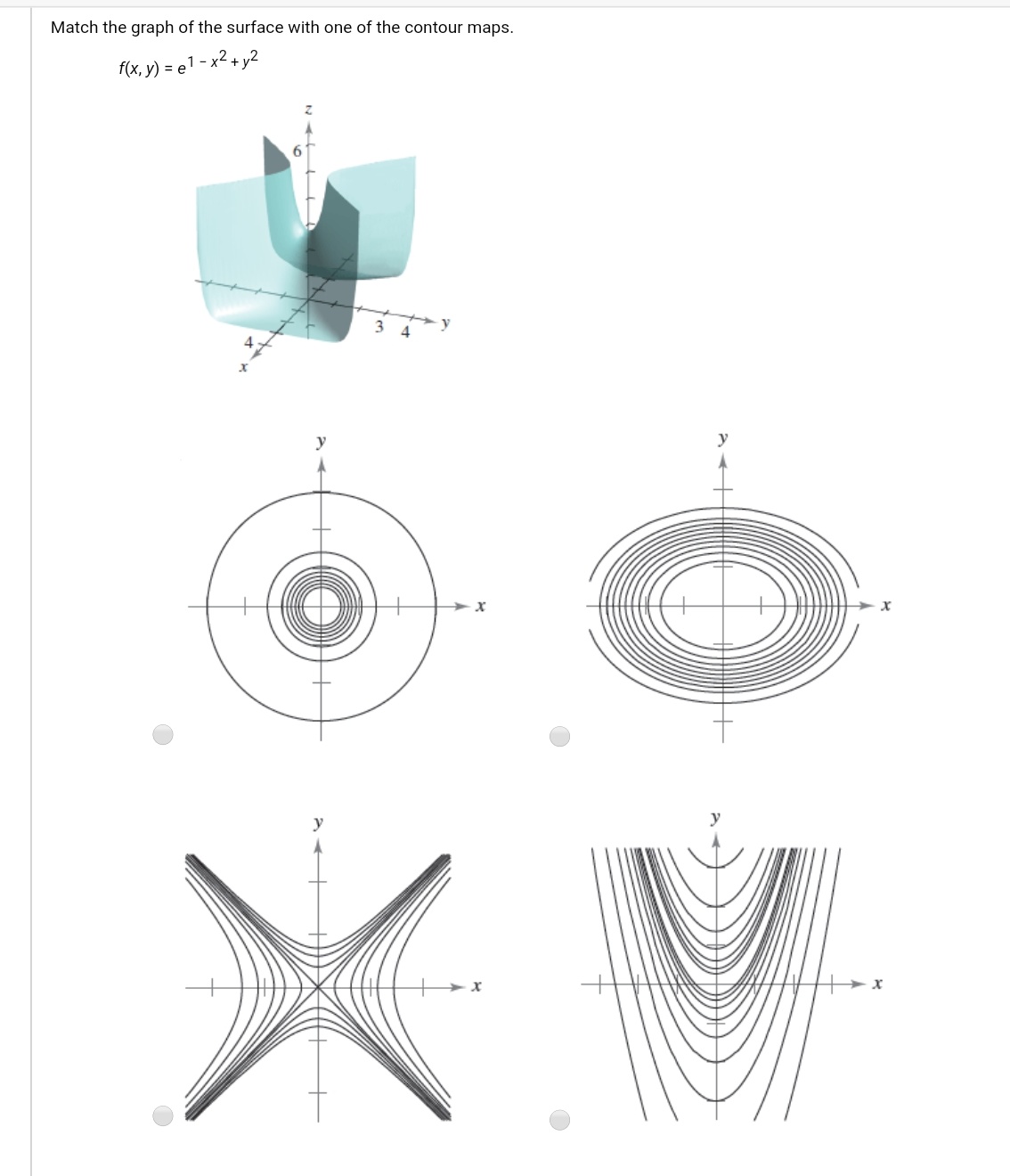
Answered Match The Graph Of The Surface With One Bartleby
A The Graph Of F X Y X 2 Y 2 The Point 0 0 Is A Download Scientific Diagram
Math Ucsd Edu

A Graph F X Y 9 X 2 Y 2 B Find The Normal Vector To The Tangent Plane For 2 1 Study Com

Contour Map Of F X Y 1 X 2 Y 2 Youtube

12 2 Graphs Of Functions Of Two Variables Visualizing A Flip Ebook Pages 1 16 Anyflip Anyflip
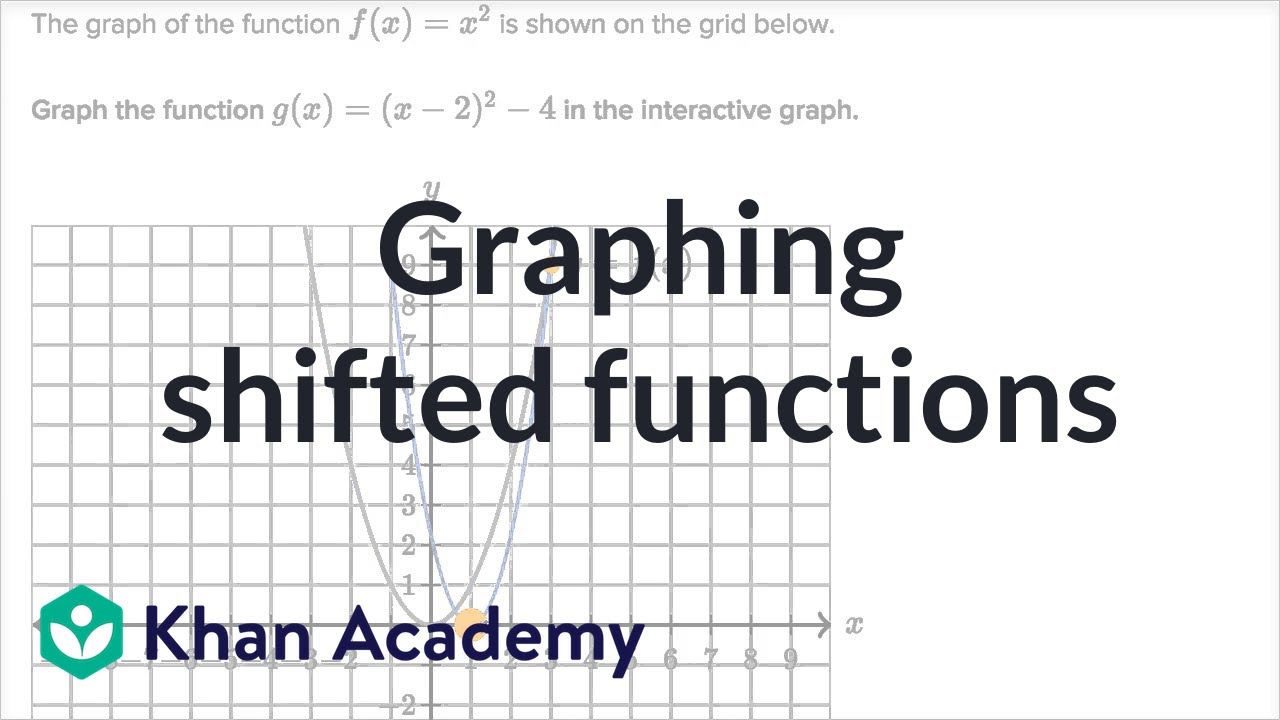
Graphing Shifted Functions Video Khan Academy
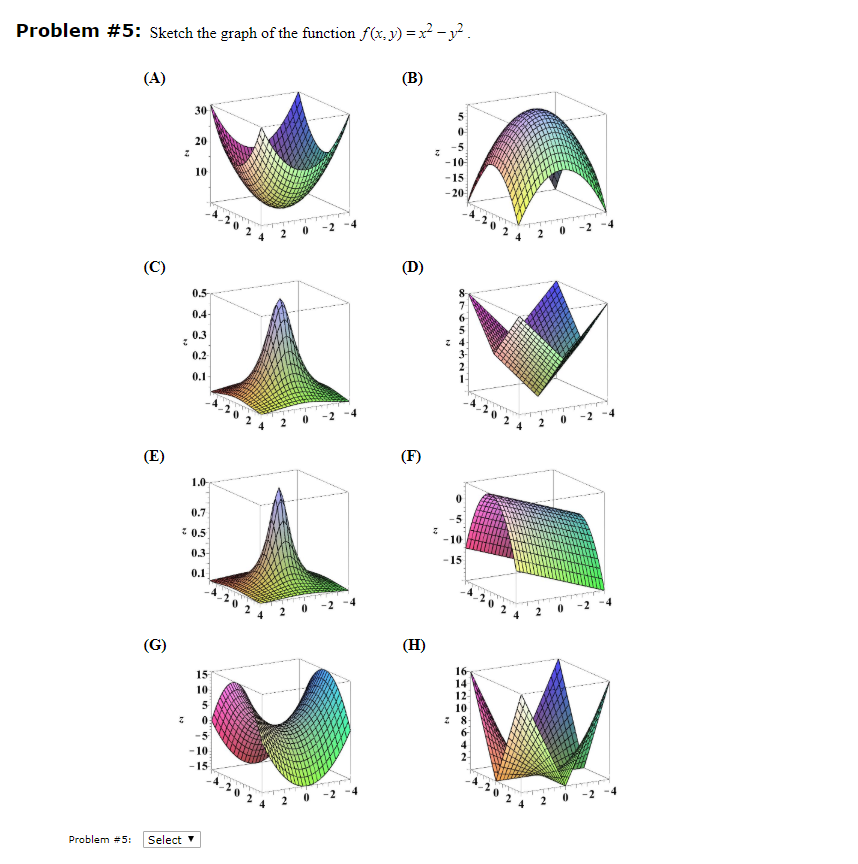
Solved Problem 5 Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Chegg Com

Matlab Tutorial
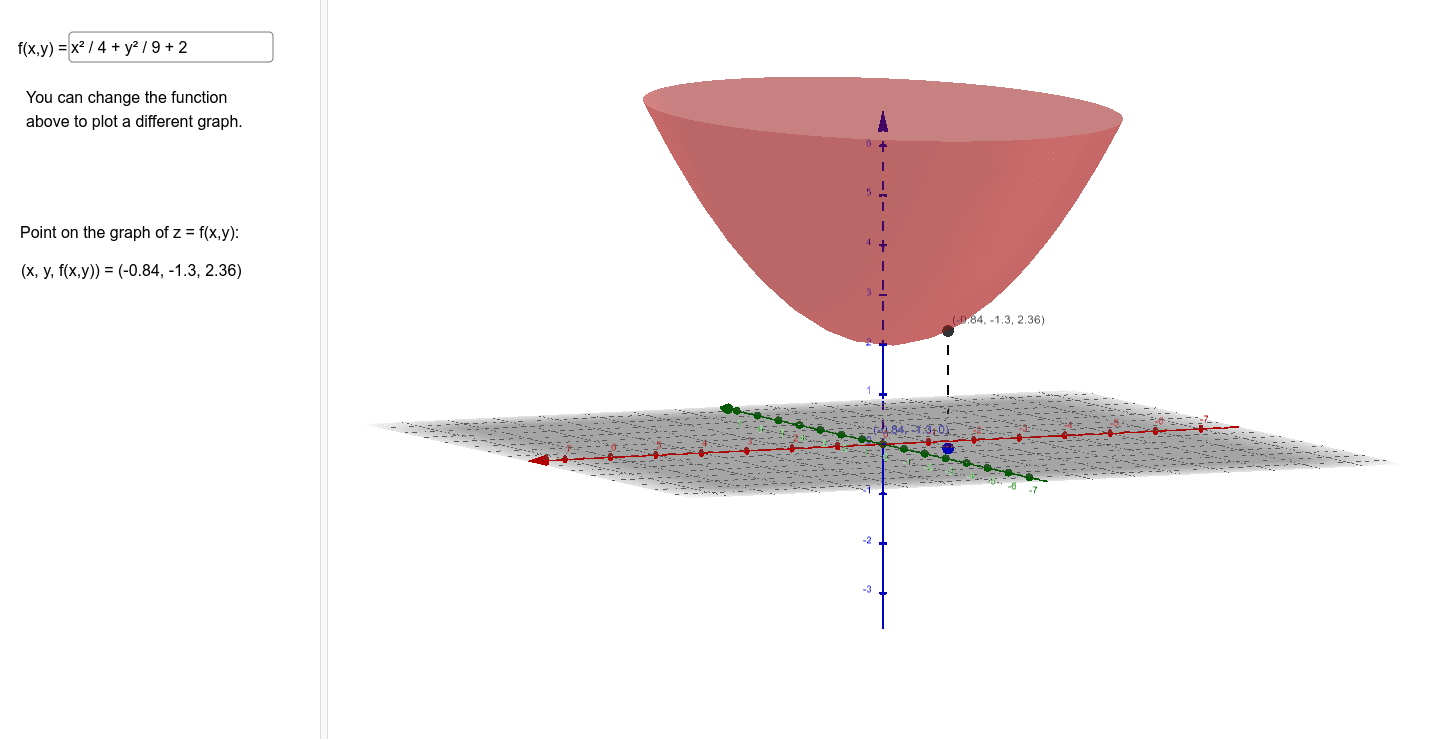
Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra

Sketch The Graph Of F X Y Sqrt 1 X 2 Y 2 State The Domain And Range Of The Function Study Com
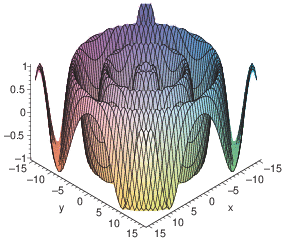
Solved Graph The Functions Below F X Y X2 Y2 Chegg Com

Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube
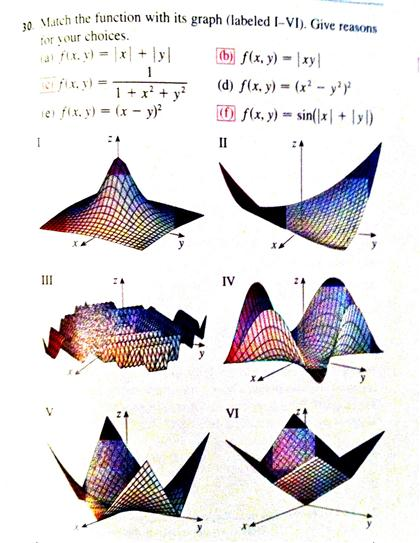
Solved Match The Function With Its Graph Labeled I Vi Chegg Com

Graphs And Level Curves

Graph And Contour Plots Of Functions Of Two Variables Wolfram Demonstrations Project

Use A Graph Or Level Curves Or Both To Find The Local Maximum And Minimum Values As Well As Saddle Points Of F X Y 9 X Y E X 2 Y 2 Then Use Calculus To

Graphing Shifted Functions Video Khan Academy

File 3d Graph X2 Xy Y2 Png Wikimedia Commons

Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download

Graphs And Level Curves
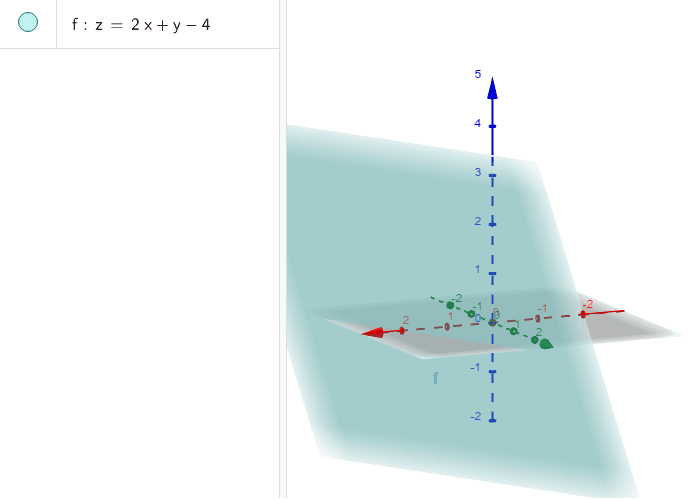
Graph Of Z F X Y 2x Y 4 Geogebra
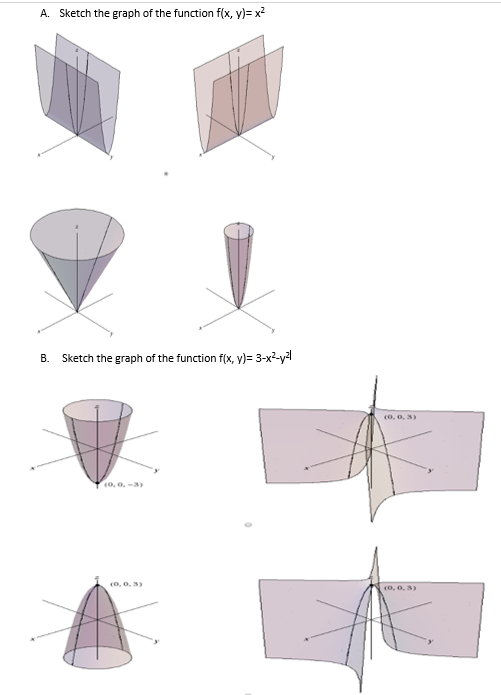
Solved A Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y X2 B Chegg Com
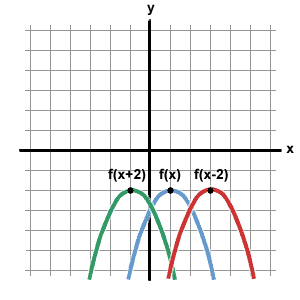
Operations On Functions Translations Sparknotes
1
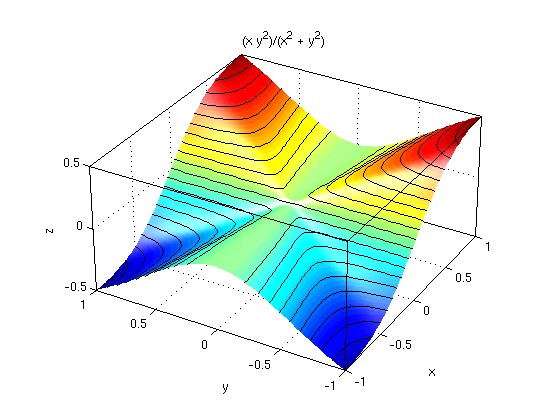
Examples Friday Feb 21
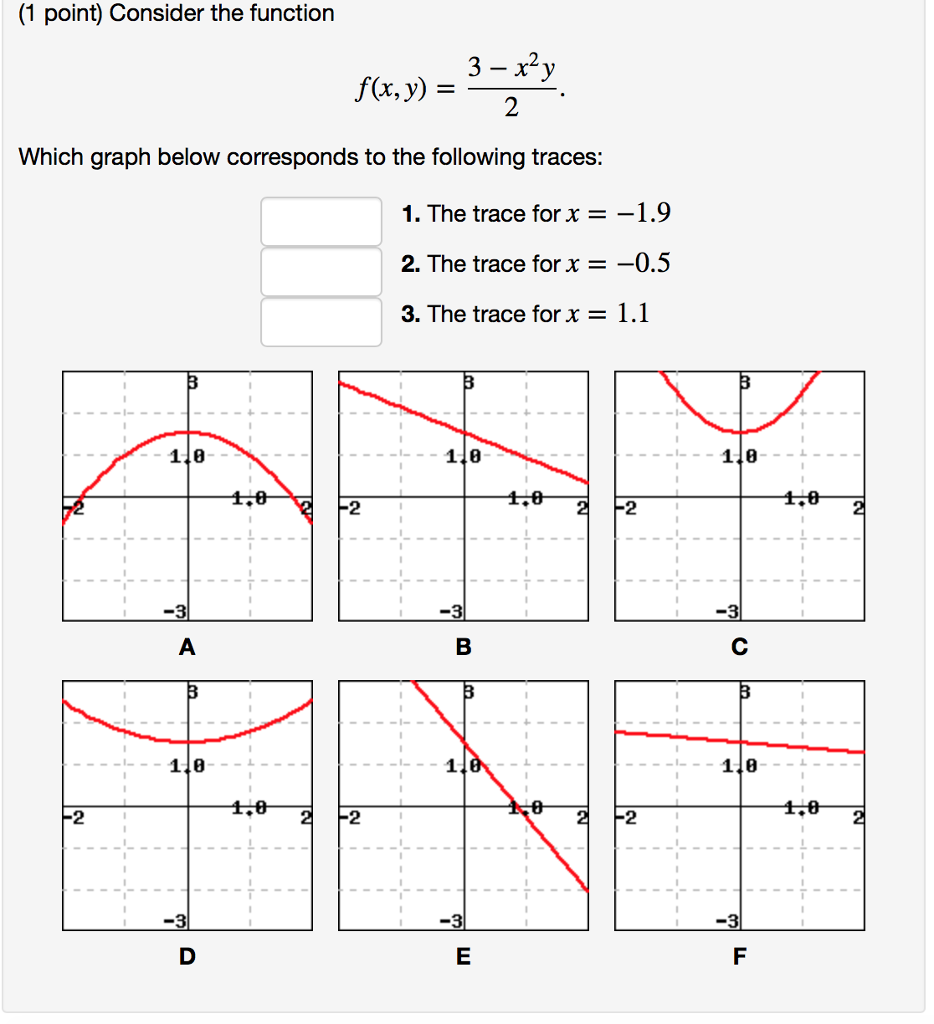
Solved Consider The Function F X Y 3 X2y2 F X Y 3 Chegg Com
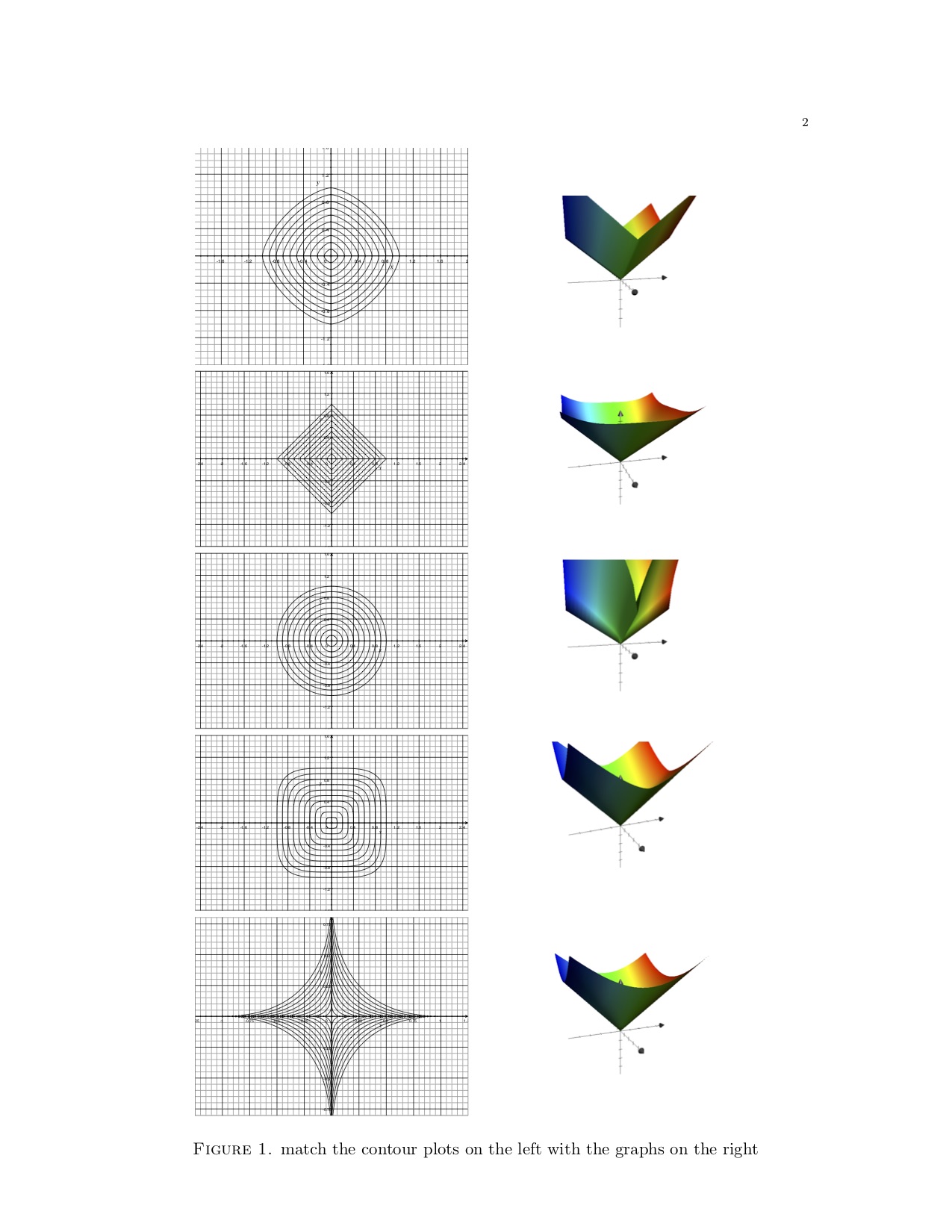
0 3 Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables
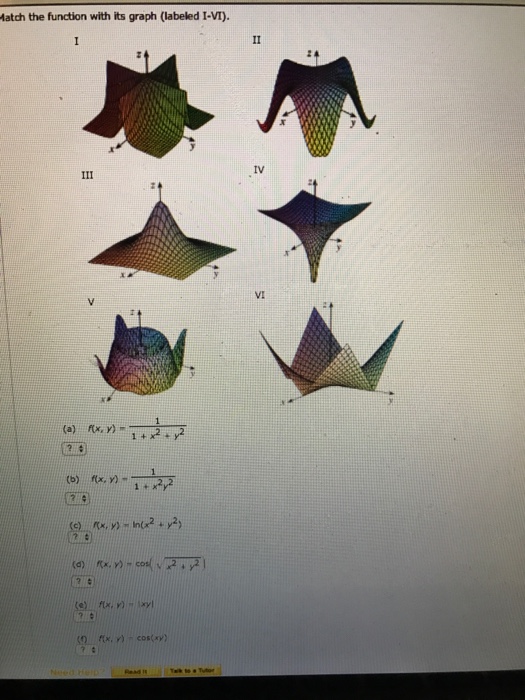
Solved Match The Function With Its Graph Labeled I Vi Chegg Com
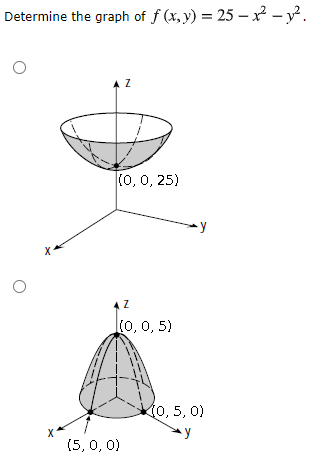
Solved Determine The Graph Of F X Y 25 X2 Y2 Az Chegg Com
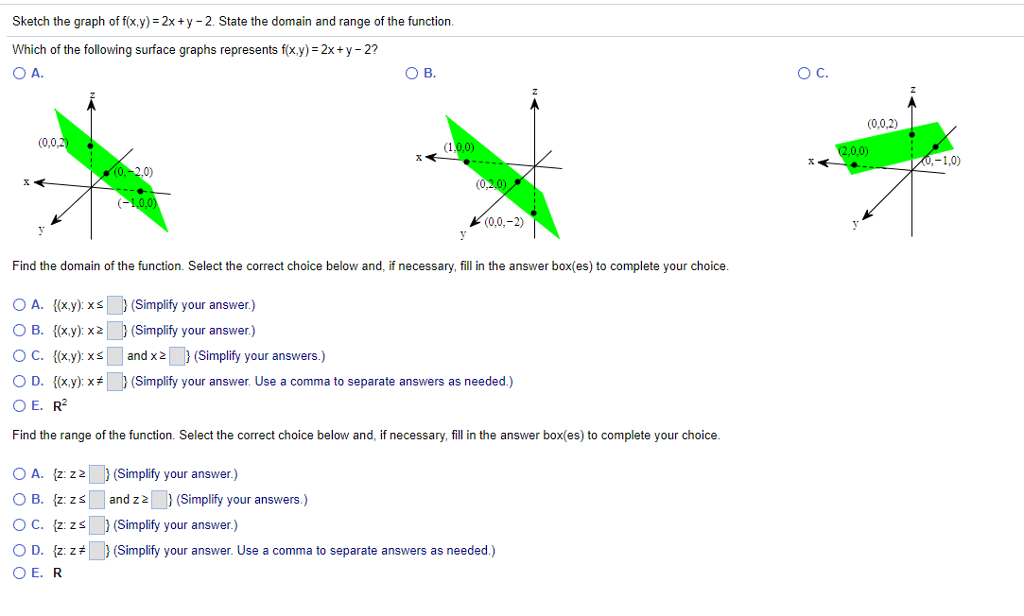
Solved Sketch The Graph Of F X Y 2x Y 2 State The Domain Chegg Com
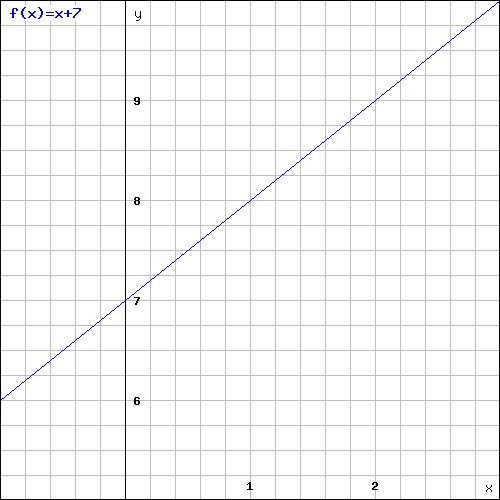
Functions And Linear Equations Algebra 2 How To Graph Functions And Linear Equations Mathplanet
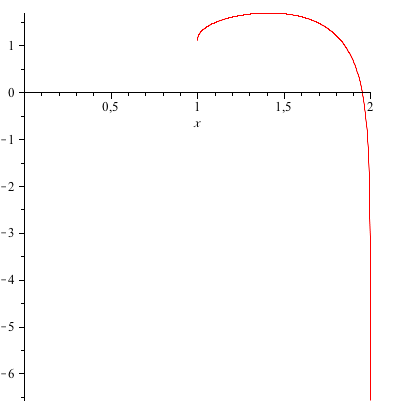
How Do You Graph F X Y Sqrt X 2 Y 2 1 Ln 4 X 2 Y 2 Socratic

F X Y Xy Geogebra
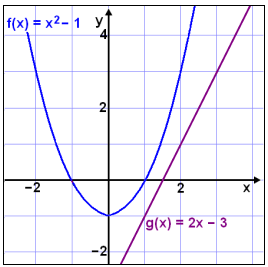
Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations
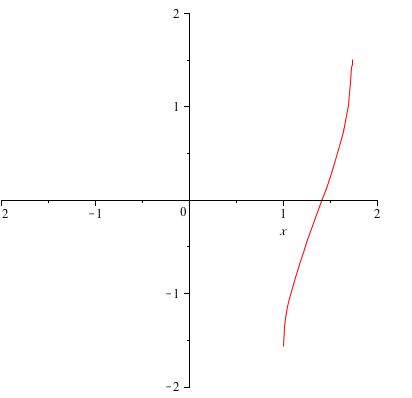
How Do You Sketch F X Y Arcsin X 2 Y 2 2 Socratic
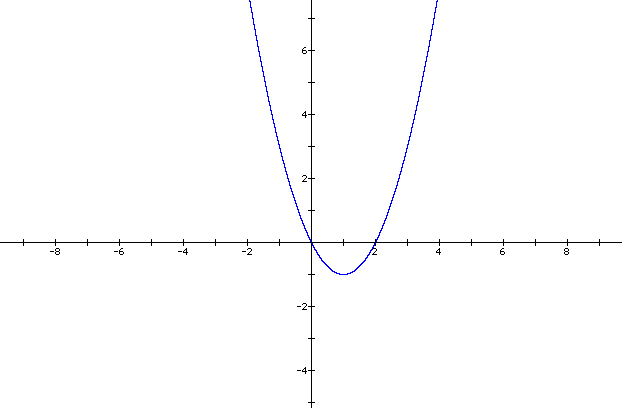
Graphing Quadratic Functions

Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Sqrt 4x 2 Y 2 Study Com
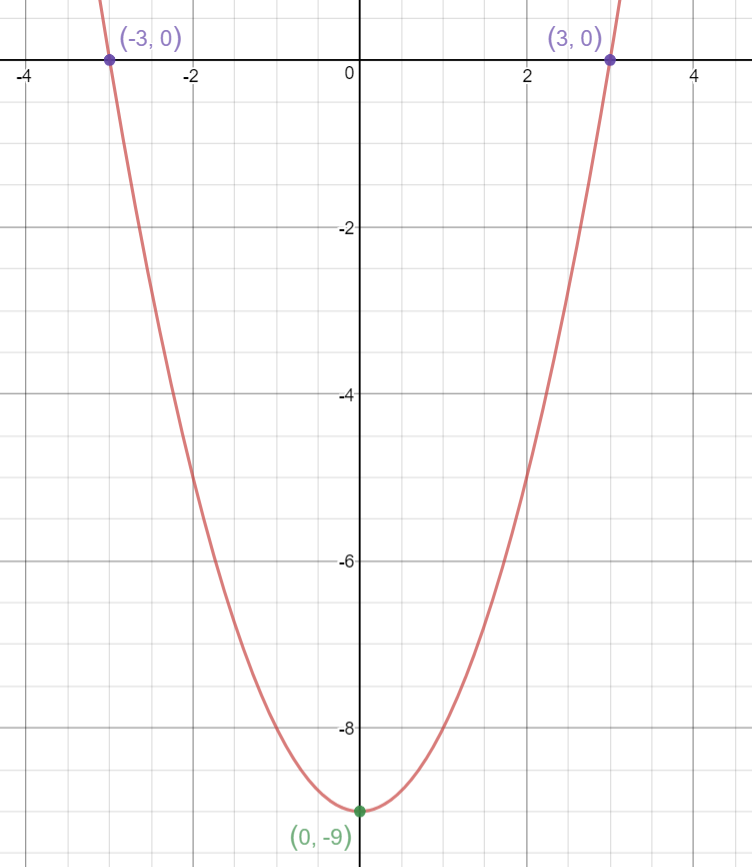
How Do You Graph Y X 2 9 Socratic
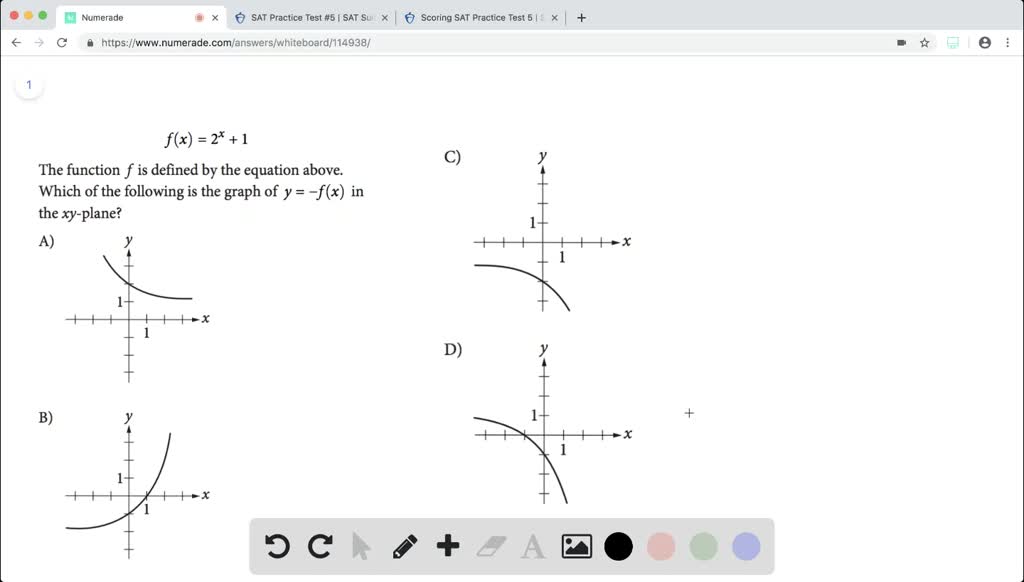
Solved F X 2 X 1 The Function F Is Defined By The Equation Above Which Of The Following Is The Graph Of Y F X In The X Y Plane
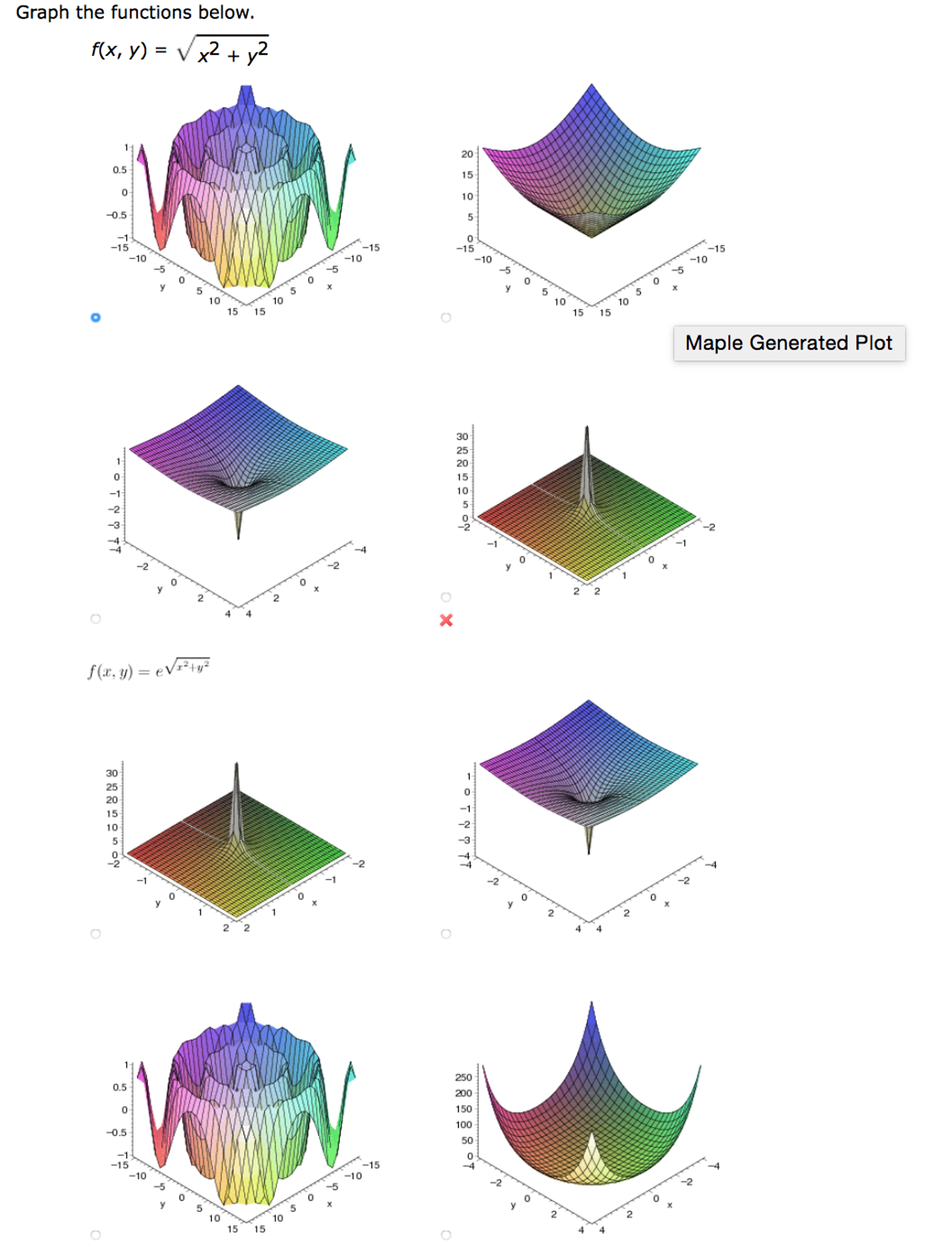
Solved Graph The Functions Below F X Y Squareroot X 2 Chegg Com

Graphs And Level Curves
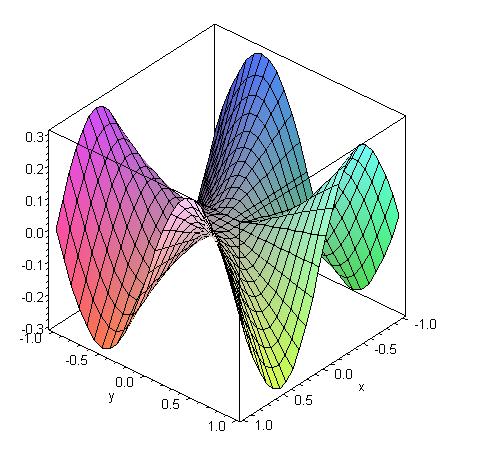
A Function For Which Fxy Fyx Graph Of The Function Given By F X Y X3y Xy3 X2 Y2 For X Y 0 0 And F 0 0 0 Graph Of Fx Note That The Slope In The Y Direction Through The Center Of The Graph Appears To Be Negative It Can Indeed Be Verified That Fxy 0

3 7 Graphs Of Functions Mathematics Libretexts
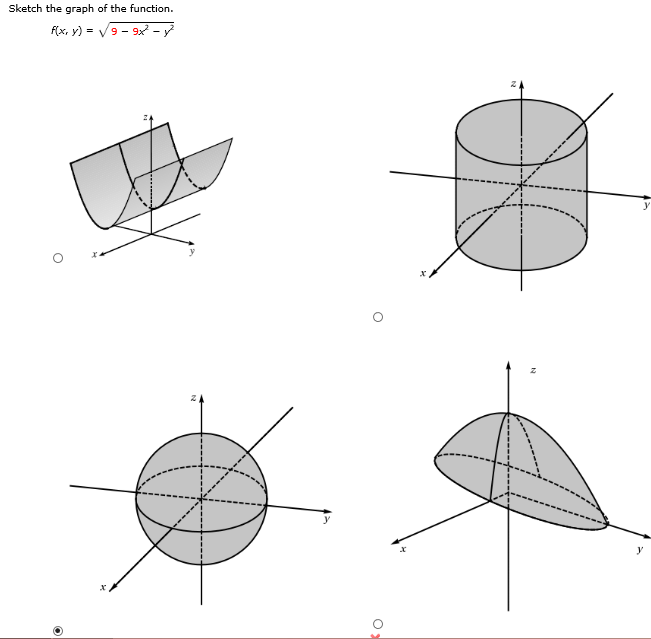
Solved Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Root Chegg Com

Reflecting Functions Examples Video Khan Academy
21 Graph Of The Function F X Y 2xy C X 2 Y 2 C Used For L And Download Scientific Diagram

If X X1 X2 Represents A Point In A Subset A Of Rn And F X Is Exactly One Point In Rm Then We Say That F
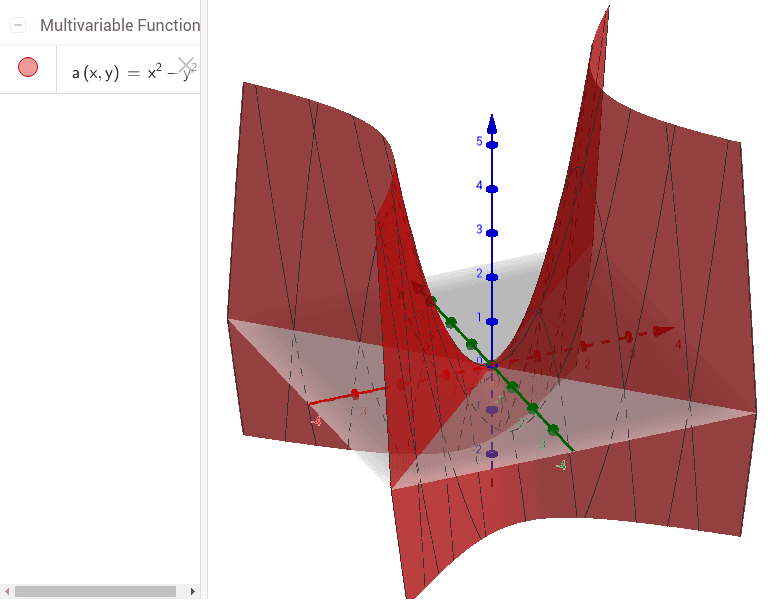
Graph Of F X 2 Y 2 Geogebra

Matlab Tutorial
Graph Domain And Range Of Absolute Value Functions
Quadratics Graphing Parabolas Sparknotes
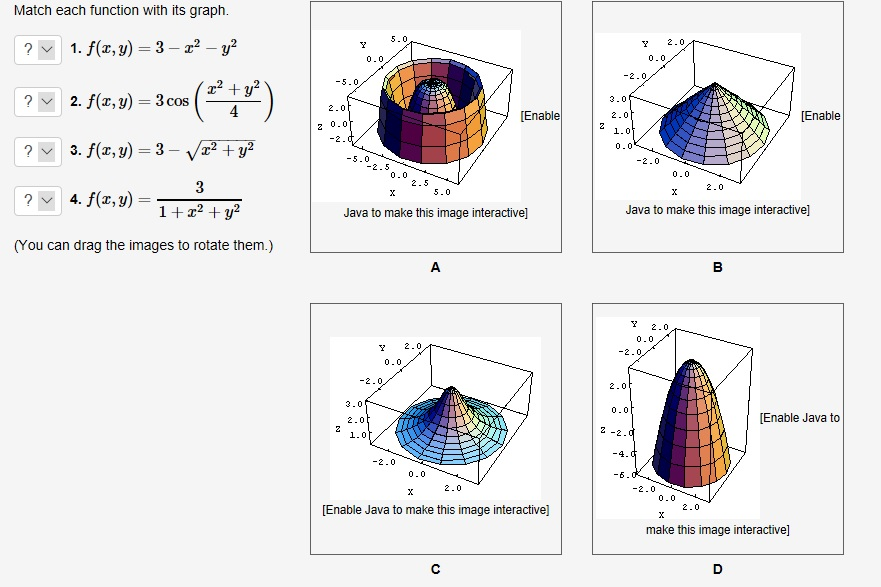
Solved Match Each Function With Its Graph 1 F X Y Chegg Com

3 This 2d Example Where X Y Are The Configuration Parameters Download Scientific Diagram

Critical Points Of Functions Of Two Variables
F X Y X 2

Plot F X Y X 2 Y 2 Tex Latex Stack Exchange

Graph Of The Function F 1 3 1 3 2 0 For The Form F X Y Xy Download Scientific Diagram

If F X Y 9 X 2 Y 2 If X 2 Y 2 Leq9 And F X Y 0 If X 2 Y 2 9 Study What Happens At 3 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange

The Function F X X 3 X 2 X 11 4 Is Graphed In The Xy Plane Above If K Is A Constant Such That The Equation F X K Has Three
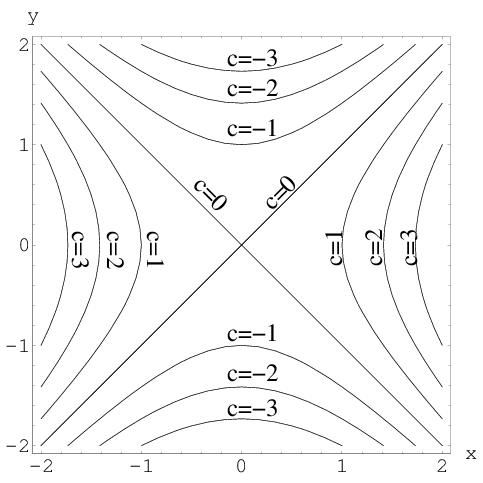
Level Set Examples Math Insight
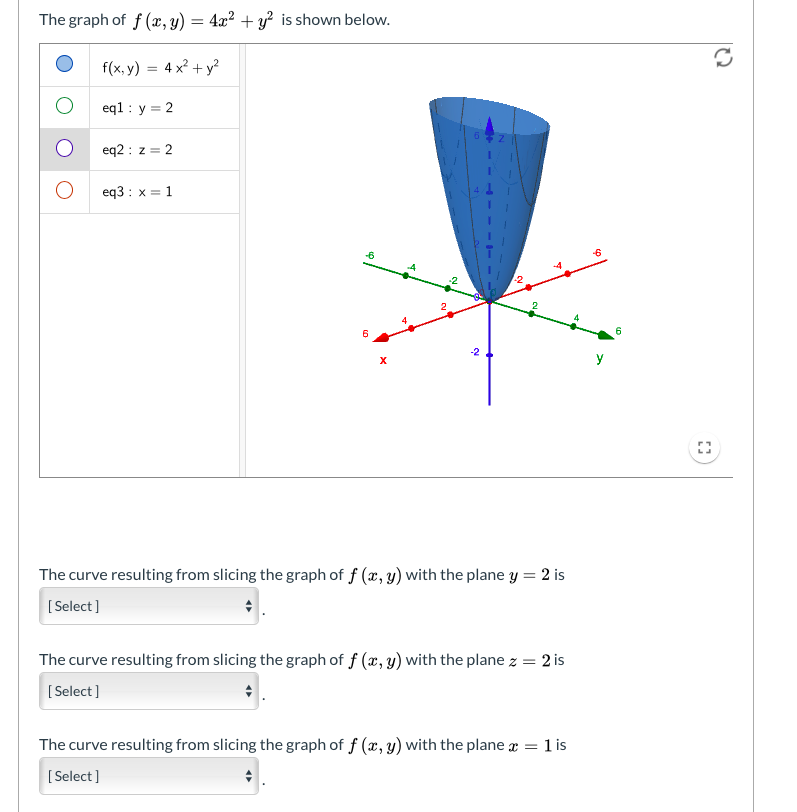
Solved The Graph Of F X Y 4 X2 Y2 Is Shown Below Chegg Com
Z Xy Surface
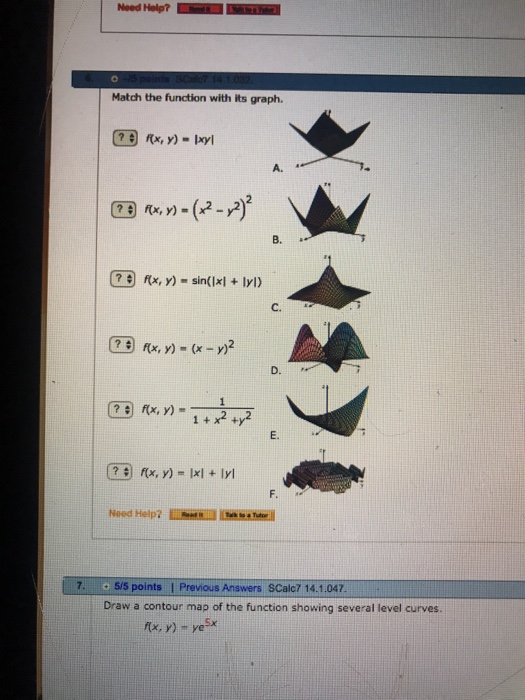
Solved Match The Function With Its Graph F X Y Xy Chegg Com
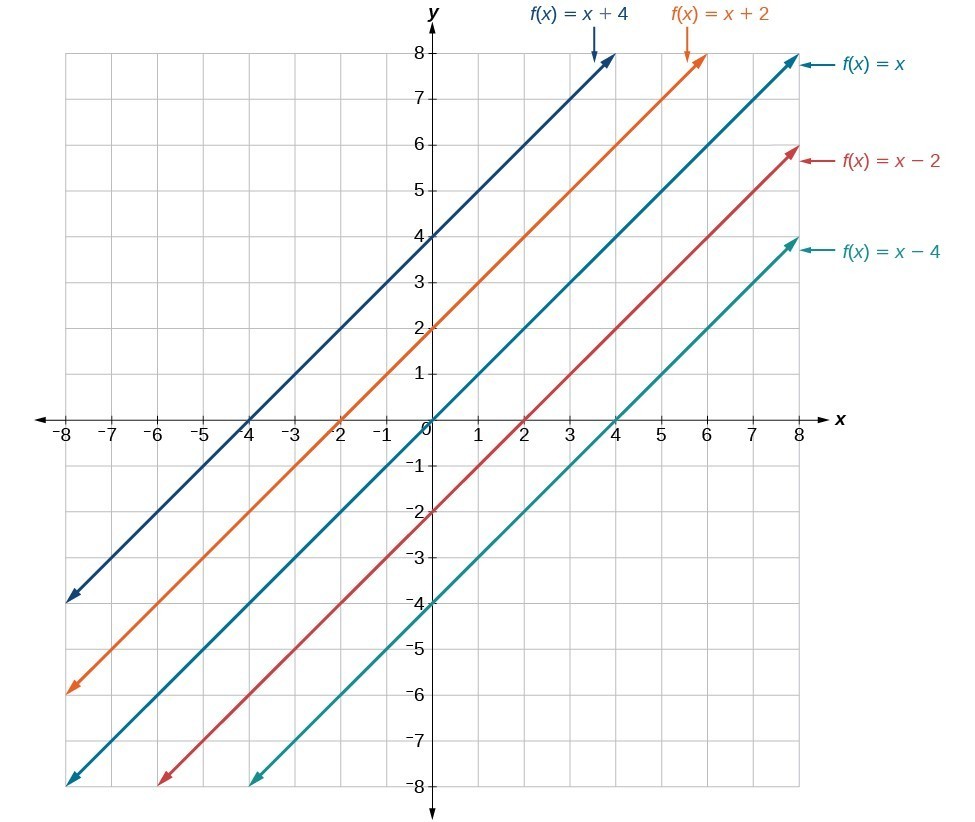
Read Transform Linear Functions Intermediate Algebra

How To Find The Graphs Of The Following Multi Variable Functions F X Y Ln 1 Xy And F X Y Frac Y E X Mathematics Stack Exchange
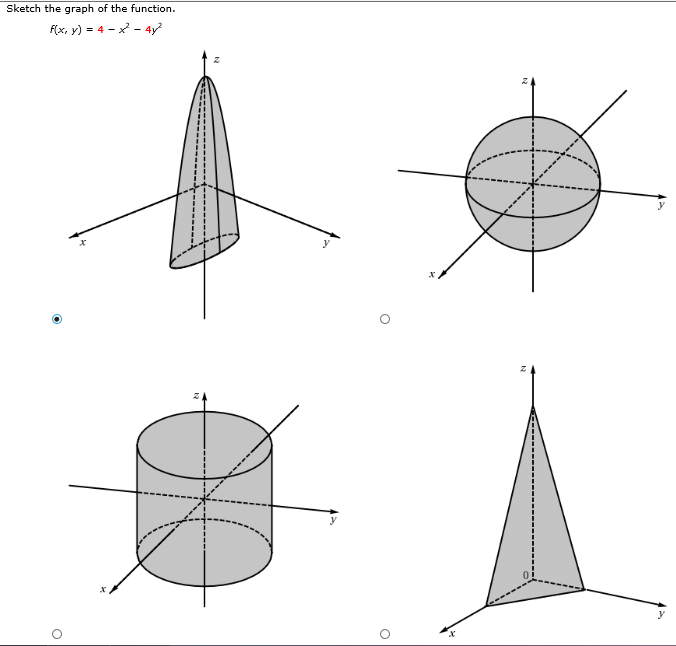
Solved Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y 4 X 2 Chegg Com
What Are The Extrema And Saddle Points Of F X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Y Socratic

Plot The Graph Of The Function F X Y 1 2x 2 2y 2 Study Com
File F X Y Cosx 2 Cosy 2 2 Png Wikipedia

Implicit Differentiation

Solved Match The Function With Its Graph F X Y X Chegg Com
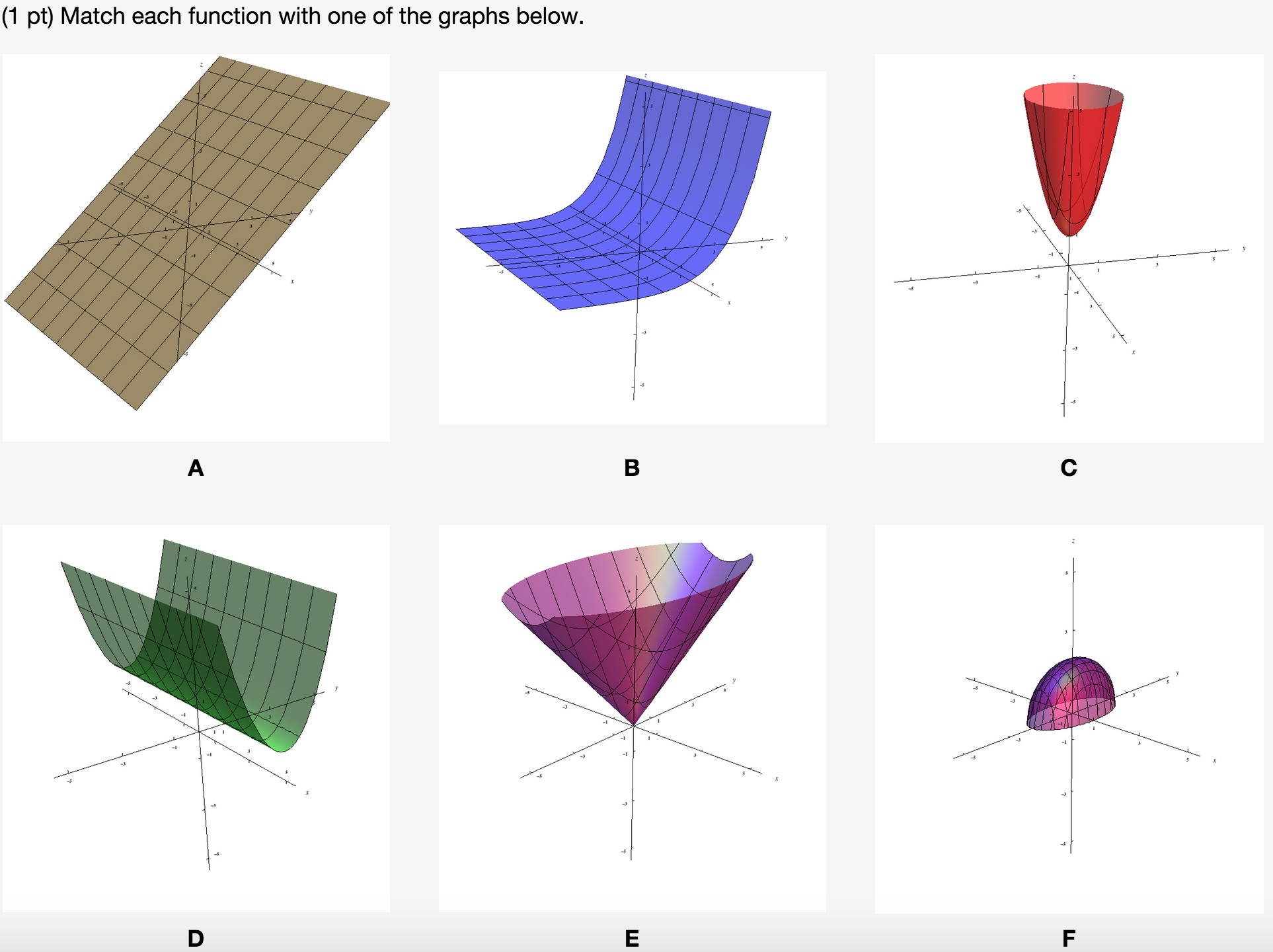
Solved Match Each Function With One Of The Graphs Below 1 Chegg Com
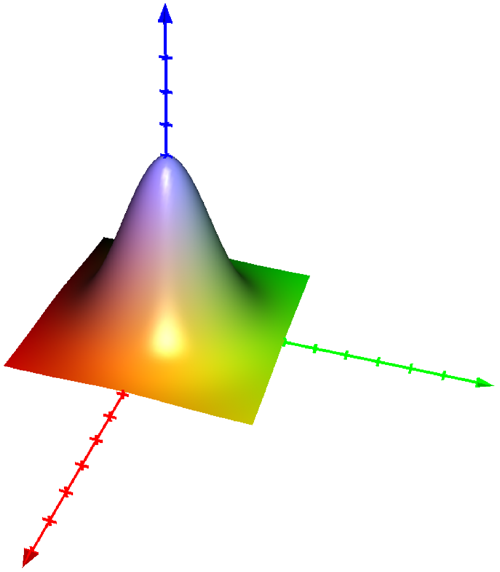
Graph Of A Function In 3d

Graph Of The Function F 1 3 1 3 2 0 For The Form F X Y Download Scientific Diagram
Evlm Stuba Sk

Matlab Tutorial
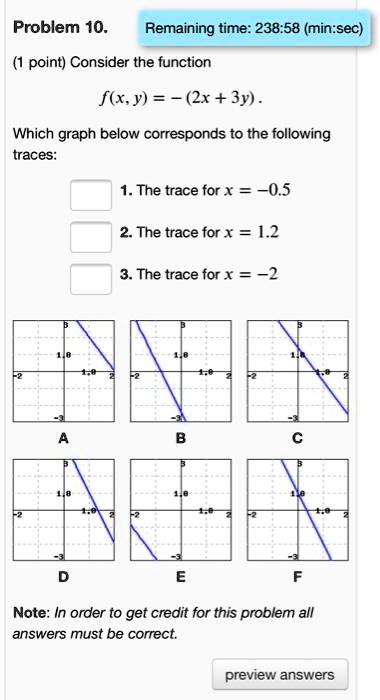
Solved Problem 10 Remaining Time 238 58 Min Sec Point Consider The Function F Xy 2x 3y Which Graph Below Corresponds To The Following Traces 1 The Trace For 4 05 2
Graph Of A Function Wikipedia
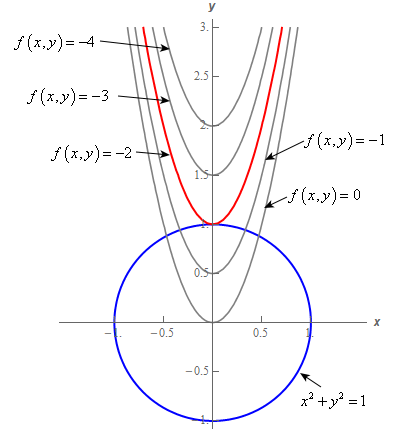
Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers
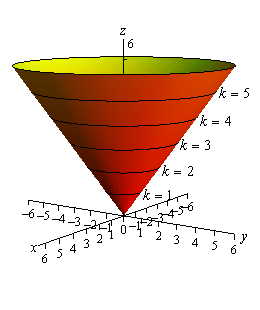
Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables
1

Let F X Y Sqrt 100 X 2 Y 2 A Sketch The Domain And The Level Sets In One Graph B Find The Gradient At The Point 2 3 C Find The Limit

Graph And Contour Plots Of Functions Of Two Variables Wolfram Demonstrations Project

13 1 Functions Of Multiple Variables Mathematics Libretexts
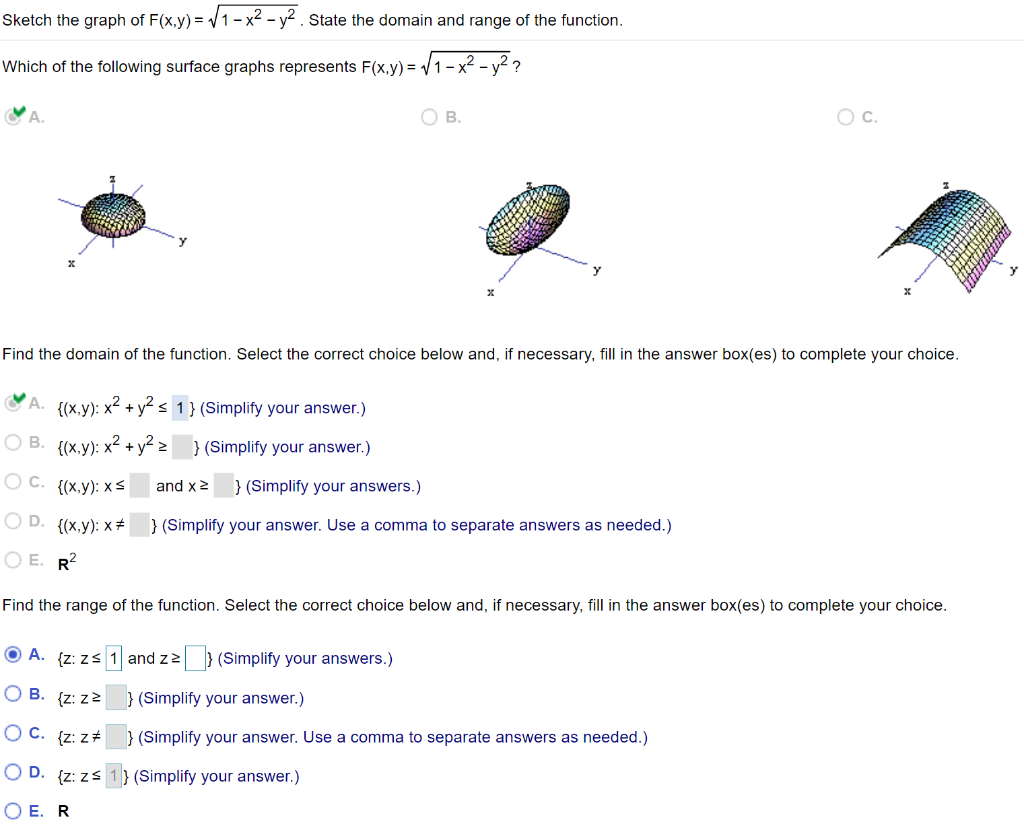
Solved Sketch The Graph Of F X Y Sqrt 1 X 2 Y 2 State The Chegg Com

Graphs And Level Curves
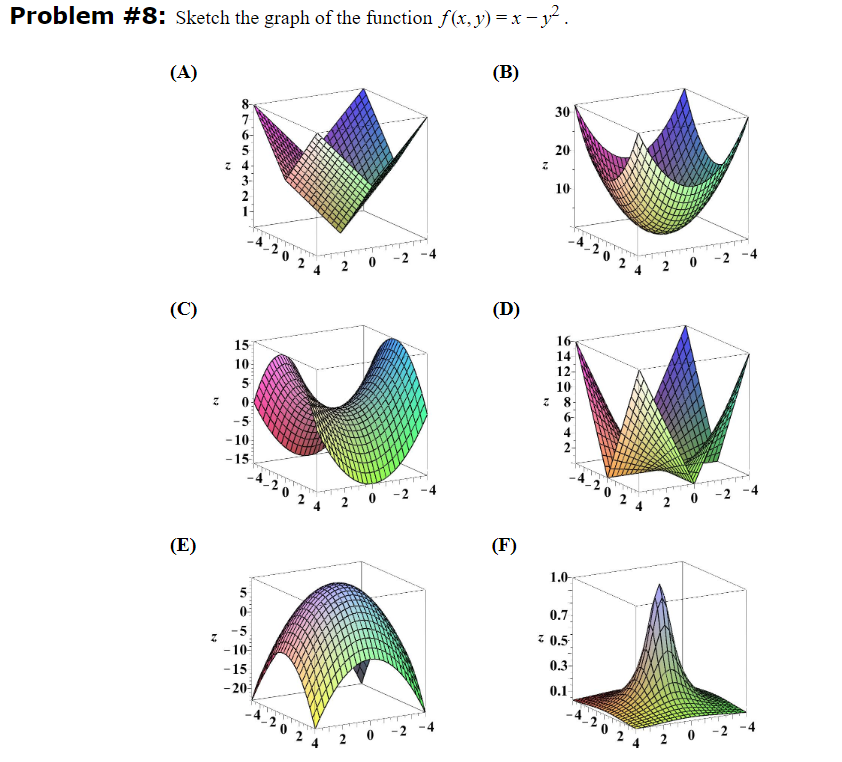
Solved Problem 8 Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Chegg Com
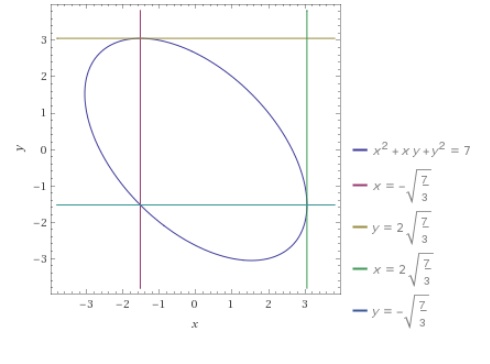
How Do You Find All Points On The Curve X 2 Xy Y 2 7 Where The Tangent Line Is Parallel To The X Axis And The Point Where The Tangent Line
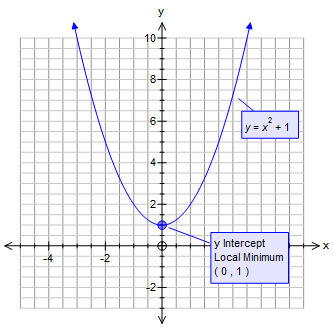
How Do You Graph Y X 2 1 Socratic
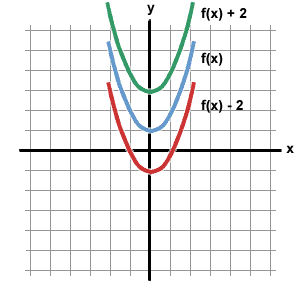
Operations On Functions Translations Sparknotes
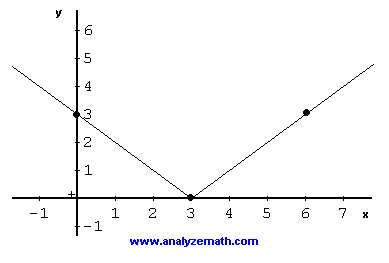
Graphing Square Root Functions




