If Ux Yx2+y2+2x 3xy Then
Harmonic conjugate v(x, y) when (a) u(x, y) = 2x x3 3xy2 Solution uxx = 6x and uyy = 6x, so uxx uyy = 0 ie u(x, y)isharmonic Let v(x, y)beaharmonicconjugate Then u(x, y) and v(x, y) satisfy the CauchyRiemann conditions v(x, y) = ∫ vydy = ∫ uxdy (since ux = vy) = ∫ (2 3x2 3y2)dy = 2y 3x2 y y3 ϕ(x), where ϕ(x) is an undetermined function of x Since vx = uy, we have.

If ux yx2+y2+2x 3xy then. This means that a function u(x,y) exists such that du = ∂u ∂x dx ∂u ∂y dy = P dxQdy = 0 One solves ∂u ∂x = P and ∂u ∂y = Q to find u(x,y) Then du = 0 gives u(x,y) = C, where C is a constant This last equation gives the general solution of P dxQdy = 0 Toc JJ II J I Back. Where gis an arbitrary function of one variable, Lis the characteristic line segment from the yaxis to the point (x;y), and the integral is a line integral (Hint Use the coordinate method) 11 Use the coordinate method to solve the equation u x 2u y (2x y)u= 2x2 3xy 2y2 Exercise 13 1. X y= 9 x2y2 Taking d dx of both sides, d dx p x y = d dx 9 x2y2 1 2 1 p x y 1 dy dx = 2xy 2 x2y dy dx Expanding left side 1 2 1 p x y dy dx 1 2 1 p x y = 2xy 2 x2y dy dx Gathering terms with and without dy dx, dy dx 1 2 p x y 2x 2y = 2xy 1 2 p x y To simplify a little we multiply both sides through by 2 p x y dy dx 1 4x2y p.
2 Answers 0 votes Remeber the formulae d/dx (uv) = uv'vu' d/dx (u/v) = (vu'uv')/v^2 y' = (3x^2yy^2)/ (2x^33xy) Apply derivative on each side with respect of x answered by david Expert Please log in or register to add a comment 0 votes. “main” 07/2/16 page CHAPTER 1 FirstOrder Differential Equations where h(y) is an arbitrary function of y (this is the integration “constant” that we must allow to depend on y, since we held y fixed in performing the integration10)We now show how to determine h(y) so that the function f defined in (198) also satisfies. Solution (i) We have u(x;y) = 2x 2xy, so uxx = uyy = 0 ) uxx uyy = 0 We nd the harmonic conjugate ux = 2(1 y) = vy) v = 2y y2 ˚(x) vx = ˚0(x) = uy = 2x ) ˚(x) = x2 c ) v = x2 y2 2yc (ii) We have ux = 2e 2x sin(2y) ) uxx = 4e 2x sin(2y) uy = 2e 2x cos(2y) ) uyy = 4e2x sin(2y) ) uxx uyy = 0 We can now determine the harmonic conjugate ux = 2e 2x sin(2y) = vy) v = e 2x.
Suppose that y = y1(x) and y = y2(x) are solutions of equation (1)Under what conditions is (2) the general solution of (1)?. $v(x, y) = 3x^2 y y^3 v(0, 0);. \tag{18}$ it is easily checked that such $v(x, y)$ satisfies the CR equations with the given $u(x, y)$;.
U(x;y) = (a2 b2) 1=2 Z L fds g(bx ay);. 17) Prove that a necessary condition for a complex function w = f(z) = u(x,y)iv(x,y) to be analytic at a point z =xiy of its domain D is that at (x,y) the first order partial derivatives of u and v with respect to x and y exist and satisfy the Cauchy – Riemann equations u x =vy and u y =−vx 18). Consider y as a function of x defined implicitly by \begin{equation*} 2x^{2}y3xy^{2}=6 \end{equation*} The derivatives of both sides should be equal The derivative of the RHS is 0,.
∂2 f ∂x2 = (1 xy)(3y) y 1 3xy) = 4y 6xy2 (1610) ∂2 f ∂y∂x = (1 xy)(3x) x 1 3xy) = 4x 6x2y (1611) ∂2 f ∂x∂y = 4x (1 xy) 2x2y 4x 6x2y (1612) ∂2 f ∂y2 = 2x2 (x) 2x3 Notice that the second and third lines are equal This is a general fact the mixed partials (the middle terms above) are equal when the second. @f @x = 2xe2x3 e 2x y;. (b) Compute the second order partials u_xx, u_yy and verify u_xx u_yy=0 (ie, u is a harmonic function);.
(iv) y y 2 x y 3 x 2 y 4 x 3 SolutionThe coefficient of x 2 in the given expression is y 3 Coefficient is the numerical factor in a term Sometimes, any factor in a term is called the coefficient of the remaining part of the term 55 Find the numerical coefficient of each of the terms (i) x 3 y 2 z, xy 2 z 3, –3xy 2 z 3, 5x 3 y 2. (c) ux 2uy (2x−y)u= 2x2 3xy−2y2 We let η= y−2xand ξ= x So y= η2ξ Then we have uξ −ηu= 5ξη−2η2, eξηu ξ = (5ξη−2η2)eξη, u= 5ξ−2η− 5 η eξηf(η), u= 9x−2y− 5 y−2x f(y−2x)exy−2x2 2 Consider the equation 3uy uxy = 0 (a) What is its type?. Therefore fxy = fyx a = 2 By inspection, 2 2 ⇔ one sees that if a = 2, f(x,y) = x y 3xy is a function with the given fx and fy 2A5.
@f @y = 3xy 2xy (c) f(x;y) = x 3y ex;. Explanation differentiate implicitly with respect to x the term 3xy is differentiated using the product rule ⇒ 2x 3(x dy dx y1) 2y dy dx = 0 ⇒ 2x 3x dy dx 3y 2y dy dx = 0 ⇒ dy dx (3x 2y) = −2x − 3y ⇒ dy dx = − 2x 3y 3x 2y. @f @y = x (d) f(x;y) = xe2x 3y;.
Where u(x;y;z) = exyz Solution. Typo/misspeak around 4 minutes 369=27Multivariable Calculus Find all local maxima/minima and saddle points for the function f(x,y) = x^3 3xy y^3 W. (x2 1 ¯1)y1 ˘(x2 1 ¯1)y2 by(x2 1 ¯1) togety1 ˘ y2 Hence(x1,y1)˘(x2,y2) Now we prove the function is surjective Let (a, b) 2 R2 Set x ˘1/3 and y a/(b2/3 ¯1) Then f(x,y) ˘ ((b2/3 ¯1) a b2/3¯1,(b1/3)3) ˘ (a,b) Itnowfollowsthat f is bijective Finally,wecomputetheinverseWritef (x ,y )˘ u v Interchangevariablesto get (x, y) ˘f.
Dy/dx = (3y2x)/(2y3x)=y/x =m returns x^2y^2= 3xy And m^2 3m1 =0 From which m= ( 3sqrt(5))/2 =03 There is a second solution, corresponding to swapping x and y, since the equation in symmetric in x and y m = 1/03 = ( 3 sqrt(5))/2 = 2618 Also, a rectangle formed by the 4 solutions at constant radius has an aspect rati. ∂u ∂y = 1/x 1(y/x)2 = x x2 y2 ⇒ ∂2u ∂y2 = −2xy (x2 y2)2 Thus ∆u = 0 and u is harmonic More generally we have the following result Theorem 1 analytic and u,v ∈ C2(Ω), then u and v are harmonic on Ω Remarks 1 The C2 hypothesis is actually unnecessary As we will see, if f is analytic, then Ref and Imf are in fact C∞. U(x, y) =min(2X, 3Y) This is an example of perfect complements The MRS is undefined at the vertex where 2X=3Y But lets graph the indifference curve, remember they L shaped We need to find the corner point To do this set the two elements of in the utility function equal to each other so there is no extra X or Y being consumed that.
QUESTIONShowthatu(x;y) = 2x¡x33xy2 isharmonic Findaconjugate harmonic function v(x;y) and identify the corresponding analytic function uiv ANSWER Easy to show uxx uyy = 0, so u is harmonic Let v be the conjugate harmonic function Then vy = ux = 2¡3x2 3y2 Thus v(x;y) = 2y¡3x2yy3 `(x) Now vx = ¡6xy`0(x) = ¡uy = ¡6xy Thus `(x. v y = u x = 3 x 2 2 y − 4 y 2 and after integration v ( x, y) = 3 x 2 y y 2 − ( 4 / 3) y 3 β ( X) and after trying to solve for β I found it equal to β = x 2 y − x 2 and after applying it to the v ( x, y) = 4 x 2 y 2 = ( 4 / 3) y 3 − x 2 which in obviously is not applying CR equations if we want to prove the solution. U (x) = e ∫ Z (x)dx = e ∫ (1/x)dx = e ln (x) = x Now that we found the integrating factor, let's multiply the differential equation by it x (3xy − y 2 )dx x (x − y)dy = 0 and we get (3x 2 y − xy 2 )dx (x 3 − x 2 y)dy = 0 It should now be exact.
@f @y = 3xe (e) f(x;y) = x y x y @f @x = x y (x y) (x y)2 = 2y 2x @u @x y @u @y = 2x3y2 sinh(xy21)4x2 cosh(xy21) 2x3y2 sinh(xy21) = 4x2 cosh(xy2 1) = 4u 11 @w @t = 1 2x 2ct 2c @2w @t2 = 4c2 (2x. Showthatu(x,y) = 2x−x33xy2 isharmonic on R2 and find a harmonic conjugate v(x,y) for it Solution Define f(z) = 2z − z3 This function is analytic on C f(xiy) = 2(xiy)−(xiy)3 = 2x2iy−(x33x2iy3xi2y2i3y3) = 2x−x33xy2i(2y−3x2yy3) We have that the real part of f(z) is u(x,y), and hence it is harmonic on R2 Also v(x,y. 3 1 3 3 1 3 2 1 2 9 7 0 0 1 1 0 7 14 28 2 1 4 12 ~ 2 0 9 9 9 0 7 14 28 2 1 4 12 ~ 4 4 11 1 33 0 7 14 28 2 1 4 12 ~ 4 11 1 33 8 3 2 2 1 4 12 , R R R R R R R R R A B solutions are obtained from above matrix by back substitution method as 2xy 4z = 12 (1) 7y 14z = 28 (2) 1z = 1 (3) from the above equations we get z=1, y=2, x=3 thus.
Section 145 (3/23/08) Directional derivatives and gradient vectors Overview The partial derivatives fx(x0,y0) and fy(x0,y0) are the rates of change of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the positive x and ydirectionsRates of change in other directions are given by directional. Fy = −sin(x2 y), fyx = −cos(x2 y)2x d) both sides are f0 (x)g 0 (y) 2 (fx)y = ax6y, (fy)x = 2x6y;. = y3 2xy2;.
Answer (1 of 6) \dfrac {dy}{du}=\dfrac{dy}{dx}\cdot\dfrac {dx}{du} Let’s calculate \frac{dy}{dx} \dfrac {dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}(x^2 2x)=\dfrac {d}{dx}(x^2. (x y)2 (x y)3 (x y)2 (x y)3 c) fx = −2xsin(x2 y), fxy = (fx)y = −2xcos(x2 y);. U(x,y)=h(x−uy) (52) The characteristic projection in the xtplane1 passing through the point (s,0) is the line x = h(s)ts along which u has the constant value u = h(s) Two characteristics x = h(s 1)t s 1 and x = h(s 2)ts 2 intersect at a point (x,t)with t =.
2 a) Find the directional derivative of scalar field f(x, y) = x 2 – 3xy along the parabola y = x 2 – x 2 at the point (1, 2) 5 b) Comment If the vector field f is differentiable at a, then f is continuous at a 5 c) State and prove matrix form of chain rule 6 3. Here we will look at solving a special class of Differential Equations called First Order Linear Differential Equations First Order They are "First Order" when there is only dy dx, not d 2 y dx 2 or d 3 y dx 3 etc Linear A first order differential equation is linear when it can be made to look like this dy dx P(x)y = Q(x) Where P(x) and Q(x) are functions of x To solve it there is a. If 3 By 2 Plus I Root3 By 2 Power 50 Equal 3 25 X Iy Where X And Y Are Real Then The Ordered Pair X Y Is If 3 sin (xy) 4 cos (xy) = 5, then dy/dx = If 3 Tan Theta Tan Phi Is 1 Then If 3 x = 4 x1, then x is equal to If 3x y k = 0 is a tangent to the circle x 2 y 2 = 10, then the values of k are If 4 Sin Inverse X Plus Cos Inverse X.
Let u = u(x)beany solution of (1) and choose any point a ∈ ISuppose that α = u(a),β= u0(a) Then u is a member of the twoparameter family (2) if and only if there are values for C1 and C2 such that C1y1(a)C2y2(a)=α C1y 0 1(a)C2y 2(a)=β If we multiply the first. U,, x2x 1 y for all real and y Then a function v yx, so that f z yu y i v x, is analytic, is a) x 2 2 y 1 b) 2 x 1 2 y c) 2 x 1 2 y d) x y C2 21 12 At the function a) is analytic b) differentiable c) doesn’t satisfy CR equation d) Satisfy CR equations but not differentiable 13. 1 Let f(z) = y 2xyi( xx2 y2)z2 where z= xiyis a complex variable de ned in the whole complex plane For what values of zdoes f0(z) exist?.
1 TRUE or FALSE There is a function f R2!R such that @f @x = y and @f @y = x2 Solution FALSE (If there were such a function, then its mixed second partial derivatives would be @ 2f @y@x = 1 @f @x@y = 2x These functions are continuous and unequal, but by Clairaut’s Theorem, if a function has continuous second partial derivatives then its. U = x y U = 2x y U = 2x 3y U = (1/2)x (3/4)y MRS The MRS is always equal to a/b, a constant That is, ICs are straight lines with slope (negative) a/b Solving for the consumer’s utility maximizing consumption bundle These cases can look “tricky” because the MRS is a constant and more often than not will not equal the price ratio. (c) Suppose v is another function such that u, v satisfy the CauchyRiemann equations.
(c) Suppose a point has coords X=1, Y=2 wrt basis u,v Find the value of q at the point two ways, using its X,Y coordinates and then again using its x,y coordinates 6 Start wit hq=x 2 3xy5y2 and make the change of variable X=xy Y=xy (a) Find q in terms of X and Y just with algebra (b) What new basis is involved when you use variables. But f yx(0;0) = lim x!0 f y(x;0) f y(0;0) x 0 = 1 They are not equal at (0;0) 4 Find @3u @x@y@z;. Solution Our plan is to identify the real and imaginary parts of f, and then check if the CauchyRiemann equations hold for them We have f(z) = y 2xy i( x x2 y2) x2 y2 2ixy = x2 2xy y y2 i( x.
∂u ∂x = y2 x2 y2 1 y = y x2 y2 = ∂v ∂y (1) − ∂u ∂y = − y2 x 2y −x y 2 = x x2 y = ∂v ∂x (2) By (1), v = 1 2 log(x2 y2)C(x), and by (2) ∂v ∂x = x x 2y C′(x) = x x y2 so C′(x) = 0andC(x) is a constant, call it D Therefore, v(x,y) = 1 2 log(x2 y2)D Question 3. Thus $f(z) = f(x, y) = u(x, y) iv(x, y) = (x^3 = 3x^2y) i(3x^2 y^3 v(0, 0)) \tag{19}$ is a holomorphic function of $z = x iy$. Lemma 54 Let z= x iyand suppose that f(z) = u(x;y) iv(x;y) is analytic Then the dot product of their gradients is 0, ie rurv= 0 Proof The proof is an easy application of the CauchyRiemann equations rurv= (u x;u y) (v x;v y) = u xv x u yv y= v yv x v xv y= 0 In the last step we used the CauchyRiemann equations to substitute v yfor.
U x 2u y (2x y)u = 2x2 3xy 2y2 Solution Let us take (x0= x 2y y0= 2x y By the Chain Rule, we then obtain (u x = u x0 @x 0 @x u y0 @y @x = u x0 2u y0 u y = u x0 @x 0 @y u y0 @y @y = 2u x0 u y0 It follows that u x 2u y = (u x0 2u y0) 2(2u x0 u y0) = 5u x0 Furthermore, we note that we can factorize the righthand side of. Summer 17 MATH10 2 When (x;y) = (0;0), f x(0;0) = 0 and f y(0;0) = 0We have f xy(0;0) = lim y!0 f x(0;y) f x(0;0) y 0 = 1;. 2 Divergence (Div) If F(x,y) is a vector field, then its divergence is written as divF(x,y) = ∇·F(r) which in two dimensions is ∇·F(x,y) = (∂ ∂x i ∂ ∂y j)·(F 1(x,y)iF 2(x,y)j), = ∂F 1 ∂x ∂F 2 ∂y It is obtained by taking the scalar product of the vector operator.
X =(5x2 7y)(2)(2x−4y3)(10x) ∂U ∂y = U y =(5x2 7y)(−12y2)(2x−4y3)(7) Example 5 U = 9y3 x−y Answer ∂U ∂x = U x = (x−y)(0)−9y3(1) (x−y) 2 = −9y3 (x−y) ∂U ∂y = U y = Therefore, at x =2, if x is increased by 001 then y will increase by 004 4 The two variable case If z = f(x,y) then the change in z is dz. @f @x = 3x2y ex;. Fall 13 S Jamshidi 4 x4 y4 z4 =1 If x,y,z are nonzero, then we can consider Therefore, we have the following equations 1 1=2x2 2 1=2y2 3 1=2z2 4 x4 y4 z4 =1 Remember, we can only make this simplification if all the variables are nonzero!.
II Let u(x, y)=2x x^3 3xy^2 x^2y^2 (a) Compute the first order partials u_x and u_y of u;. U(x,y) = x3 −3xy2 is harmonic To find a harmonic conjugate v of u, we must have u x(x,y) = v y(x,y) and u y(x,y) = −v x(x,y) From the first we have v y(x,y) = 3x2 −3y2, from which it follows that v(x,y) = 3x2y −y3 ϕ(x) for some function ϕ of x It now follows from the second equation that −6xy = −v x(x,y) = −(6xy ϕ0(x)), and so ϕ0(x) = 0 Hence for any real number c, the function.
100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
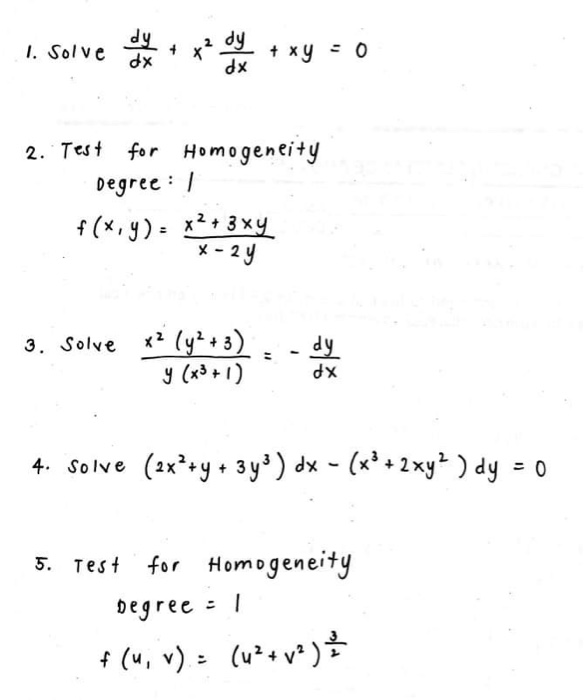
Solved 1 Solve Dy Dx 뿄 X Du Je 뿄 Xy 0 2 Test For Chegg Com

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
If Ux Yx2+y2+2x 3xy Then のギャラリー

If X Iy 3 U Iv Then Show That U X V Y 4 X 2 Y 2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

Partial Differentiation If U X 2 Y 2 X At 2 Y 2at Find әu әt Youtube

Solved 8 Let F X Y 5 2x 3xy A Find The Equation Chegg Com

Chapter 7 Calculus Of Several Variables

Ex 2 5 9 Verify I X 3 Y 3 X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Teachoo

Ex 5 3 5 Find Dy Dx In X2 Xy Y2 100 Class 12
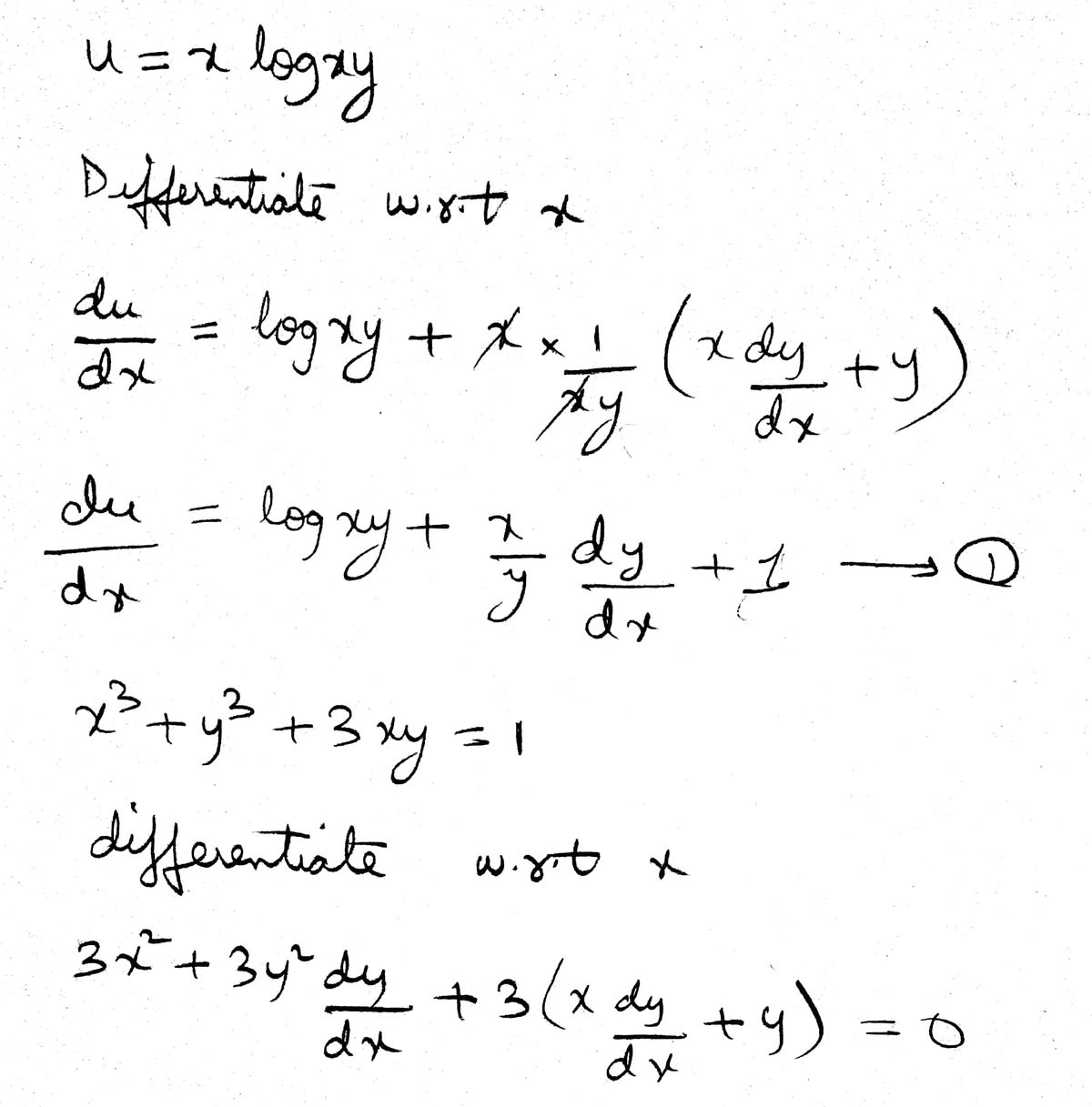
100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
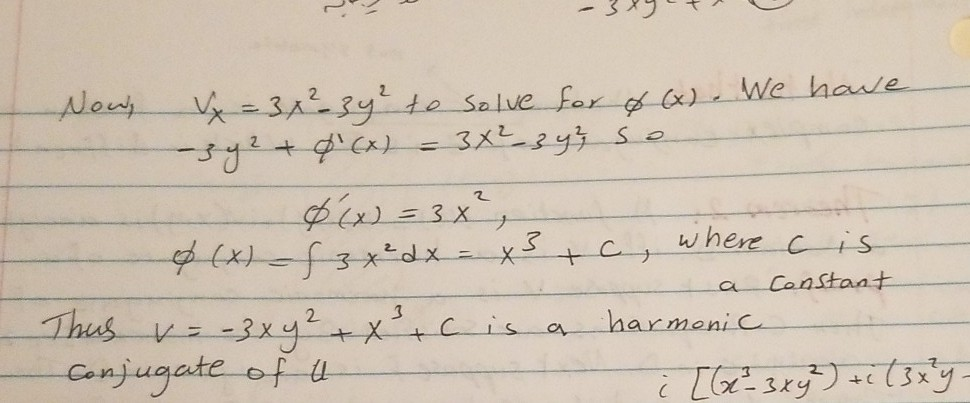
Solved Exercises 1 Show That U X Y Is Harmonic In Some Chegg Com
2

Doc Partial Derivative Mcq S Assignement Innocentboy Nishant Academia Edu
Differential Equations

If X 2 Y 2 3xy Then Choose The Correct Answer Of 2log X Y Form The Following Option
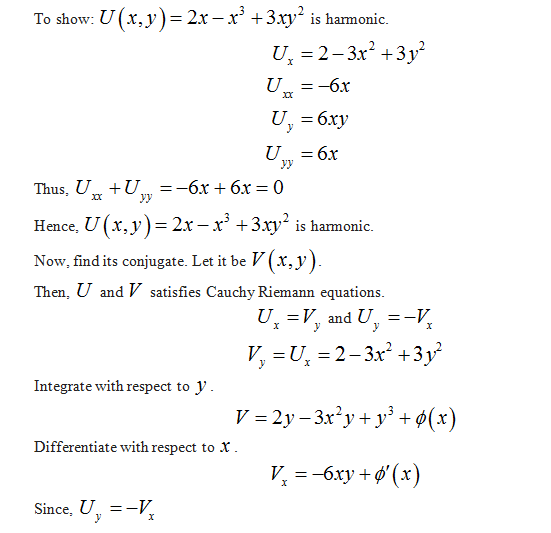
Answered Show That U Y Is Harmonic Function Bartleby
If X Y 2 Then What Is The Value Of X Y 6xy Quora

Solved 1 Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Following Chegg Com

11 Business Math Stats Vol 2 Em Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
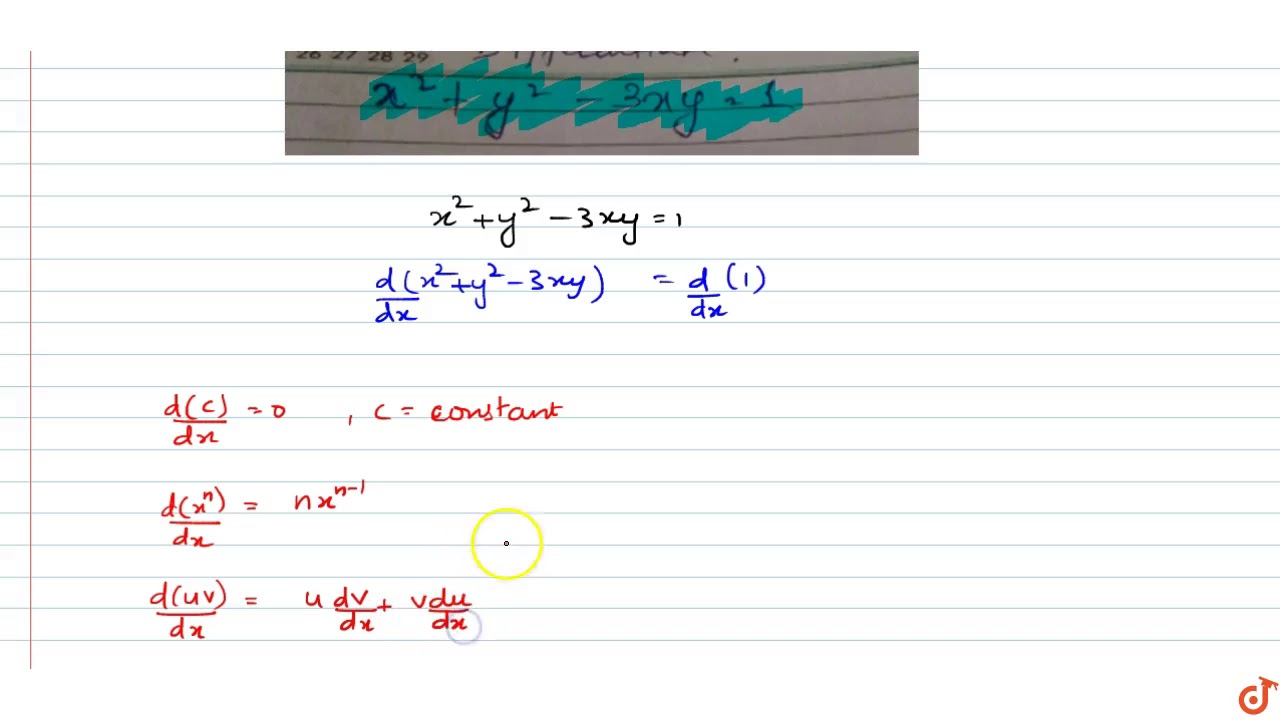
Differentiate X 2 Y 2 3xy 1 Youtube

Solved Solve Each System Use Any Method You Wish 2x 2 Chegg Com

If 2x 2 3xy Y 2 X 2y 8 0 Then Dy Dx Youtube

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
If W X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 X E T Y E T Sin T And Z E T Cos T Find Dw Dt Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Show That 2x 2 3xy 2y 2 3x Y 1 0 Represents A Pair Of Perpendicular Lines

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

If U F R Where R 2 X 2 Y 2 Then 2u X 2 2u Y 2

Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 8 Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Download Free Pdf

If X 3 Y 2 3xy X Y Then Log X Y 3
If X 2 3xy Y 2 60 Where X And Y Are Real Determine The Maximum Possible Value Of Xy Quora

Solved 1 Construct An Analytic Function Whose Real Part Is Chegg Com

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

If U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u X Y

Solved Let F X Y X 3 3xy 2 2y 3 Show That The Chegg Com
100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
Verify Euler S Theorem For The Function U X 3 Y 3 3xy 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
2
What Is The General Solution Of The Differential Equation X 3 Y 3 Dx 3xy 2dy 0 Quora
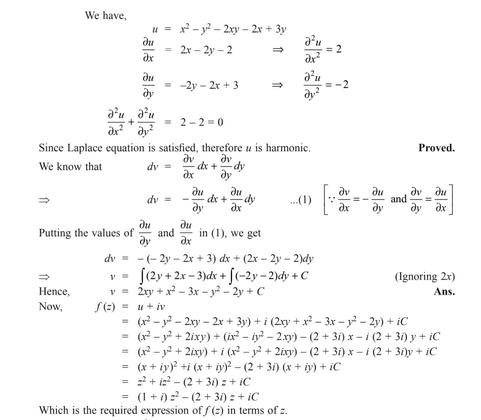
Prove That U X 2 Y 2 2xy 2x 3y Is Harmonic And Find Harmonic Conjugate V Edurev Iit Jam Question

Solved Let F X Y 3xy X 2 Y 2 If X Y Notequalto 0 Chegg Com

Find Dydx Where X 2 Y 2 3xy 1
2
Prove That F X Y X 3 2x 2y 3xy 2 Y 3 Is Homogeneous What Is The Degree Verify Euler S Theorem For F Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

The Curves X 3 3xy 2 A And 3x 2 Y Y 3 B Where A And B Are Constants Cut Each Other At An Angle Of

Ex 12 2 4 What Should Added To X 2 Xy Y 2 To Obtain 2x 2 3xy

Misc 4 Prove X2 Y2 C X2 Y2 2 Is General Solution Of
100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
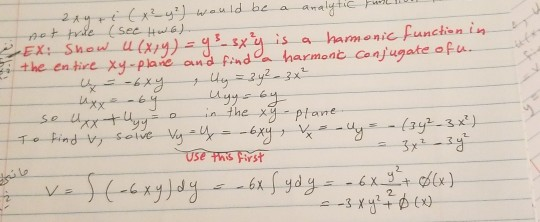
Solved Exercises 1 Show That U X Y Is Harmonic In Some Chegg Com
X X X Y Y Video Song Download
1

Solve 3xy 2ay 2 Dx X 2 2axy Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
D Dx Formula
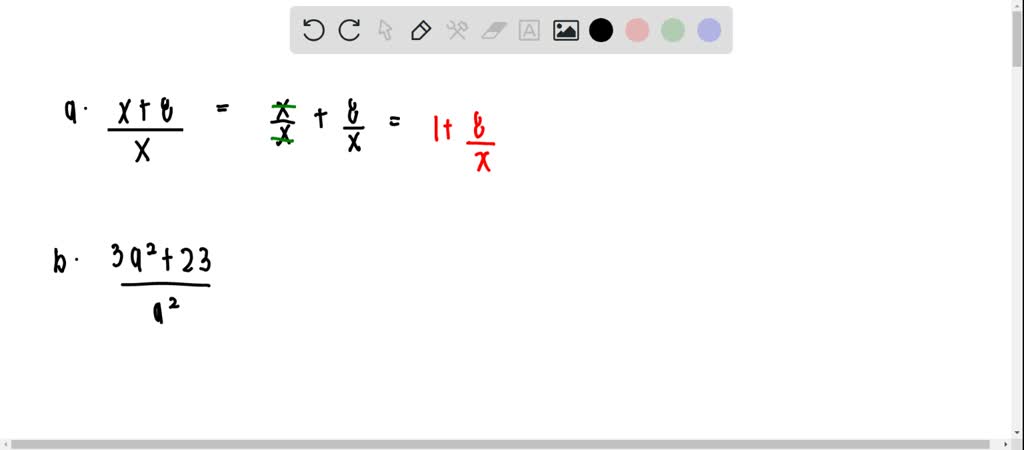
2b Simplify 0 B8a 4a B421 21 32r 48simpli Itprospt

Solved A Harmonic Conjugate Of U 2x X3 3xy2 Is Select Chegg Com

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

Solved Example 4 A If Z F X Y X2 3xy Y2 Find The Chegg Com
If U Log X 2 Y 2 Xy Then X U X Y U Y Is A 0 B U C 2u Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Show That The Equation Tex X 2 3xy 2 Y 2 2x 3y 35 0 Tex For Every Real Value Brainly In
If U X 2 3xy Y 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u Y X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Worked Example Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy
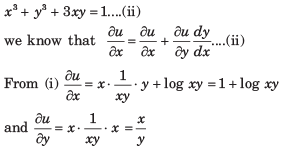
If U X Log Xy Wherex3 Y3 3xy 1 Then Du Dx Is Equal Toa B C D Correct Answer Is Option A Can You Explain This Answer Edurev Electronics And Communication Engineering Ece

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

If X 2 Y 2 3xy Then Choose The Correct Answer Of 2log X Y Form The Following Option

Solved Find The Points On The Curve X 2 3xy Y 2 5 That Chegg Com

If U Sin 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Then Show That X Du Dx Y Du Dy Tan U Mathematics 1 Question Answer Collection
2

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

Solved Problem 2 Cauchy Riemann Equations Harmonic Chegg Com

Prove That X2 Y2 C X2 Y2 2 Is The General Solution Of The Differential Equation X3 3xy2 Dx Y3 3x2y Dy Where C Is Parameter Mathematics Shaalaa Com

Solved Exercises 1 Show That U X Y Is Harmonic In Some Chegg Com
If U X Y Z Xy 2z 3 X Sin T Y Cos T Z 1 E 2t Find Du Dt Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Second Partials Test For F X Y X 3 3xy Y 3 Youtube

Multivariate Functions And Partial Derivatives Sage Research Methods

Solved Verify That The Differential Equation 3xy Y 2 Chegg Com
If Math X 3 Y 3 3xy 1 Math What Is The Minimum Value Of Math X 2 Y 2 Math Quora
What Should Be Added To X2 Xy Y2 To Obtain 2x2 3xy Algebraic Expressions Maths Class 7
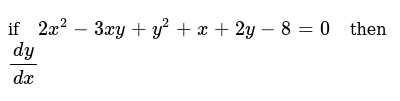
If 2x 2 3xy Y 2 X 2y 8 0 Then Dy Dx

Ex 9 5 15 Class 12 Find Solution 2xy Y 2 2x 2 Dy Dx 0 When

Solved Implicit Differentiation Find Dy Dx If Y 2 3xy X 2 7 Chegg Com

Find If Y 2 3xy X 2 7 Find For 2x 2 Xy 3y 2 Ppt Download
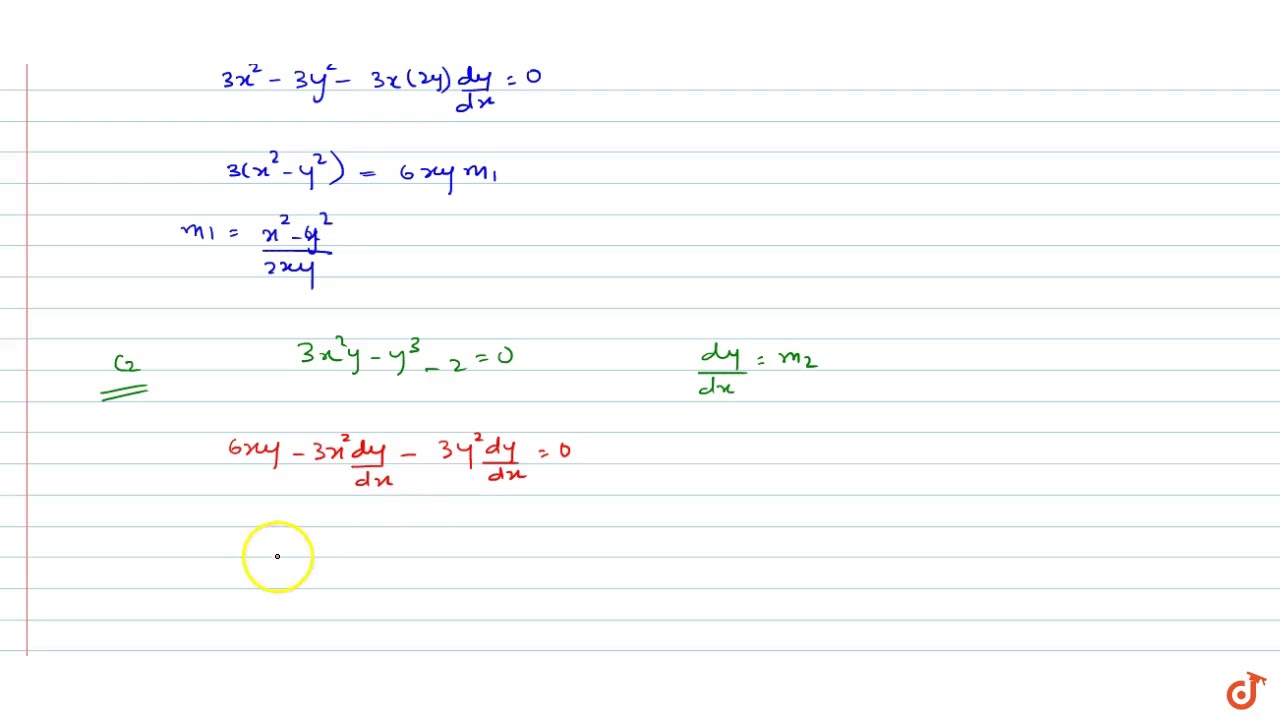
The Two Curves X 3 3xy 2 2 0 And 3x 2y Y 3 2 0 Youtube
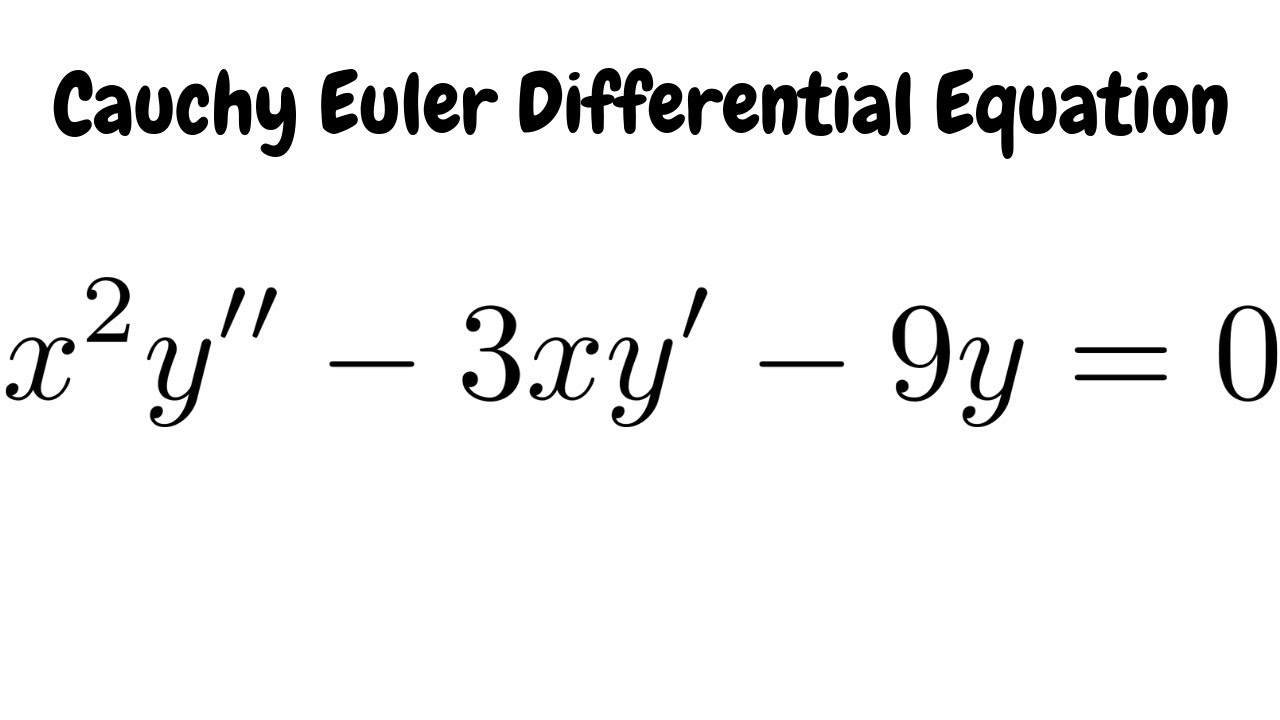
Solve X 2y 3xy 9y 0 Cauchy Euler Differential Equation Youtube
If U X 2tan 1 Y X Y 2tan 1 X Y Prove That 2u Y X X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Find An Analytic Function Whose Real Part Is U X 3 3xy 2 3x 2 3y 2 3y 2 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
2

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk

Ex 5 3 6 Find Dy Dx In X3 X2y Xy2 Y3 81 Cbse

Solved 7 F X Y X Y Subject To X 2 Xy Y 2 Chegg Com
Solved Exercises 1 Show That X Y Is Harmonic In Some Chegg Com

X 3 3xy 2 Dx Y 3 3x 2y Dy Youtube

Solved If U X Y 2x X3 3xy2 2xy Is Harmonic In R2 Chegg Com

100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
Solved Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation X 2 Y 2 Chegg Com
If U X Y Y 3 3x 2 Y Y Determine V X Y So That F U Iv Is An Analytic Function Youtube

For What Value Of N Is Following A Homogeneous Differential Equation
100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
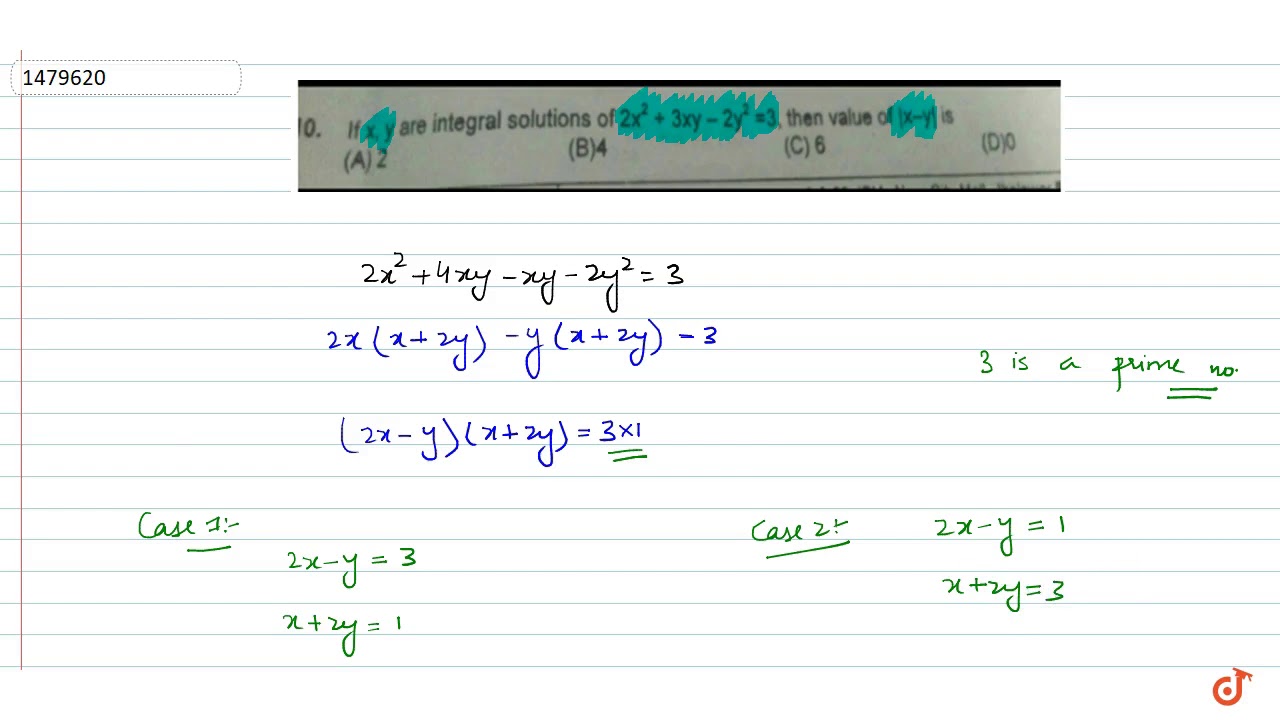
If X Y Are Integral Solutions Of 2x 2 3xy 2y 2 3 Then Value Of X Y Is Youtube

Ejercicios 36 38




