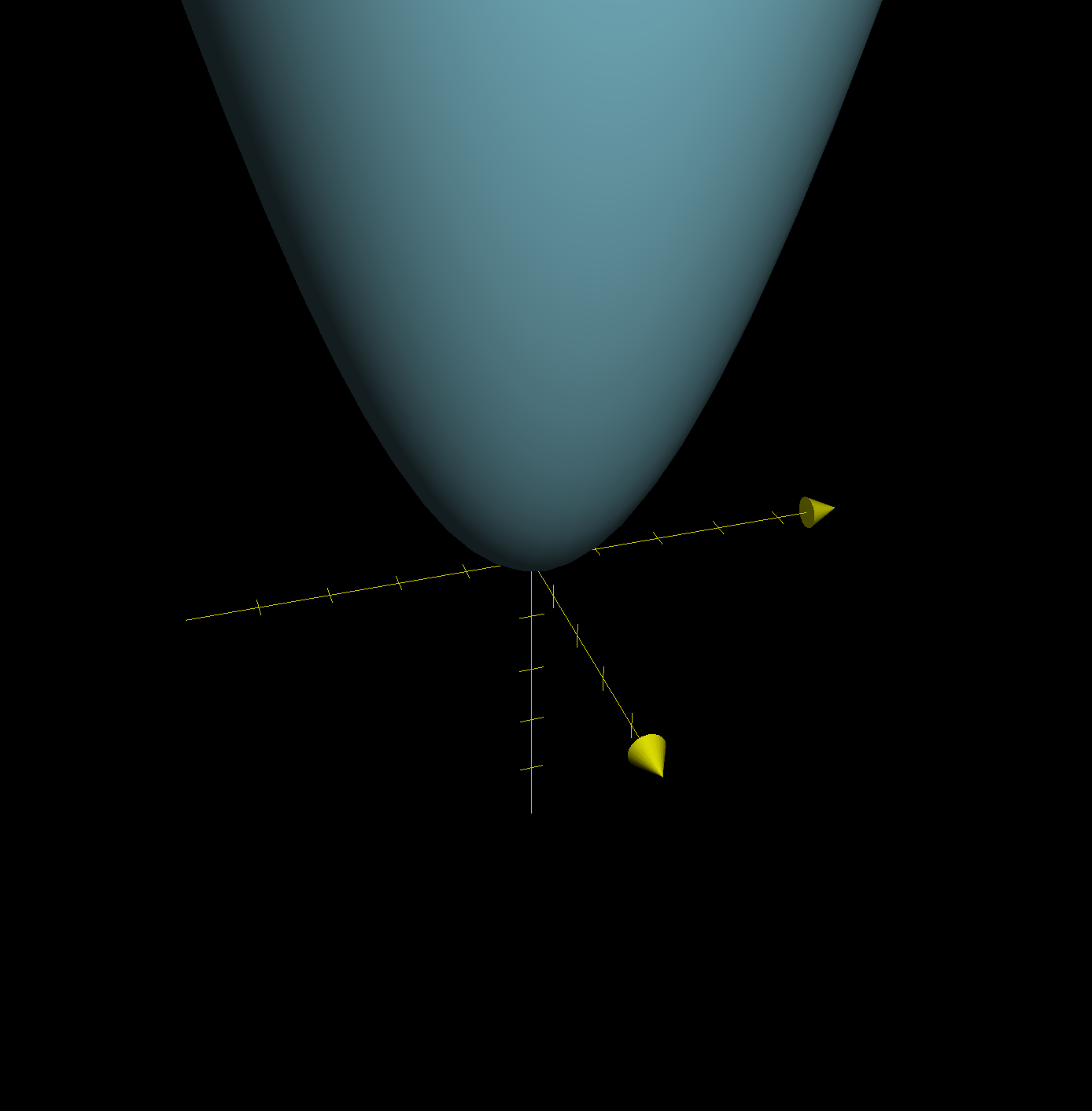
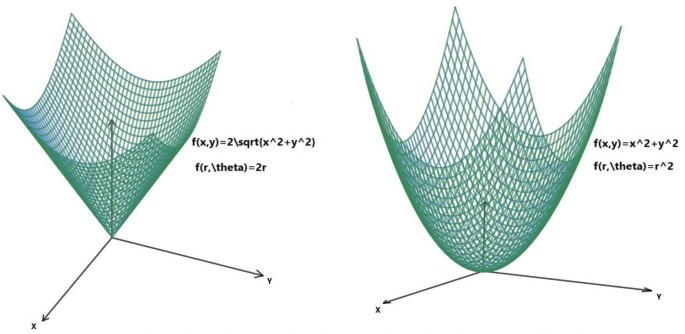
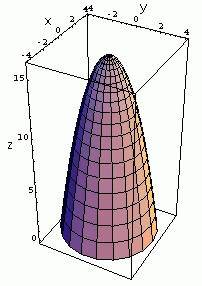
Fx Yx2+y2 Graph
In particular, the peak of the original curve has shifted from #x=1# to #x=1/2# On the other hand, the graph for #y=f(x/2)# is Note that this graph is twice as broad (squeezing by #1/2# being the same as stretching by a factor of 2), and the peak has also moved from #x=1# to #x=2# A special mention must be made of the case where #b# is negative It is best perhaps to.
Fx yx2+y2 graph. Find stepbystep Calculus solutions and your answer to the following textbook question Suppose the line tangent to the graph of f x=2 is y=4x1 and suppose y=3x2 is the line tangent to the graph of g at x=2 Find an equation of the line tangent to the following curves at x=2 a y=f(x)g(x), b y=$\frac { f ( x ) } { g ( x ) }$. The graph of a function on its own doesn't determine the codomain It is common to use both terms function and graph of a function since even if considered the same object, they indicate viewing it from a different perspective Graph of the function f ( x ) = x 4 − 4 x {\displaystyle f (x)=x^ {4}4x}. Answer (1 of 3) The same way you plot anything Even with this equation being complicated looking, just assume that this elliptical mapping has some yvalue(s) for whatever xvalue(s) Since this is second order, we can expect it to have some values So, start off by making a.
Thus, "x 2 y 2" is written "x*x y*y" or "x^2 y^2" 2 For example, f(x,y) = x 2 y 2 will be graphed as in the image below 3 You may wish to save the graph image as a file on your PC it will use about 35 KB. F (x,y)=x^2y^2 WolframAlpha Volume of a cylinder?. How do you graph y=x2Video instruction on how to graph the equation y=x2.
2 y2) To understand the graph of z= f(x;y), we can study trace curves The vertical trace curves are curves made by intersecting the graph with planes of either constant xor y Clearly, if y= kis constant, the equation z= 4 1 4 (x 2 k2) gives a downward opening parabola. Curves in R2 Three descriptions (1) Graph of a function f R !R (That is y= f(x)) Such curves must pass the vertical line test Example When we talk about the \curve" y= x2, we actually mean to say the graph of the function f(x) = x2That is, we mean the set. In this video I try to explain what a function in maths is I once asked myself, why keep writing y=f(x) and not just y!??.
When I type "S x^2 y^2 z^2 = 1" into the input bar, this works perfectly;. The graph of y = f(x) will shift right precalculus What transformation produce the graph of g(x)=5^(x2) from the graph of the parent function f(x)=5^x?. Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Substitute the x x value − 2 2 into f ( x) = √ − x f ( x) = x In this case, the point is ( − 2, ) ( 2, ).
Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with 0 0 in the expression f ( 0) = ( 0) 2 − 2 ⋅ 0 − 2 f ( 0) = ( 0) 2 2 ⋅ 0 2 Simplify the result. A function may be thought of as a rule which takes each member x of a set and assigns, or maps it to the same value y known at its image x → Function → y A letter such as f, g or h is often used to stand for a functionThe Function which squares a number and adds on a 3, can be written as f(x) = x 2 5The same notion may also be used to show how a function affects particular values. Similarly, the graph of y = x 2 3 is 3 units below the graph of y = x 2 The constant term "c" has the same effect for any value of a and b Parabolas in the vertexform or the ahk form, y = a(x h) 2 k To understand the vertexform of the quadratic equation, let's go back our orginal equation, f(x) = x 2 In this equation, remember.
The graphs of \(y = f (x)\) and \(y = g(x)\) are said to be translations (or shifts) of the graph of \(y = x^2\text{}\) They are shifted to a different location in the plane but retain the same size and shape as the original graph In general, we have the following principles Vertical Shifts. This tool graphs z = f (x,y) mathematical functions in 3D It is more of a tour than a tool All functions can be set different boundaries for x, y, and z, to maximize your viewing enjoyment This tool looks really great with a very high detail level, but you may find it more comfortable to use less detail if you want to spin the model. Subtracting from the output of a function moves the graph down Here are the graphs of y = f (x), y = f (x) 2, and y = f (x) 2 Note that if (x, y1) is a point on the graph of f (x), (x, y2) is a point on the graph of f (x) 2, and (x, y3) is a point on the graph of f (x) 2, then y2 = y1 2 and y3 = y1.
Tangent planes Tangent Plane to determine the equation of the tangent plane to the graph of z = f ( x, y), let P = ( a, b, f ( a, b)) be a point on the surface above ( a, b) in the x y plane as shown to the right below Slicing the surface with vertical planes y = b and x = a creates two curves on this graph, both passing through P. F (x, y) = 4 − x 2 − y 2 f (x, y) = 4 − x^2 − y^2 f (x, y) = 4− x 2 − y 2 Find the point on the graph of f which has tangent plane parallel to P P P. This means x2y2= k, which we recognize as the equation of a circle of radius √ k So the graph of f(x,y) has parabolic crosssections, and the same height everywhere on concentric circles with center at the origin This fits with what we have already discovered 0 −3 −3 −2 −2 2.
I've since realised that 'y' can b. Remember f(x) reflects the graph to the right of the. The result is y = / Sqrt 2 x x^2 Note when x = 0, y = 0 When x = 1, y = 1 and 1 and when x = 2, y = 0 For x > 2, y is imaginary and for x < 0, y is imaginary Now calculate y for as many values of x between 0 and 2 as you want to see the graph 35K views.
Steps for Solving Linear Equation y = f ( x ) = 2 ( x 1 ) y = f ( x) = 2 ( x 1) Use the distributive property to multiply 2 by x1 Use the distributive property to multiply 2 by x 1 y=2x2 y = 2 x 2 Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side. $$ y = f(1) = 1^22\cdot12 = 1 2 2 = 1 $$ The yintercept is $$ y = f(0) = 0^22\cdot02 = 0 0 2 = 2 $$ In this case xintercept doesn't exist since equation $x^22x2=0$ does not has the solutions (use quadratic equation solver to check ) So, in this case we will plot the graph using only two points. Free tangent line calculator find the equation of the tangent line given a point or the intercept stepbystep.
I took a Matlab course over the summer, and now have to graph a problem in calculus I am rusty on my commands, so I'm not sure which one to use I am trying to make a 3d plot of a function f(x,y)=(x^21)^2(x^2yx1)^2 Do I have to open a function, or can I just use a command with a script?. Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. S is defined as a sphere However, when I type "S f(x,y,z) = 1" into the input bar, nothing is graphed and the algebra window shows S as an undefined Implicit Curve I need to keep the function f, so that it can be modified by the user using an input box I'd like.
The graph of a function f is the set of all points in the plane of the form (x, f (x)) We could also define the graph of f to be the graph of the equation y = f (x) So, the graph of a function if a special case of the graph of an equation If you want to. Graph of z = f(x,y) New Resources SSS Triangle Exploration;. To zoom, use the zoom slider To the left zooms in, to the right zooms out When you let go of the slider it goes back to the middle so you can zoom more You can clickanddrag to move the graph around If you just clickandrelease (without moving), then the spot you clicked on will be the new center To reset the zoom to the original click.
H(x)=x 2 5 Vertical translation by 5 units upwards;. The level curves of f(x,y) = x 2 y 2 are curves of the form x 2 y 2 =c for different choices of c These are circles of radius square root of c Several of them are shown below One can think of the level curve f(x,y)=c as the horizontal crosssection of the graph at height z=c When each level curve f(x,y)=c is plotted at a height of c units above the xyplane, we get the figure. Get the free "Surface plot of f(x, y)" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Engineering widgets in WolframAlpha.
The x−y is the the inside of the ellipse x2 y2 9 = 1 in the first quadrant, which may be described as a ysimple region in the 2D x − y plane n (x,y) 0 ≤ y ≤ 3 √ 1− x2,0 ≤ x ≤ 1 o So, the integral above is the same as Z 1 0 Z 3 √ 1−x2 0 Z 2 q 1−x2−y 2 9 0 f(x,y,z)dzdydx Treating S as a x simple region, we have for. Point (x;y) which satisfies the original relation (in other words, a point on the curve defined by the relation),and to take an implicit function h(x) for which y = h(x) (that is, an implicit function for which (x;y) is on the graph of that function) We call h(x) the implicit function of the relation at the point (x;y)For example, we have the relation x2 y2 = 1 and the point (0;1). Piece of cake Unlock StepbyStep Natural Language Math Input.
Open Middle PointSlope Exercise (2). Select all that apply a reflection over the xaxis b reflection over the yaxis c horizontal shift to the left 2 units d. 2 = e− 2 = f(x) and lim x→±∞ e− (−x)2 2 = 0, the graph is symmetry wrt the yaxis, and the xaxis is a horizontal asymptote • Wehave f0(x) = e−x 2 2 (−x) = −xe− x2 2 • Thus f ↑ on (−∞,0) and ↓ on (0,∞) • Atx = 0, f 0(x) = 0 Thus f(0) = e = 1 is the (only) local and absolute maximum • Fromf0(x) = −.
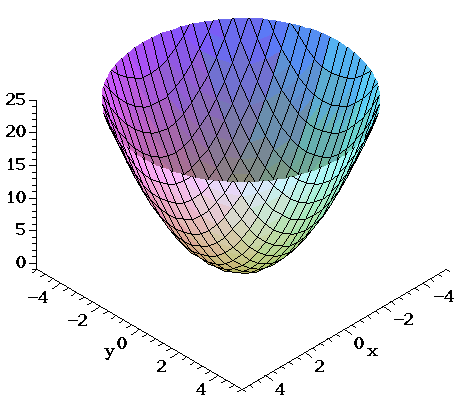
For example, here is the graph of \(z = 2{x^2} 2{y^2} 4\) This is an elliptic paraboloid and is an example of a quadric surface We saw several of these in the previous section We will be seeing quadric surfaces fairly regularly later on in Calculus III. The line y= 0 f(x;0) = x2 2x Computing the derivative and setting it to 0 we find 2x 2 = 0 =)x= 1 This gives the corner (1;0) as before the line y= 2 f(x;2) = x2 2x4 with critical point x= 1 which is again a corner Finally, we check the four corners ( 1;0);(1;0);( 1;2);(1;2) The values of. Solution for Sketch the graph of y = f(x 2) 1, where f(x) = x 2 for 2 < X < 2 Q Assume f is an even function and g is an odd functionAssume f and g are defined for all real numbe A Since you have posted a question with multiple subparts, we will solve first three subparts for.
Y=f(x) and y 2 =f(x) intersect where y=0 or 1 As long as y>0, the gradients of y=f(x) and y 2 =f(x) have the same sign for a certain x value, and they have stationary points located at the same x values y 2 =f(x) is symmetrical about the xaxis At the x values where y=f(x) passes through the xaxis, provided f'(x)≠0, y 2 =f(x) passes vertically through the xaxis. We are given the quadratic function y = f (x) = (x 2)2 For the family of quadratic functions, the parent function is of the form y = f (x) = x2 When graphing quadratic functions, there is a useful form called the vertex form y = f (x) = a(x −h)2 k, where (h,k) is the vertex Data table is given below (both for the parent function and the given function). (left panel)) One can think of the graph as “mountains” of height f(x,y) on the xy plane p Example 163 Sketch the graph of the function f(x,y) = 1− (x/2)2 − (y/3)2 Solution The domain is the portion of the xy plane D = {(x,y)(x/2)2 (y/3)2 ≤ 1} It is bounded by the ellipse with semiaxes 2 and 3 The graph is the surface.
Graphs can be used to represent functions The graph that represents y =x 2 is graph (3) The function is given as A linear function is represented as Where m represents slope and c represents the yintercept So, by comparison The above highlights mean that, the graph of has a slope of 1, and a yintercept of 2 The graph that represents these highlights is graph (3). Section 145 (3/23/08) Directional derivatives and gradient vectors Overview The partial derivatives fx(x0,y0) and fy(x0,y0) are the rates of change of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the positive x and ydirectionsRates of change in other directions are given by directional. To start, let’s consider the quadratic function y=x 2 Its basic shape is the redcoloured graph as shown Furthermore, notice that there are three similar graphs (bluecoloured) that are transformations of the original g(x)=(x5) 2 Horizontal translation by 5 units to the right;.
It cannot be done Suppose to the contrary that it can be done We will derive a contradiction Suppose that \frac{x^2}{\sqrt{x^2y^2}}=f(x)g(y) for some functions f and g.
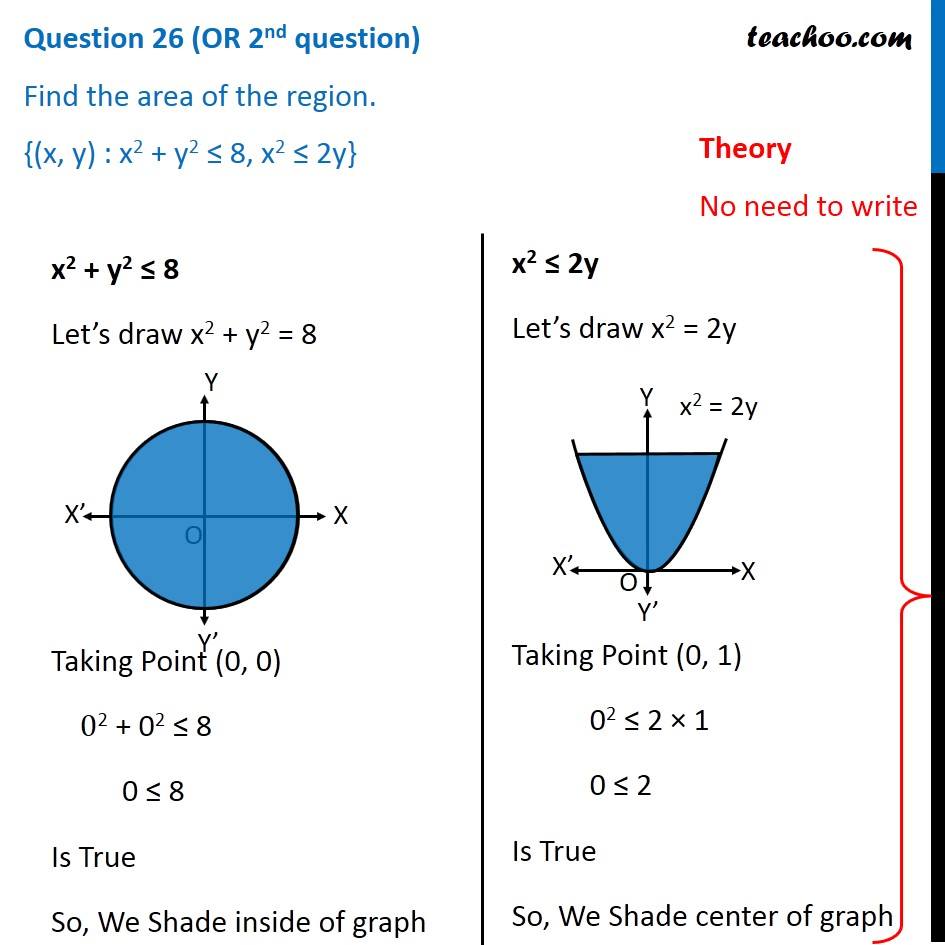
Find The Area Of The Region X Y X 2 Y 2 8 X 2 2y
Y X 2

14 1 Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Libretexts
Fx Yx2+y2 Graph のギャラリー

Critical Points Of Functions Of Two Variables

13 1 Functions Of Multiple Variables Mathematics Libretexts
Evlm Stuba Sk

Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube
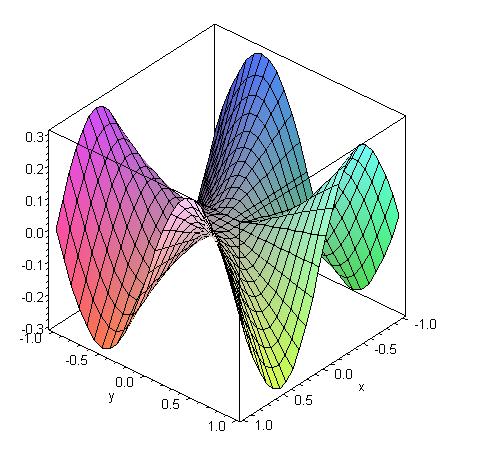
A Function For Which Fxy Fyx Graph Of The Function Given By F X Y X3y Xy3 X2 Y2 For X Y 0 0 And F 0 0 0 Graph Of Fx Note That The Slope In The Y Direction Through The Center Of The Graph Appears To Be Negative It Can Indeed Be Verified That Fxy 0

Graph And Contour Plots Of Functions Of Two Variables Wolfram Demonstrations Project

Plot The Graph Of The Function F X Y 1 2x 2 2y 2 Study Com
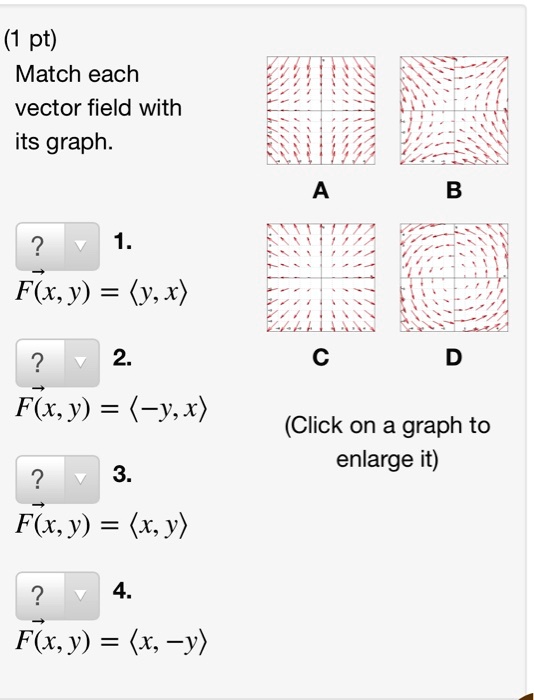
Solved Pt Match Each Vector Field With Its Graph F X Y Y X 2 F X Y Y X Click On A Graph To Enlarge It 3 F X Y X Y 4 F X Y X Y
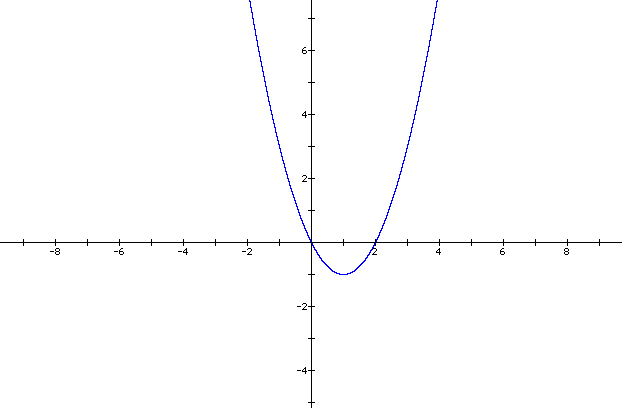
Graphing Quadratic Functions
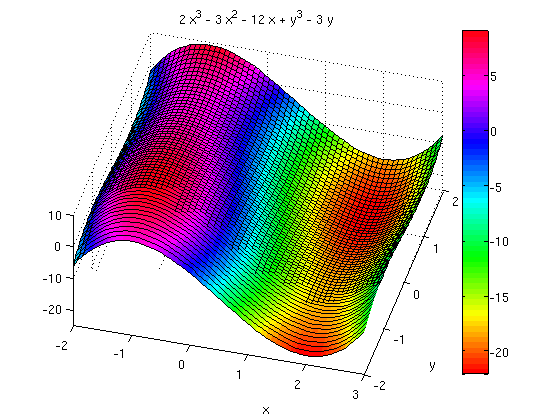
Maxima And Minima Of Functions Of 2 Variables

Conjuntos De Nivel Y Sus Aplicaciones A La Optimizacion De La Funcion De Utilidad Del Consumidor Pdf Descargar Libre
Math Ou Edu
Lesson Finding Inverse

12 2 Graphs Of Functions Of Two Variables Visualizing A Flip Ebook Pages 1 16 Anyflip Anyflip
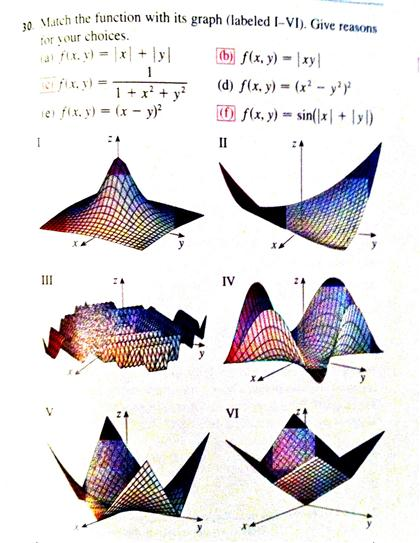
Solved Match The Function With Its Graph Labeled I Vi Chegg Com
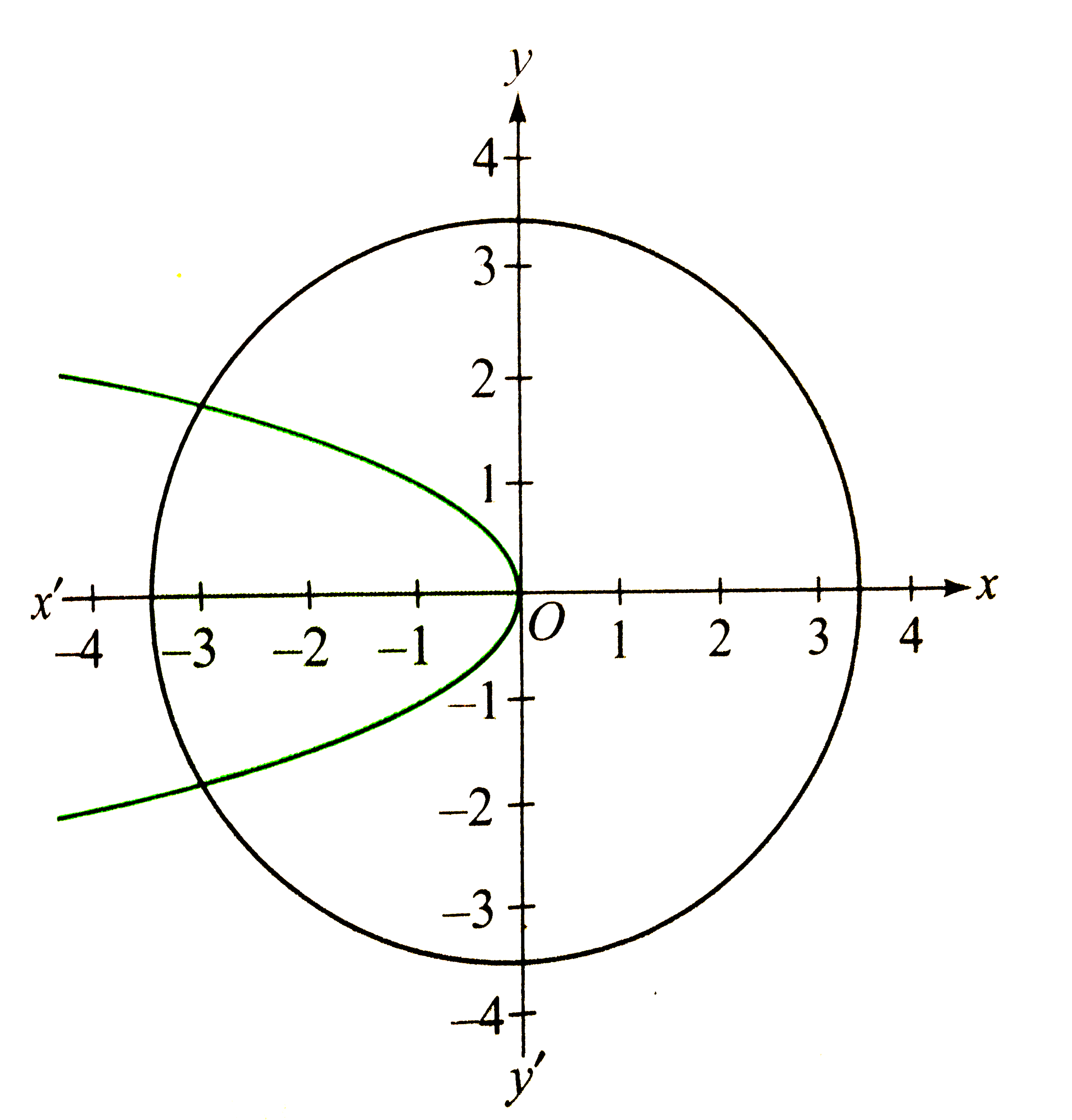
Two Curves C 1 Equiv F Y 2 3 F X 1 3 0 And C 2 Equiv F Y 2 3 F X 2 3 12 Satisfying The Relation X Y F X Y X Y F X Y 4xy X 2 Y 2 The Area Bounded By The Curve C 1 And C 2 Is

Graphs And Level Curves

Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Sqrt 4x 2 Y 2 Study Com

Functions Of 2 Variables

Solved Match The Function With Its Graph F X Y X Chegg Com

Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download

3 This 2d Example Where X Y Are The Configuration Parameters Download Scientific Diagram
Contour Maps Article Khan Academy
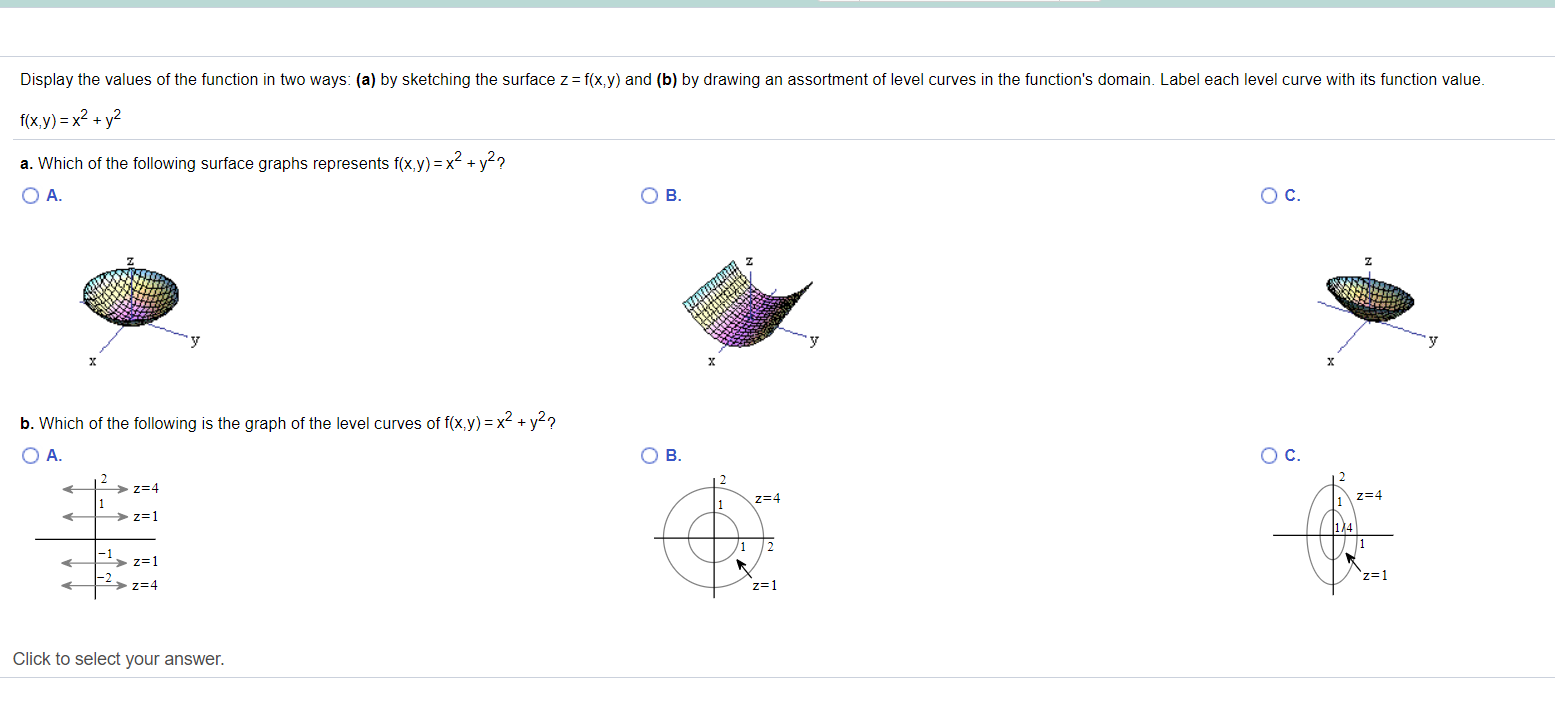
Solved Display The Values Of The Function In Two Ways
Fx Y X2 Y2 រ បភ ពប ល ក Images Ii
How Do You Graph F X Y Sqrt X 2 Y 2 1 Ln 4 X 2 Y 2 Socratic
2 D And 3 D Plots Matlab Simulink

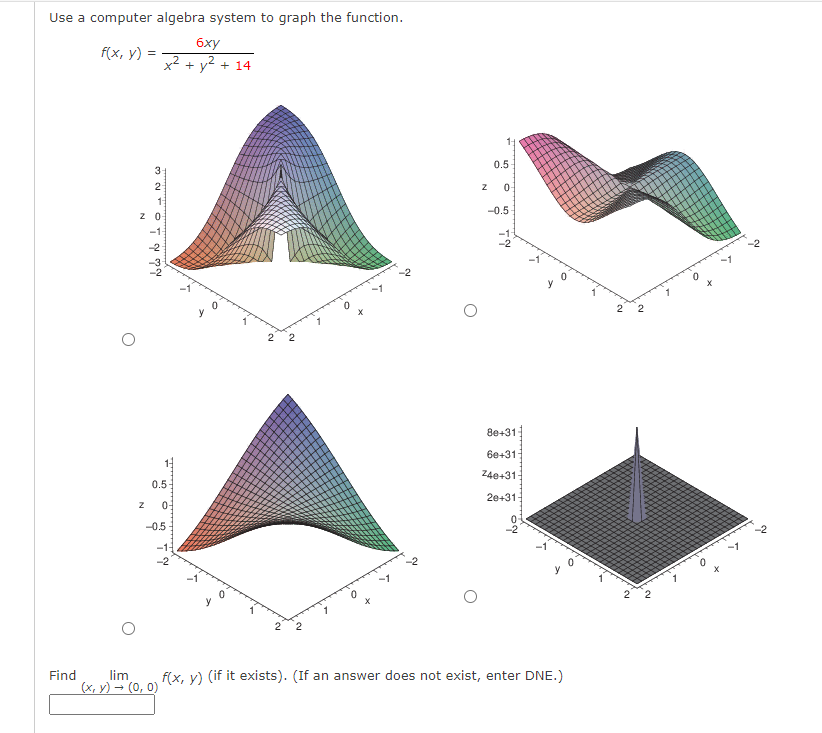
Answered Use A Computer Algebra System To Graph Bartleby

Plot F X Y X 2 Y 2 Tex Latex Stack Exchange
Math Drexel Edu
21 Graph Of The Function F X Y 2xy C X 2 Y 2 C Used For L And Download Scientific Diagram
Math Ntu Edu Tw

If F X Y 9 X 2 Y 2 If X 2 Y 2 Leq9 And F X Y 0 If X 2 Y 2 9 Study What Happens At 3 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Hermite Hadamard S Trapezoid And Mid Point Type Inequalities On A Disk Springerlink

Saddle Point Wikipedia
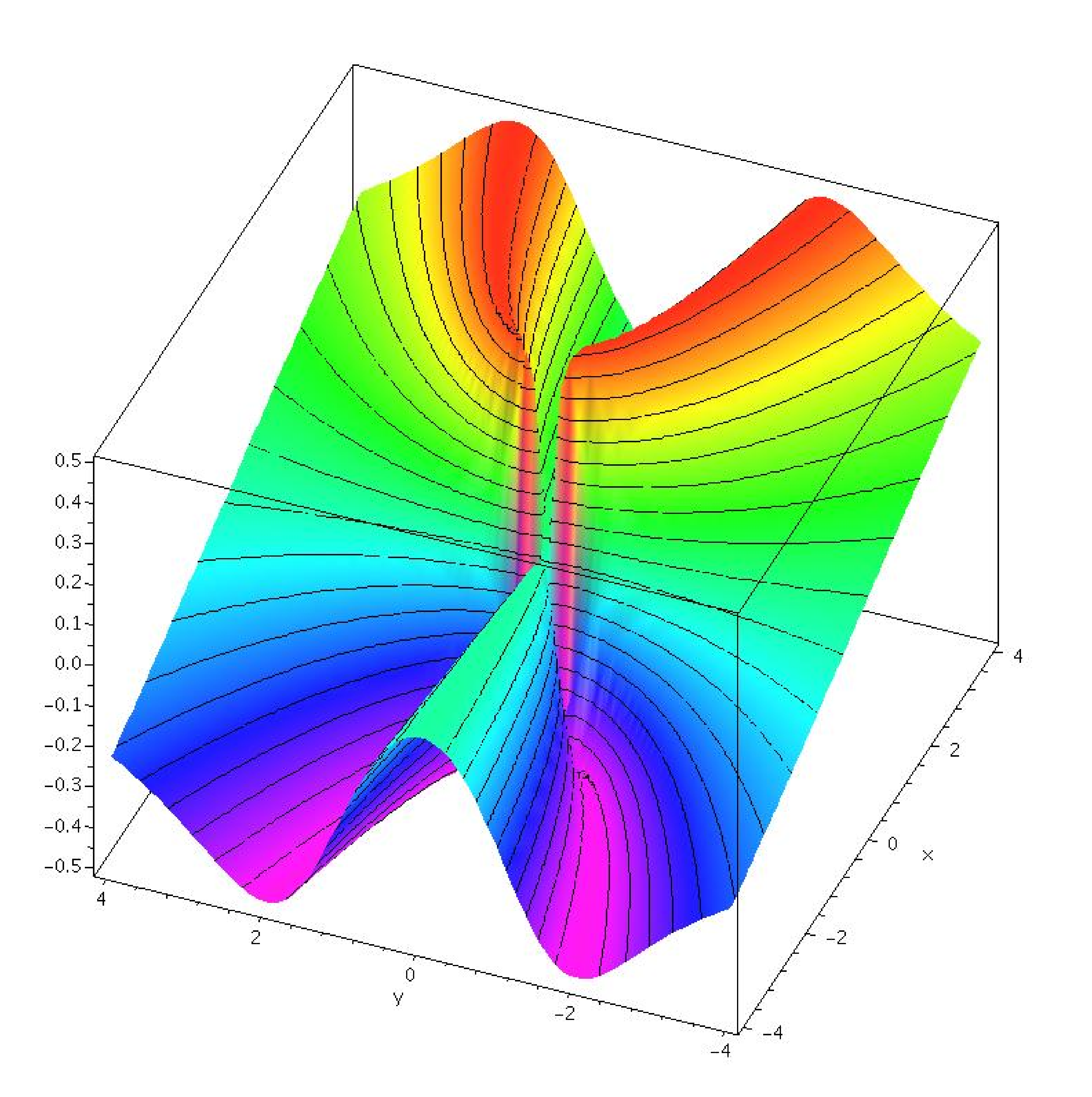
14 2 Limits And Continuity

Simple Graph Models Of Information Spread In Finite Populations Royal Society Open Science
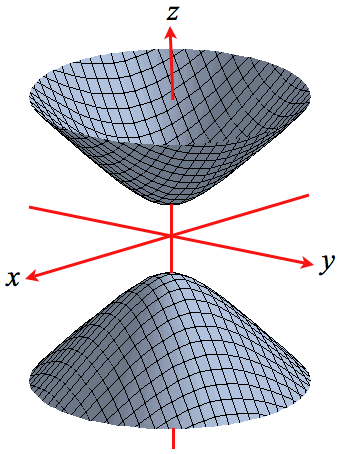
Level Surfaces

Implicit Differentiation
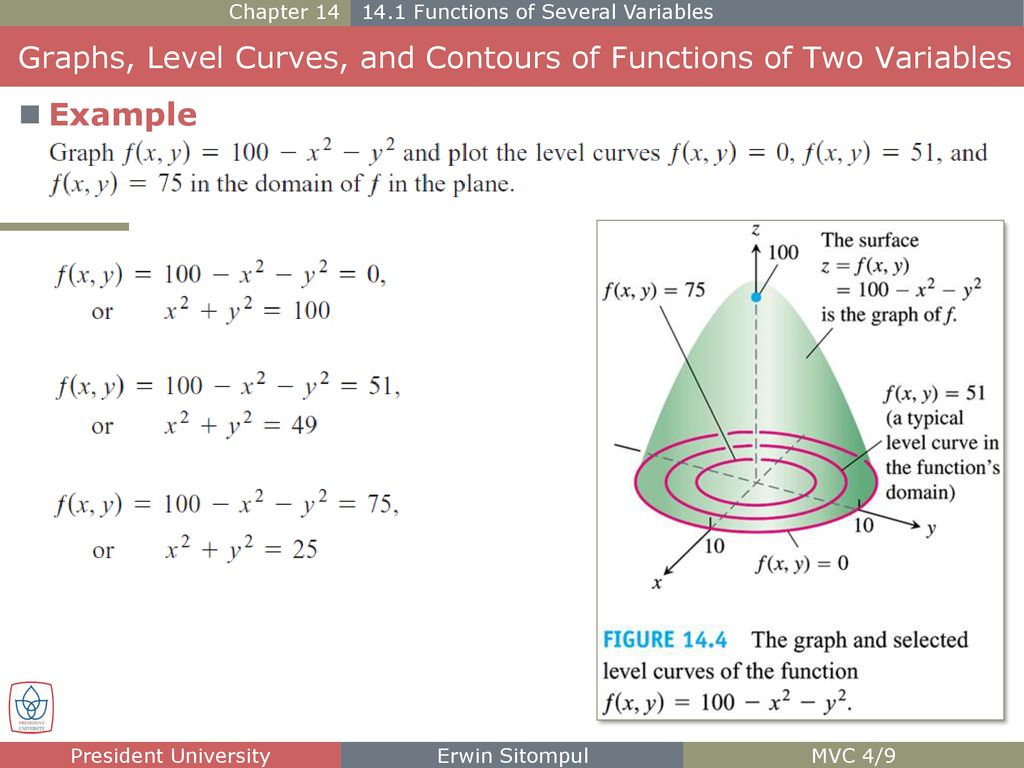
Chapter 14 Partial Derivatives Chapter 14 Partial Derivatives Ppt Download

Find The Area Of The Region X Y X 2 Y 2 8 X 2 2y
What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora
Surface Area
Canvas Instructure Com

Graphs And Level Curves
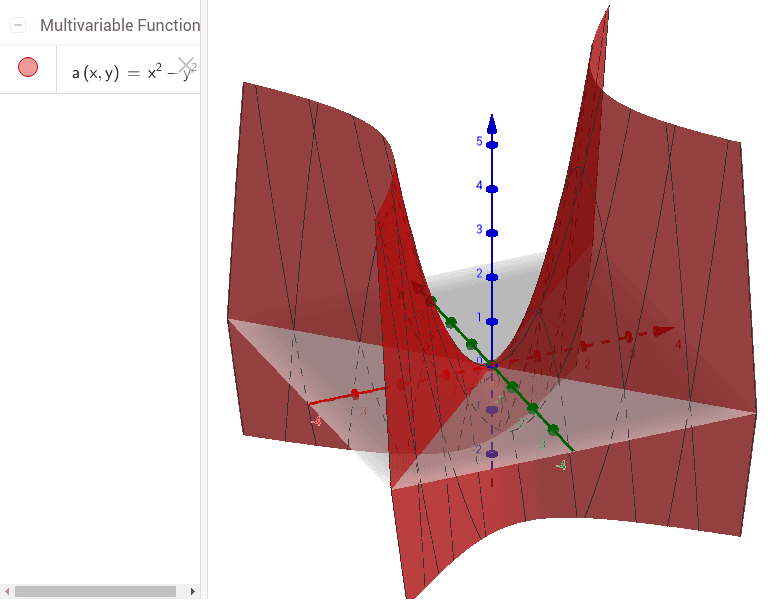
Graph Of F X 2 Y 2 Geogebra
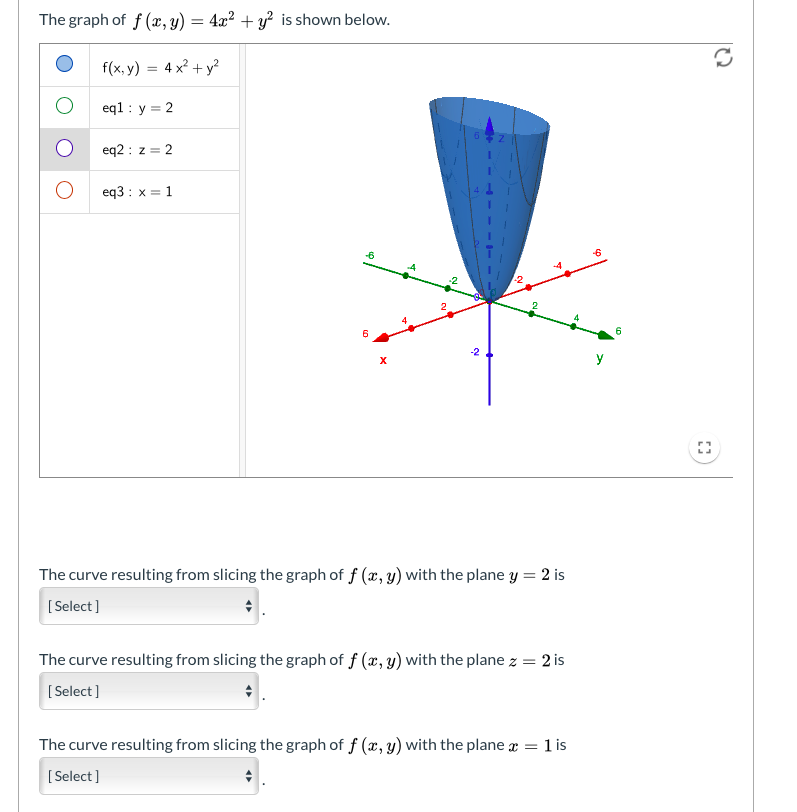
Solved The Graph Of F X Y 4 X2 Y2 Is Shown Below Chegg Com
Wssd K12 Pa Us

Graphs And Level Curves
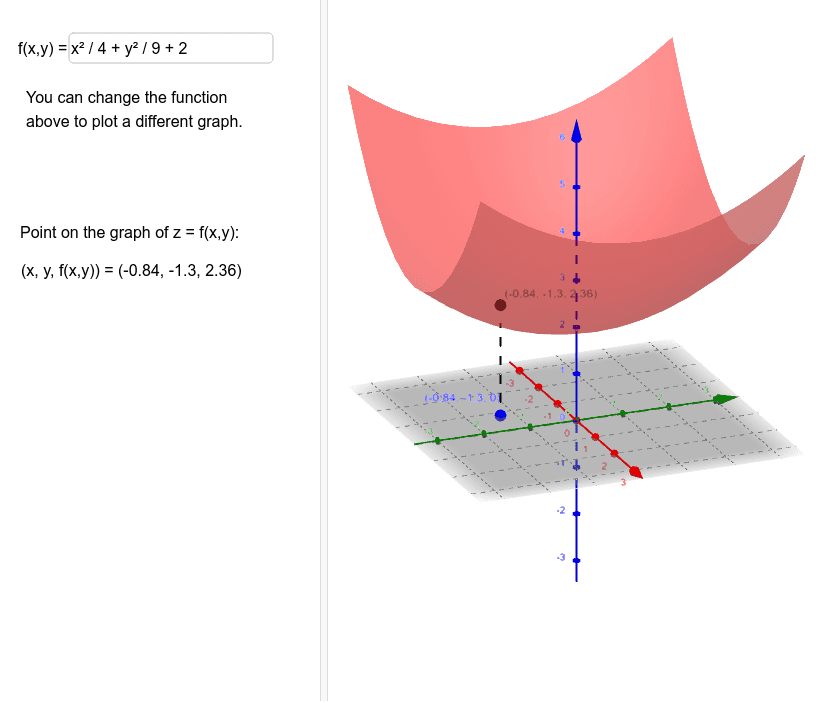
Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra
What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 3 X 2 2 1 Quora
Numerical Gradient Matlab Gradient
Surfaces Part 2

Plotting In 3d

Sketch The Graph Of F X Y Sqrt 1 X 2 Y 2 State The Domain And Range Of The Function Study Com
File F X Y Cosx 2 Cosy 2 2 Png Wikipedia
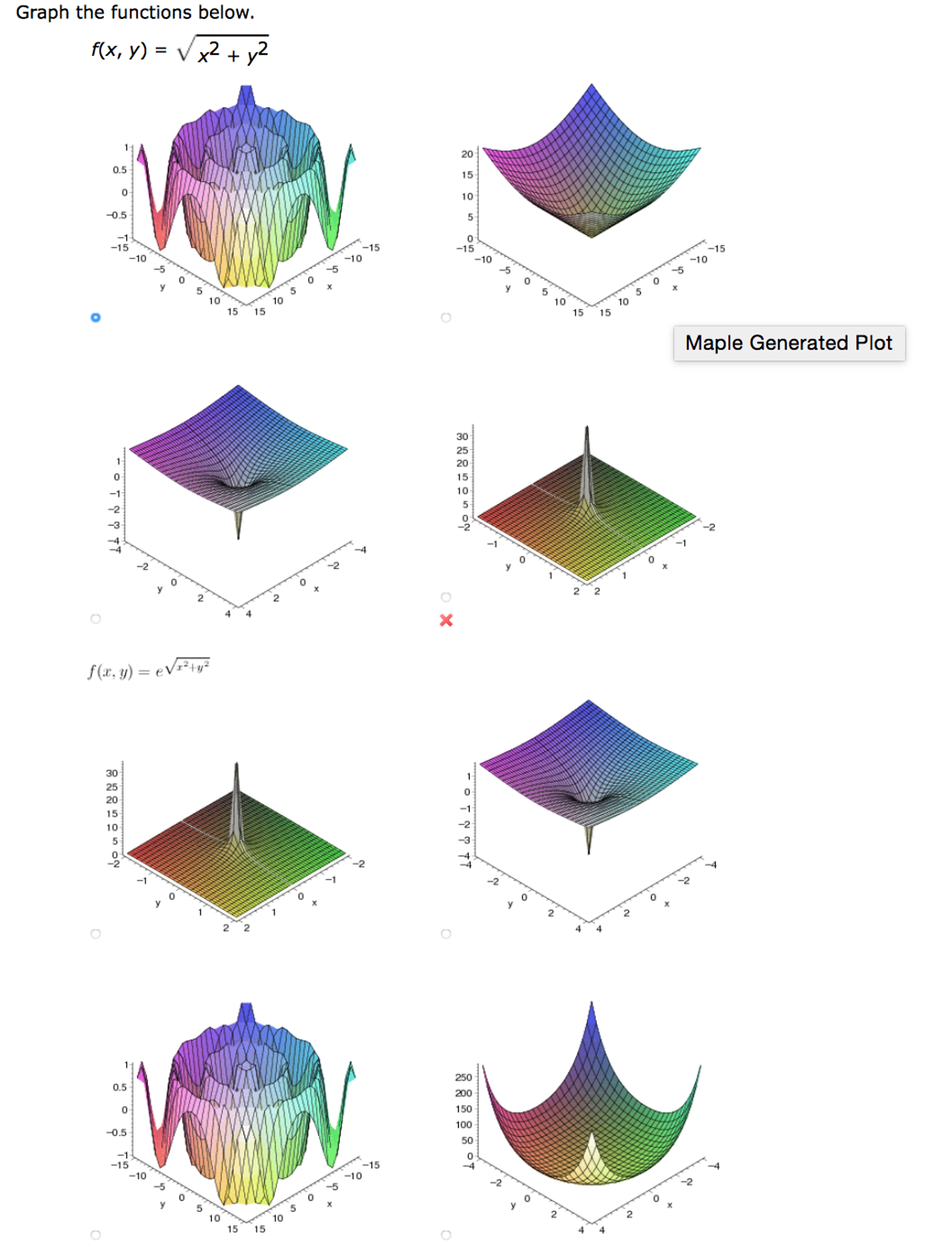
Solved Graph The Functions Below F X Y Squareroot X 2 Chegg Com
Math Ntu Edu Tw
%20(x%5E2+2x+y).jpg)
Wykresy

Graph Y X 2 2 Image Galleries Karimunjawa Net

Use A Graph Or Level Curves Or Both To Find The Local Maximum And Minimum Values As Well As Saddle Points Of F X Y 9 X Y E X 2 Y 2 Then Use Calculus To
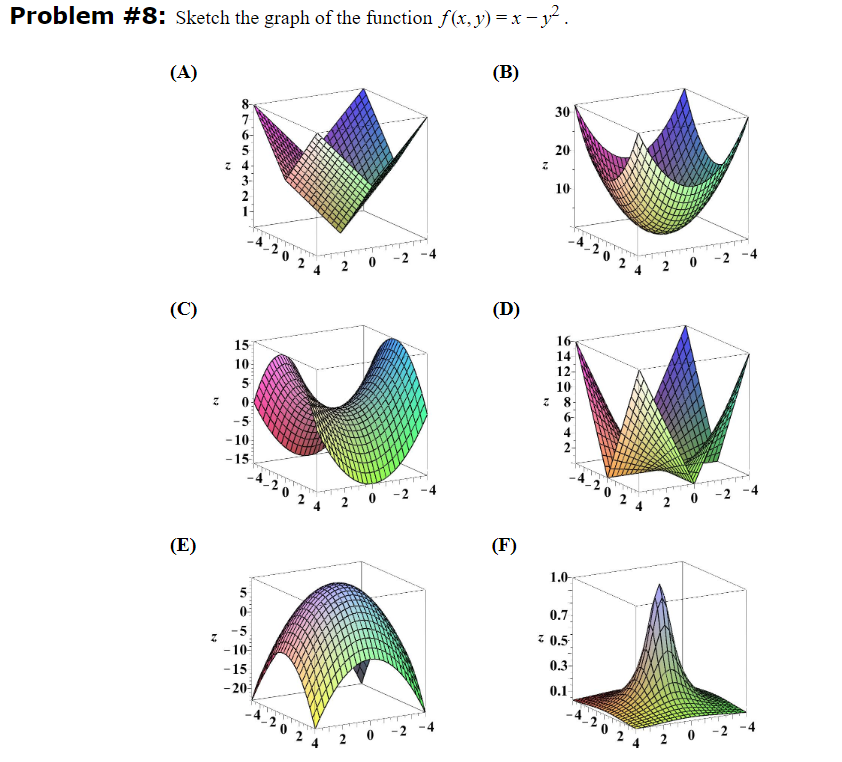
Solved Problem 8 Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Chegg Com
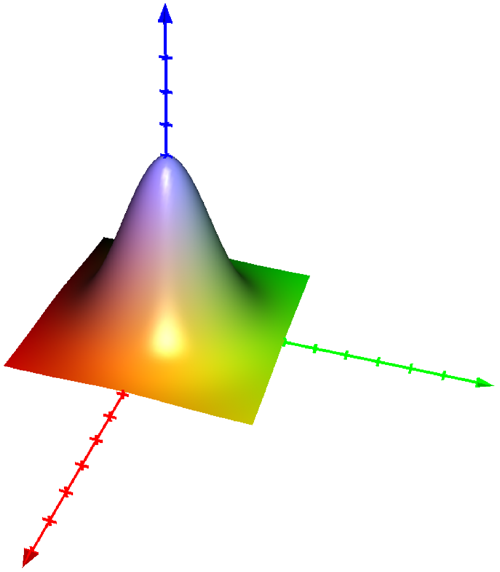
Graph Of A Function In 3d
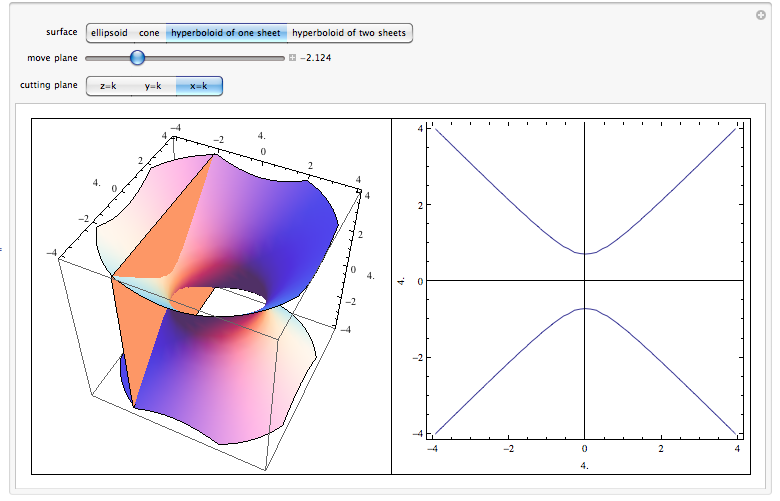
Level Surfaces
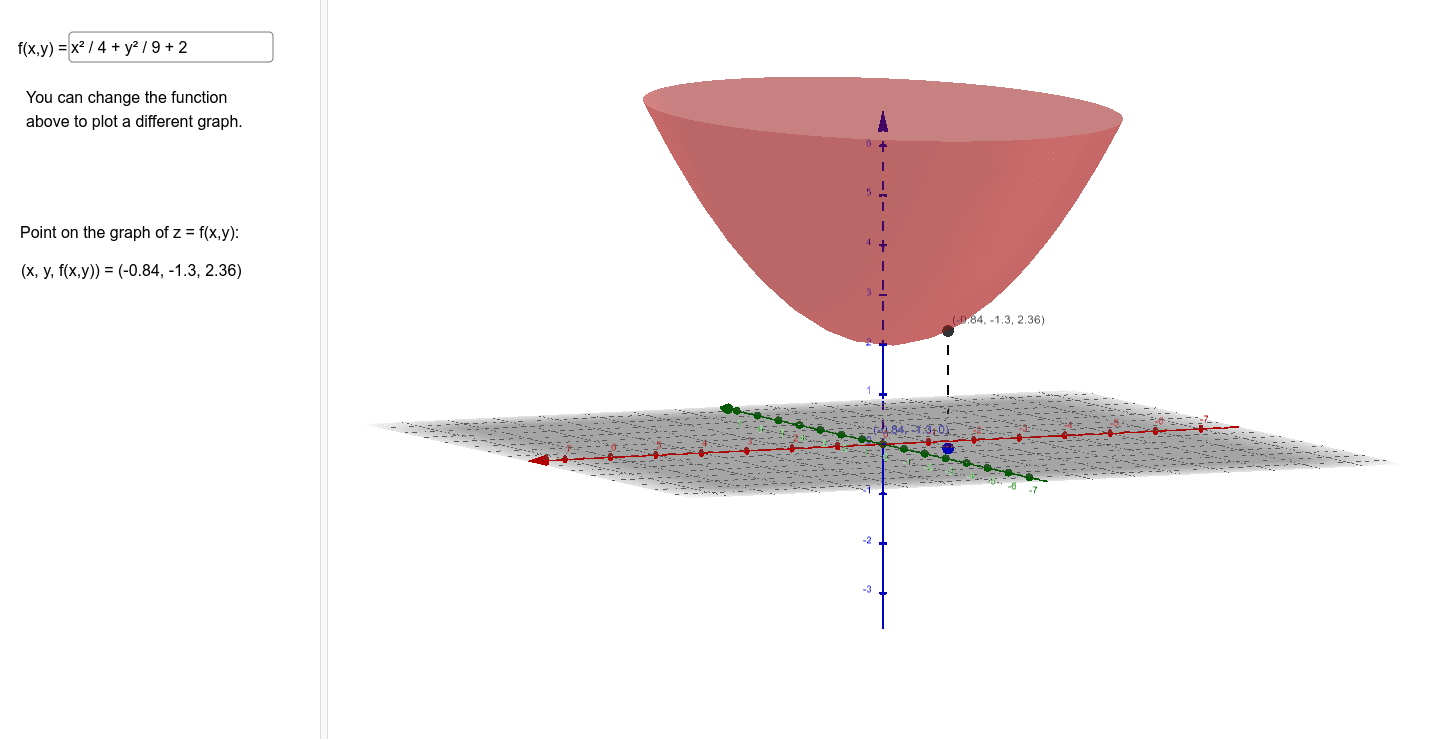
Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra

If X X1 X2 Represents A Point In A Subset A Of Rn And F X Is Exactly One Point In Rm Then We Say That F

Graph Of The Function F 1 3 1 3 2 0 For The Form F X Y Xy Download Scientific Diagram

Graph And Contour Plots Of Functions Of Two Variables Wolfram Demonstrations Project
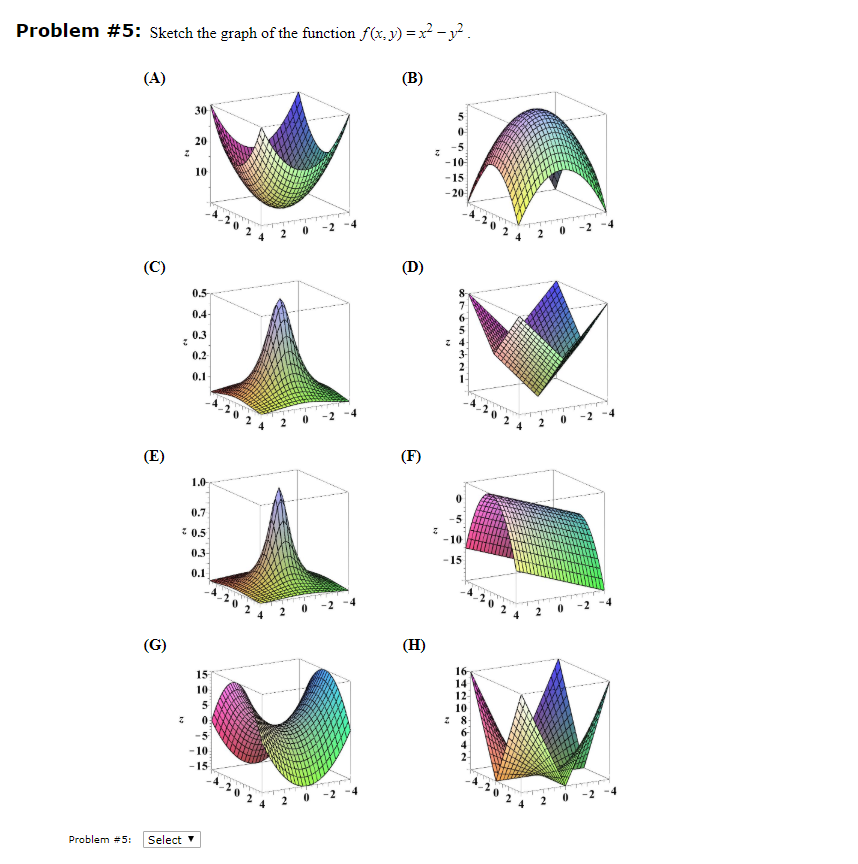
Solved Problem 5 Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Chegg Com
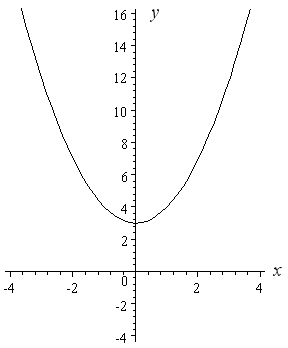
How To Draw Y 2 X 2 Interactive Mathematics
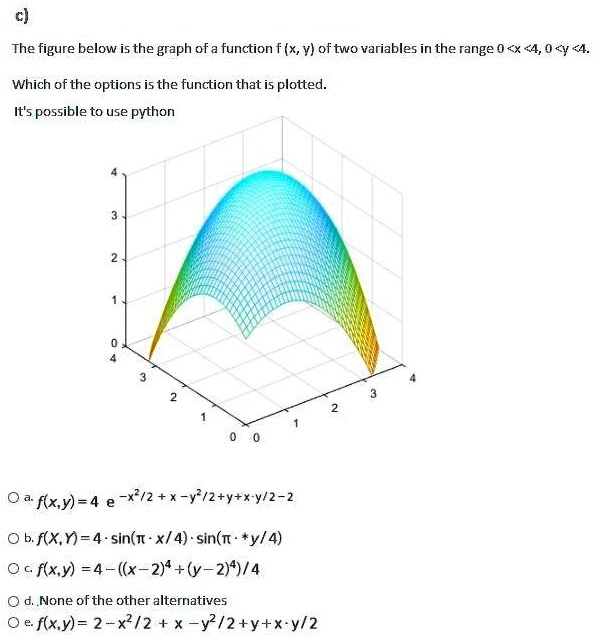
Solved The Figure Below Is The Graph Of A Function X Vl Oftwo Variables In The Range X 4 0 V 4 Which Ofthe Options Is The Function That Is Plotted It S Possible To Use Python Flx Y
3d Surface Plotter Academo Org Free Interactive Education
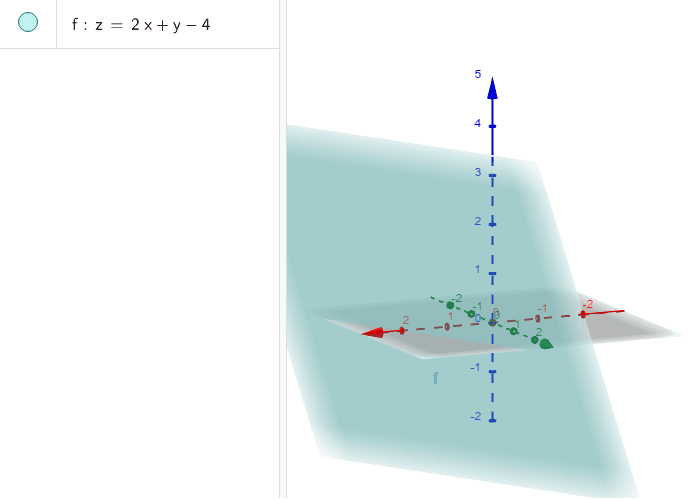
Graph Of Z F X Y 2x Y 4 Geogebra
How Do You Graph F X Y Sqrt X 2 Y 2 1 Ln 4 X 2 Y 2 Socratic
What Are The Extrema And Saddle Points Of F X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Y Socratic
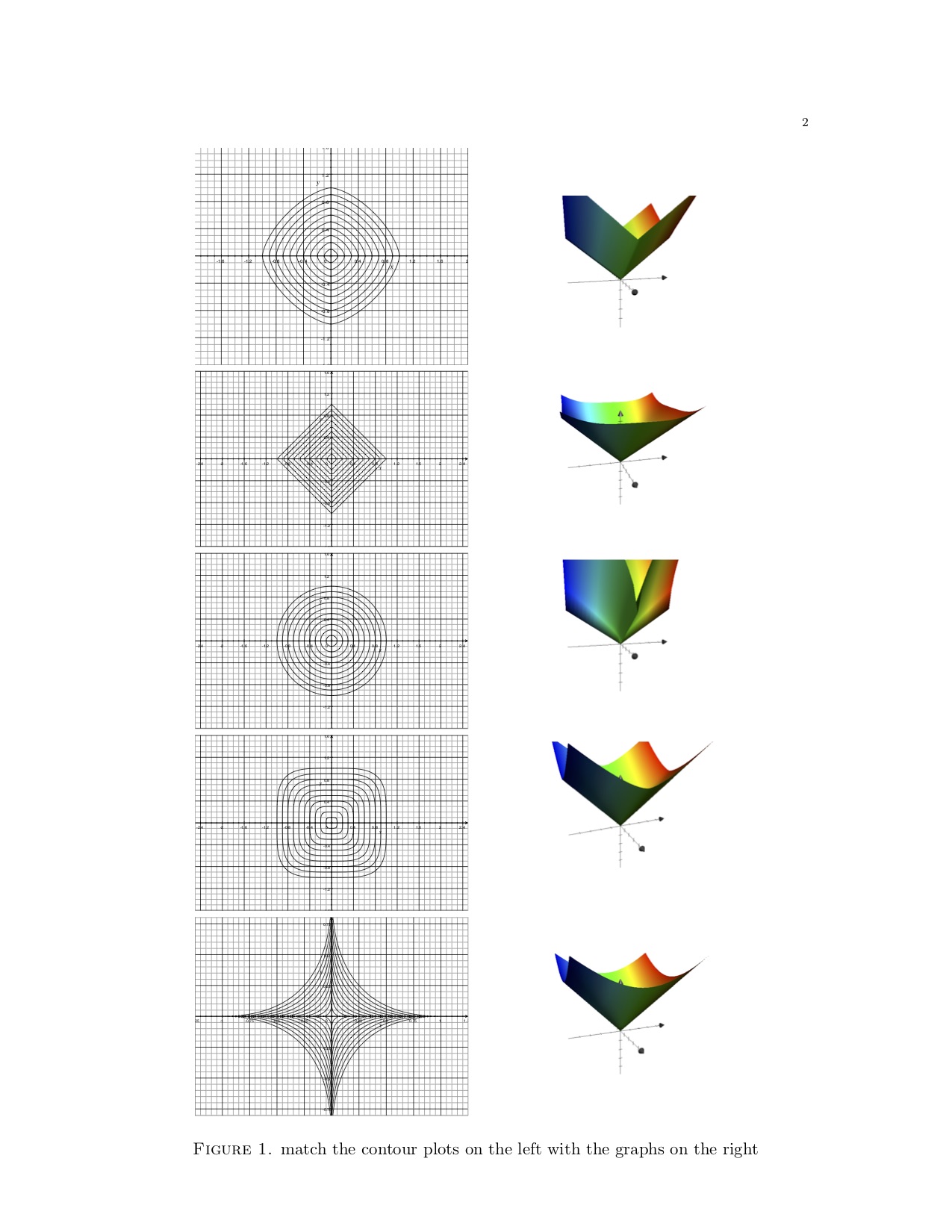
0 3 Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables
Arxiv Org
Graphing Square Root Functions

How To Find The Graphs Of The Following Multi Variable Functions F X Y Ln 1 Xy And F X Y Frac Y E X Mathematics Stack Exchange

Implicit Differentiation
Graph Of X Y

Graphs And Level Curves
Web Mnstate Edu

A Graph F X Y 9 X 2 Y 2 B Find The Normal Vector To The Tangent Plane For 2 1 Study Com

Contour Map Of F X Y 1 X 2 Y 2 Youtube
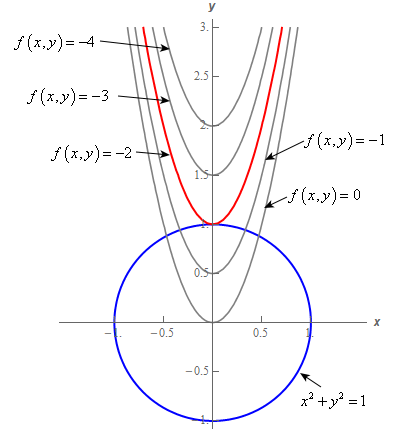
Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers
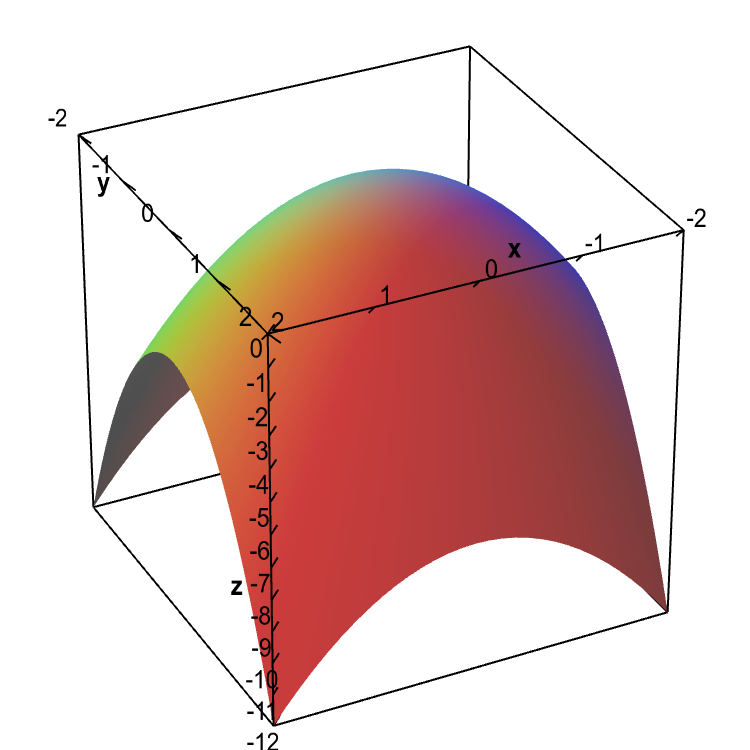
Level Sets Math Insight

13 7 Extreme Values And Saddle Points Mathematics Libretexts

File 3d Graph X2 Xy Y2 Png Wikimedia Commons
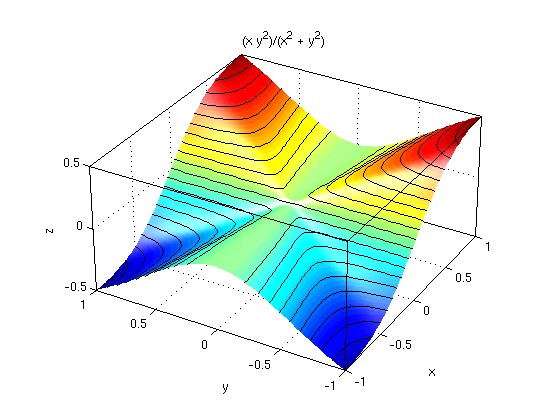
Examples Friday Feb 21
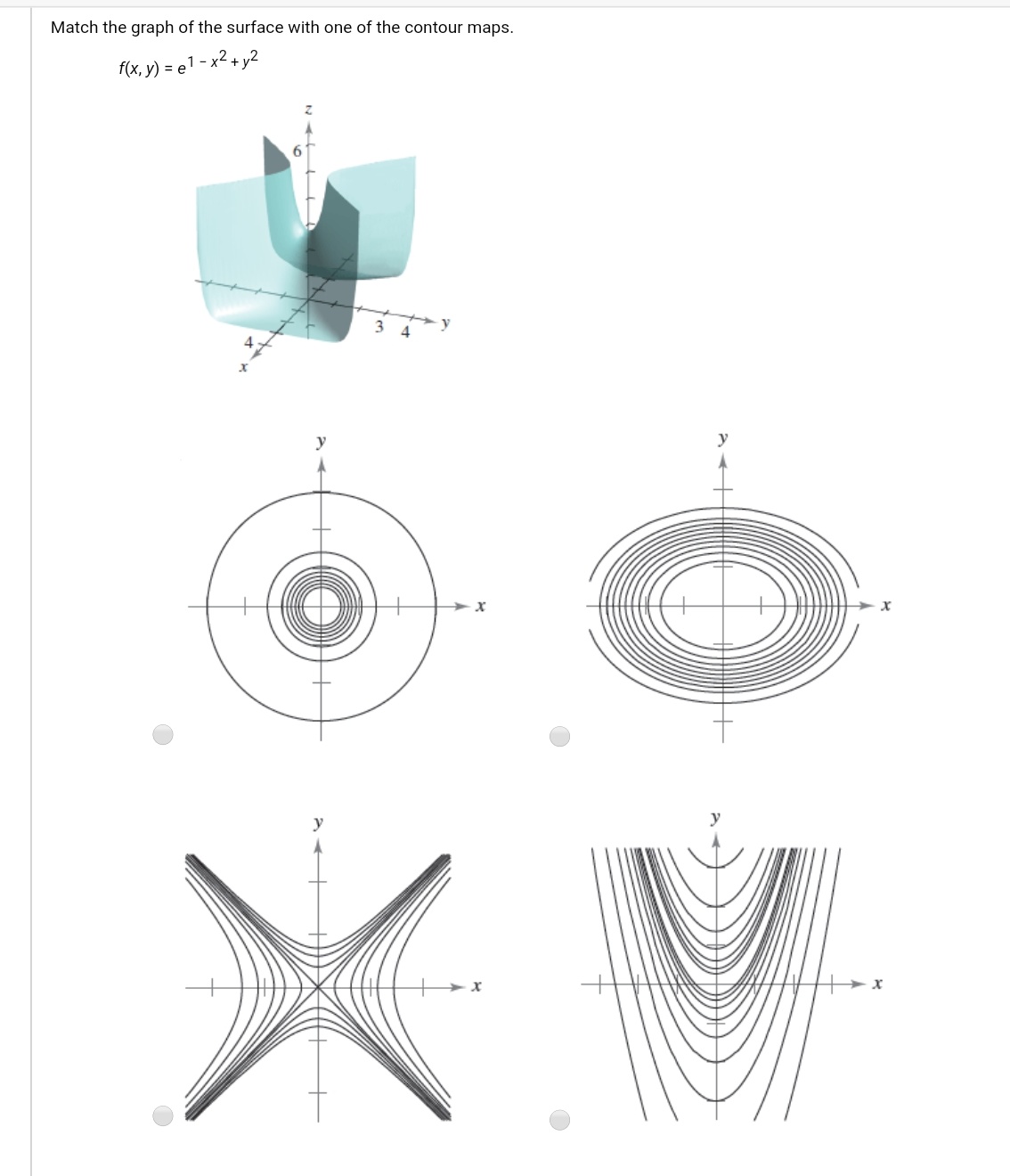
Answered Match The Graph Of The Surface With One Bartleby
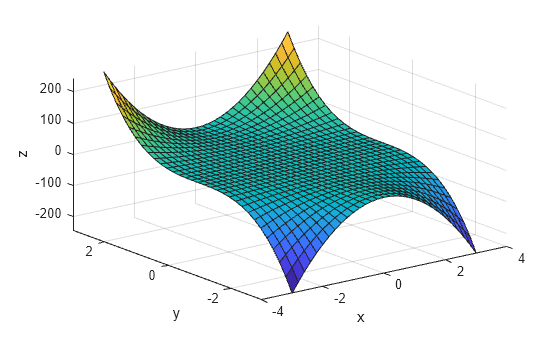
X 2 Y 2 0

Finding The Minima Maxima And Saddle Point S Of Multivariable Functions By Naja Mogeltoft Oct 21 Medium
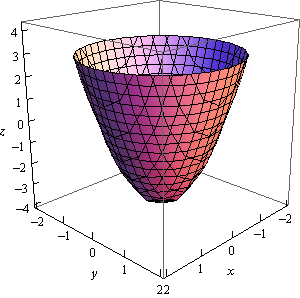
Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables
X 2 Y 2 1

X 2 Y 2 1 0 Chaimmy
A The Graph Of F X Y X 2 Y 2 The Point 0 0 Is A Download Scientific Diagram

Lie Symmetry Analysis Optimal System And Generalized Group Invariant Solutions Of The 2 1 Dimensional Date Jimbo Kashiwara Miwa Equation Chauhan Mathematical Methods In The Applied Sciences Wiley Online Library

Simple Graph Models Of Information Spread In Finite Populations Royal Society Open Science
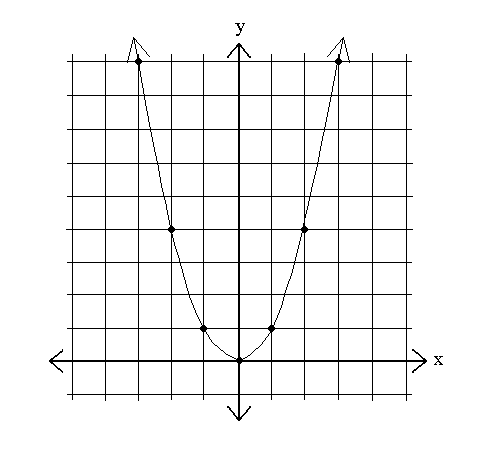
Quadratics Graphing Parabolas Sparknotes
Math Ucsd Edu




