Fx+y+z X2+y2+z20 Pde
3 If z = f(x,y) = xexy, then the partial derivatives are ∂z ∂x = exy xyexy (Note Product rule (and chain rule in the second term) ∂z ∂y = x2exy (Note No product rule, but we did need the chain rule) 4 If w = f(x,y,z) = y xyz, then the partial derivatives are ∂w ∂x = (xy z)(0)−(1)(y) (xy z)2 = −y (xy z)2 (Note.

Fx+y+z x2+y2+z20 pde. Let f(x,y,z) = xyz, x = st, y = s t, z = t We consider f as a function of s and t and we want to calculate ∂f ∂t Method 1 Substitute the expressions for x, y and z into f This gives F(s,t) = s2t2 st3 (12) Diffirentiating 12 with respect to t gives dF dt = 2s2t3st2 (13) Method 2 Use the chain rule (9) or (10) Here we use (9) This gives ∂f ∂t = ∂f. And u,v for the preimage space F−1(R2) Similarly, in 557 and 558 we’ll use different variables for the vectors in R 3 x,y,z for the space that contains S;. SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS FROM ASSIGNMENT 2 Problems 132d and 133d Statement Find general solutions of yu xy 2u x= xusing ODE techniques, as well as its particular solution satisfying the side conditions u(x;1) = 0 and u(0;y) = 0.
Answer The function F( x^2 y^2 , Z xy ) = 0 , with Z =Z(x,y) can be written as F ( u , v ) =0 , with u = x^2 y^2 , v = Z xy Differentiating respect to x and y F_x = (F_u)2x (F_v)( Z_x y ) =0 F_y = (F_u)2y (F_v)( Z_y x ) =0 Elimination of F_u and F_v gives 2x( Z_y x ) 2y(. Math 42/52 Introduction to PDE’s Homework #1 Solutions 1 Find the most general solution to the following PDEs (a) aux buy cu= 0 where a, band. Y)on C through the relation r = h x;.
Across time & space (x,t), (x,y), (x,y,z), or (x,y,z,t) 2 Partial Differential Equations (PDE's) A PDE is an equation which includes derivatives of an unknown function with respect to 2 or more independent variables 3 Now PDE is second order in time t x u(x=0,t) given on boundary. Equations involving only p and q Such equations are of the form f (p,q)=0 z = ax by c (1) is a solution of the equation f (p, q) = 0 provided f (a, b) = 0 (means put p = a and q = b) (2) solving (2) for b, b = F (a) Hence the complete integral is z = ax F (a)y c where a and c are arbitrary constants. 2 Gauss's Divergence Theorem Let F(x,y,z) be a vector field continuously differentiable in the solid, S S a 3D solid ∂S the boundary of S (a surface) n unit outer normal to the surface ∂S div F divergence of F Then ⇀ ⇀ ⇀ ˆ ∂S S.
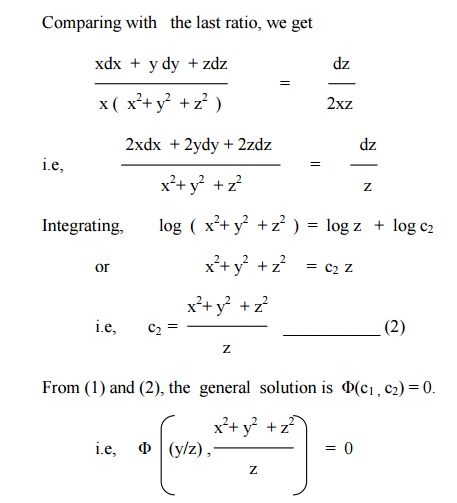
On integration L x m y n z= c2 Hencefrom(1) and(2) therequired solution is f(x 2y 2z 2,lxmynz)=0 APPLICATIONS OF PDEs 1 WAVE EQUATIONS The simplest situation to giverise to the onedimensionalwave equation. 1;0) with values f(x;y;z) = 5 and 1 Case 2 If z ̸= 0, the third equation gives = 1 Then the second equation gives 2y = 2y or y = 4 Then plugging. 0=x 2y ycosx Now we find Fx and Fy Fx =2xysinx Fy =2y cosx Then, dy dx = 2xysinx 2y cosx 133 of 146 Multivariate Calculus;.
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music. 3 For each solution ( x,y,z,,µ), find f(x,y,z) and compare the values you get The largest value corresponds to maximums, the smallest value corresponds to minimums 5 Examples Example 51 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraints xy z =0and x2 2z2 =1 f(x,y,z. Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music.
The general solution of a firstorder, quasilinear PDE a(x,y,u) u x b(x,y,u) u y = c(x,y,u) (239) satisfies F(Φ,Ψ)=0, (240) where Fis an arbitrary function of Φ(x,y,u) and Ψ(x,y,u), and any intersection of the level sets of Φ and Ψ is a solution of the characteristic equations dx. Partial Differential Equations Exam 1 Review Solutions Spring 18 Exercise 1 Verify that both u= log(x2y2) and u= arctan(y=x) are solutions of Laplace’s equation u xx u yy= 0 If u= log(x2 y2), then by the chain rule u x= 2x x 2 y) u xx= (x2 y2)(2) (2x)(2x) (x 2 y) 2y2 2x2 (x y2)2 and by the symmetry of uin xand y,. 0 d ( xy ) 2 zdz = 0 Integrating, we get xy z 2 = b (3) Therefore the general solution of the given equation is f ( x y z, xy z 2 ) = 0 (3)Show that the integral surface of the PDE x( y 2 z ) p − y ( x 2 z ) q = ( x 2 − y 2 ) z.
Y x 2 y =4 (1) ie, a circle of radius 2 cen tered at the origin W e start b y asso ciating p osition v ector r to eac h p oin t(x;. Partial Differential Equations MCQ 1 The solution of the following partial differential equation is 2 Consider the following partial differential equation For this equation to be classified as parabolic, the value of B 2 must be 3 Consider a function f (x,y,z) given by The partial derivative of this function with respect to x at the. Ellipsoids are the graphs of equations of the form ax 2 by 2 cz 2 = p 2, where a, b, and c are all positive In particular, a sphere is a very special ellipsoid for which a, b, and c are all equal Plot the graph of x 2 y 2 z 2 = 4 in your worksheet in Cartesian coordinates Then choose different coefficients in the equation, and plot a.
7 Form the partial differential equation by eliminating f from 2 1 z x f x2 log y = Solution Let 2 1 z x f x2 log y = (1) Differentiate (1) partially wr t x and y z p x f x2 2 log' 1 1 x y x ∂ = = ∂ (2) ' 2 1 1 2 log z q f x y y y ∂ − = = ∂ (3) Eliminating f ' from (2) & (3). F(y,x 1,x 2)=0 has well defined continuous partial derivatives ∂F ∂y = F y ∂F ∂x 1 = F x 1 ∂F ∂x 2 = F x2 and if, at the values where F is being evaluated, the condition that ∂F ∂y = F y 6=0 holds, then y is implicitly defined as a function of x The partial derivatives of y with respect. De ned by z= x 2 y2 and x 2y2 z2 = 7 at the point ( 1;1;2) Hint Think about the geometry of the gradient vectors You don’t have to parametrize the curve to do this problem Solution The surface z= x2 y2 can be written as the level surface F(x;y;z) = x 2 y z= 0;.
The data for this problem consists of two functions f(x;y) 2R2 nDand h(x;y) defined on the boundary @D The above The above problem, ie the PDE along with the boundary condition and the radiation condition at 1is wellposed. Fall 13 S Jamshidi Example 5607 2 Find @z @y for 4=x2 2y2 z 2z We begin by putting the equation in the correct form, find the relevant partials, and then plug in 0=x2 2y2 z 2z 4,F y =2y, Fz =2z 2 @z. This answer is useful 6 This answer is not useful Show activity on this post We set u = x y z 2, v = x y z, then the operation of d on (1) leads to d F ( u, v) = ∂ F ( u, v) ∂ u d u ∂ F ( u, v) ∂ v d v Thus 0 = d F ( u, v) 0 = d u = d ( x y z 2).
Thus, to solve the equation of the form Pp Qq = R, we have to follow this solution procedure 1) Form the subsidiary equations as d x P = d y Q = d z R 2) Solve any two simultaneous equations by any method giving u = a and v = b as its solutions 3) Write the. Z = 0 Point (0;0) z = 1 Circle x 2 y = 1 z = 2 Circle x 2 y = 2 z = 3 Circle x2 y2 = 3 (b) Sketch all the traces that you found in part (a) on the same coordinate axes (c) Compute equations for the traces in the y = 0, y = 1, y = 2, and y = 3 planes Plane Trace y = 0 Parabola z = x2 y = 1 Parabola z = x2 1 y = 2 Parabola z = x2 4 y. Eg x2p y2q = z is a linear in z and of first order Further, a pde is said to be quasilinear if degree of highest order derivative is one, no product of partial derivatives are present eg z – z xx (z y)2 = 0 is a quasilinear 2nd order 112 FORMATION OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS.
PDP persamaan yg memuat suatu fs dgn 2 atau lebih variabel bebas berikut derivatif parsial fs tsb thd variabel bebasnya Penyelesaian PDP sembarang fs yg memenuhi PD sec identik PUPDP penyelesaian yg terdiri dari sejumlah fs sembarang yg bebas linier yg banyaknya sama dgn. The directional derivative of z = f(x,y) is the slope of the tangent line to this curve in the positive sdirection at s = 0, which is at the point (x0,y0,f(x0,y0)) The directional derivative is denoted Duf(x0,y0), as in the following definition Definition 1 The directional derivative of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the direction of the unit vector. Method of Lagrange Multipliers Plug in all solutions, (x,y,z) ( x, y, z), from the first step into f (x,y,z) f ( x, y, z) and identify the minimum and maximum values, provided they exist and ∇g ≠ →0 ∇ g ≠ 0 → at the point The constant, λ λ , is called the Lagrange Multiplier.
3 (Exercise ) Find the minimum/maximum of f(x;y;z) = x2 y2 z2 subject to x y = 1 and y2 z2 = 1 Solution The gradient equation gives 2x = ;2y = 2 y;2z = 2 z Case 1 If z = 0, y2 z2 = 1 implies y = 1 and from x y = 1 we get the points (2;1;0) and (0;. X,Y,Z for the space containing the image. Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange.
X and y are nonnegative When y = 0 we get f(x,y) = √ x, the familiar square root function in the xz plane, and when x = 0 we get the same curve in the yz plane Generally speaking, we see that starting from f(0,0) = 0 this function gets larger in every direction in roughly the same way that the square root function gets larger For example,. F(x,y,z,p,q) = 0 (2) The equations of the type (2) arise in many applications in geometry and physics For instance, consider the following geometrical problem EXAMPLE 1 Find all functions z(x,y) such that the tangent plane to the graph z= z(x,y) at any arbitrary point (x0,y0,z(x0,y0)) passes through the origin characterized by the PDE xzx. Let f(x,y,z) = x2 2y2 3z3, so that the equation for the ellipsoid becomes f(x,y,z) = 1 A normal vector to the plane 3x−2y3z= 1 is h3,−2,3i A normal vector for the tangent plane at the point (x0,y0,z0) on the ellipsoid is given by → ∇f(x0,y0,z0) = h2x0,4y0,6z0i Since the tangent plane is parallel to the given plane we must have →.
Answer (1 of 6) Taking first partial derivatives yields z_x = f(x^2 y^2) (x y) \cdot 2x \, f'(x^2 y^2) \text{ and } z_y = f(x^2 y^2) (x y) \cdot (2y. For f(x,y,z,a,b) = 0 differentiating wrto x,y partially and eliminating constants a,b we get a PDE Example 1 From the equation x2 y2 z2 = 1 form a PDE by eliminating arbitrary constant Solution z2 = 1 x2 y2 Differentiating wrto x,y partially respectively we get y y z x d z x z 2z 2 2 2 w w w w p = = x/z and q= = y/z z = x/p = y/ q qx = py is required PDE. X,Y for the image space F(R2);.
Partial Derivative of functions is an important topic in Calculus If we have a function f (x,y) ie a function which depends on two variables x and y, where x and y are independent to each other, then we say that the function f partially depends on x and y The derivative of f. Section 15 Functions of Several Variables In this section we want to go over some of the basic ideas about functions of more than one variable First, remember that graphs of functions of two variables, z = f (x,y) z = f ( x, y) are surfaces in three dimensional space For example, here is the graph of z =2x2 2y2 −4 z = 2 x 2 2 y 2 − 4. Level surfaces For a function $w=f(x,\,y,\,z) \, U \,\subseteq\, {\mathbb R}^3 \to {\mathbb R}$ the level surface of value $c$ is the surface $S$ in $U \subseteq.
Use Lagrangian multipliers x,y,z, We get the ratio in (1) logx logylogz=log b Hence the general solution is, F (x2y2z2 , logx logylogz)=0 The auxiliary equation is m32m2=0 Replace D by m and D’ by 1 m2(m2)=0 m=0,0 and m=2. "The value of `(x^2(yz)^2)/((xz)^2y^2)(y^2(xz)^2)/((xy)^2z^2)(z^2(xy)^2)/((yz)^2x^2)`is`1`(b) 0 (c) 1 (d) None of these". Let f(x,y,z) =x2−y2−z2 f ( x, y, z) = x 2 − y 2 − z 2 and let S be the level surface defined by f (x,y,z) = 4 (a) Find an equation for the plane tangent to S at P 0(1,−1,−2) P 0.
Since z satisfies 0. 12 Examples Example 11 u x= 0 Remember that we are looking for a function u(x;y), and the equation says that the partial derivative of uwith respect to xis 0, so udoes not depend on x Hence u(x;y) = f(y), where f(y) is an arbitrary function of y Alternatively, we could simply integrate both sides of the equation with respect to x. F(x,y,z,zx,zy) = 0 This is a PDE for the unknown function of two independent variables Exercise 21 Let f(x,y,a,b) = (x−a)2(y−b)2 Get a PDE by eliminating the parameters a and b (Answer u2 x u2 y = 4u) 2 Unknown function of known functions.
Y i (2) The co ordinates x and y in (2)are not arbitrary {they are related through equation (1) This means that w e are free to assign a v alue only one of the co. 3 Find the PDE of all spheres whose centre lie on the (i) z axis (ii) xaxis 4 Form the partial differential equations by eliminating the arbitrary functions in the following cases (i) z = f (x y) (ii) z = f (x2 –y2) (iii) z = f (x2 y2 z2) (iv) f(xyz, x y z) = 0 (v) F (xy z2, x y z) = 0. And so the gradient of Fis rF(x;y;z) = h2x;2y;.
1 BASICCONCEPTS 2 2 Verify that for all pairs of differential functions f and g of one variable, u(x,y) = f(x)g(y) is a solution of the PDE uuxy = uxuy Solution First, compute ux, uy and uxy ux = g(y)f′(x) uy = f(x)g′(y) uxy = f′(x)g′(y) Substituting into the PDE, we have.

Solved An Equation Which Involves Partial Derivatives Of A Chegg Com
2

The Decision Of Three Methods Of The Solutions Dx P Dy Q Dz R Mathematics Stack Exchange
Fx+y+z X2+y2+z20 Pde のギャラリー

Assignment 5 Pde

Partial Differential Equations Formation Of Pde By Differential Equations Formation Of Pde By Eliminating The Arbitrary
Solved Form Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function F Ax By Cz X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Also Find Order And Degree Of The Course Hero

One Dimentional Wave Eqn

1 First Order Ordinary Differential Equations Free Download Pdf
2

Pdf The Solution Of The Variable Coefficients Fourth Order Parabolic Partial Differential Equations By The Homotopy Perturbation Method

Solved Questi On L Characterize Each Of The Following Chegg Com

One Dimentional Wave Eqn
2

Ma 1 Partial Differential Equations Lecture 2 Linear First Order Pdes Integral Surfaces Passing

Partial Differential Equation Notes

Partial Differential Equation Notes
2

Ode Pde Laplace Transforms And Vector Analysis Unit

Math 21a Midterm I Review
Partial Differential Equations Solved Examples

Unit 1 Pdf Partial Differential Equation Equations

Ode Pde Laplace Transforms And Vector Analysis Unit
How To Determine The Extreme Values Of The Function Math F X Y Z X 2y 2z Math For Condition Math X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Math Quora
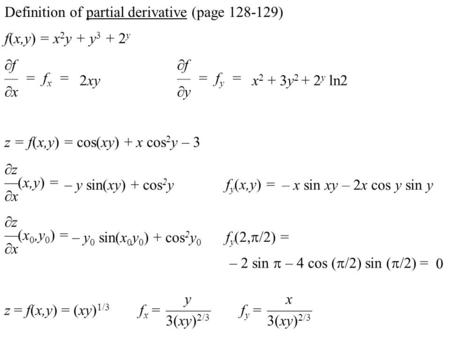
Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download
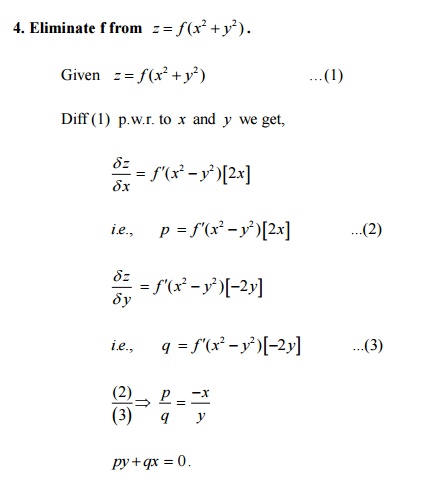
Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations

Ma2211 Unit 3 Pdf Equations Differential Calculus

Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations

Partial Differential Equations
2

Solve The Equation X 2p 2 Y 2q 2 Z 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection
What Is The Form A Pde By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function Phi From Phi X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Z 2 2xy 0 Can Someone Solve It Quora

Lagranges Pde Y 2 Z 2 X 2 P 2xyq 2zx Youtube

Chapter 1 Maths 3

Ad Eng Math 6 8 15 Pages 1 244 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
2
2
2
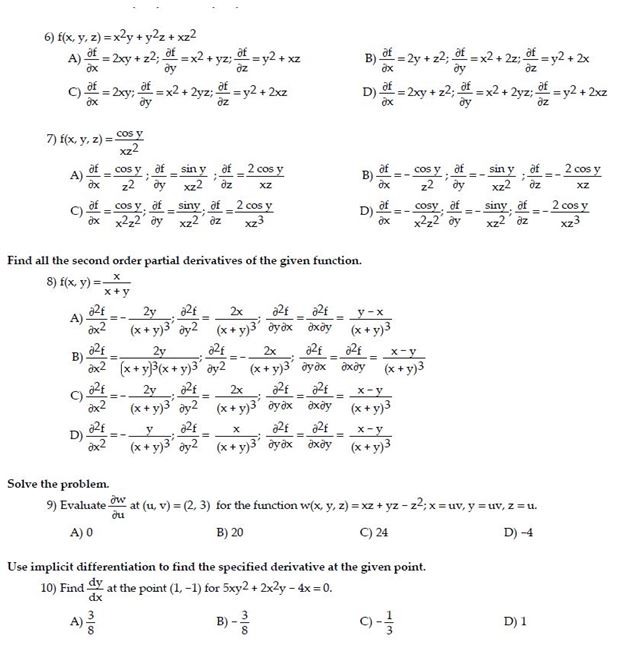
Solved F X Y Z X 2y Y 2z Xz 2 Partial Differential Chegg Com
2

If U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u X Y

Verifying Solutions To Differential Equations Video Khan Academy

Math 9 Solutions To Assignment 7 X 2y 1 X 2y I 2 F X Cos Y Z F Y X Z Sin Y Z F Z Xy Z 2 Sin Y Z Pdf Free Download
1
Partial Elimination Of Arbitrary Functions Solved Problems
Solved Solve The Pde Using Lagrange Methode Z Xp Yq Y 2 X 2 Y Z Yz P Z X Zx Q X Y Xy Course Hero

Chapter 9 Partial Differential Equations 13 Studocu
2

2 Partial Differentiation

Chapter 1 Maths 3
What Is The Form A Pde By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function Phi From Phi X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Z 2 2xy 0 Can Someone Solve It Quora

Doc Partial Derivative Mcq S Assignement Innocentboy Nishant Academia Edu
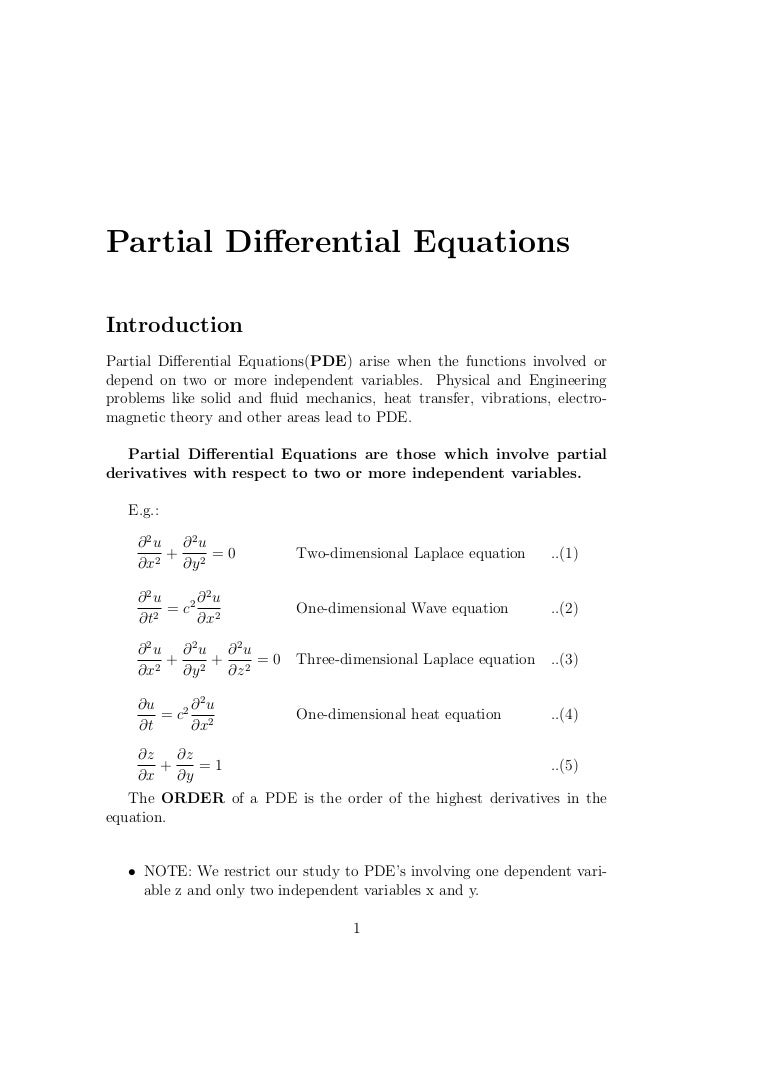
Partial Differential Equation Notes
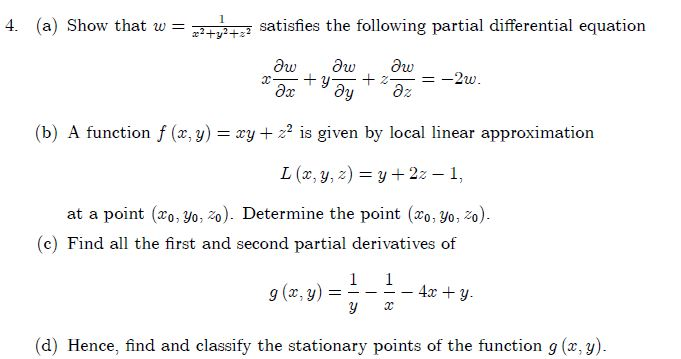
Solved Show That W 1 X2 Y2 Z2 Satisfies The Following Chegg Com

How Is Frac Dx Z X Y Frac Dy Z X Y Frac Dz X 2 Y 2 Equivalent To Frac Y Dx Xdy Zdz 0 Frac Xdx Ydy Zdz 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange

Lct 08 18mat21 Module 3 Formation Of Pde From F X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Lx My Nz 0 Youtube
11 Partial Differential Equations Pdfcoffee Com

Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
Solved Solve The Pde Using Lagrange Methode Z Xp Yq Y 2 X 2 Y Z Yz P Z X Zx Q X Y Xy Course Hero

Unit V Pde Converted Pdf Unit V Partial Differential Equations U27a2 Formation Of Partial Differential Equations By Elimination Of Arbitrary Constants Course Hero

Form The Partial Differential Equation From Z A 2 X A Y 2 B Infintynotes
2
How To Eliminate The Arbitrary Function And Hence Obtain The Partial Differential Equation Z X Y F X 2 Y 2 Quora
Solved Form Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function F Ax By Cz X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Also Find Order And Degree Of The Course Hero
Prove That Det Yx X 2 Zx Y 2 Xy Z 2 Zx Y 2 Xy Z 2 Yz X 2 Xy Z 2 Yz X 2 Zx Y 2 Is Divi Youtube
2

Form A Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating Arbitrary Function From Z F X 2 Y 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection
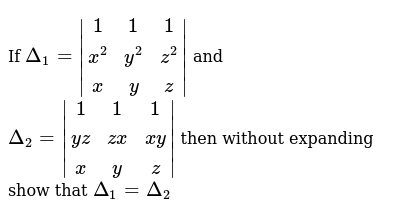
If Delta 1 1 1 1 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 X Y Z And Delta 2 1 1 1 Yz Zx Xy X Y Z Then Without Expanding Show That Delta 1 Delta 2

Math 467 Partial Differential Equations Exercises Millersville

Intro To Pdes Pdf Partial Differential Equation Equations

Solved Find The General Solution Of The Following Partial Chegg Com

If X 2 Y 2 Z 2 2 X Y Z 3 Find The Value Of 2x 3y 4z Youtube

Pdf Engineering Mathematics Ii 15mat21 Veeresh Kumar Academia Edu
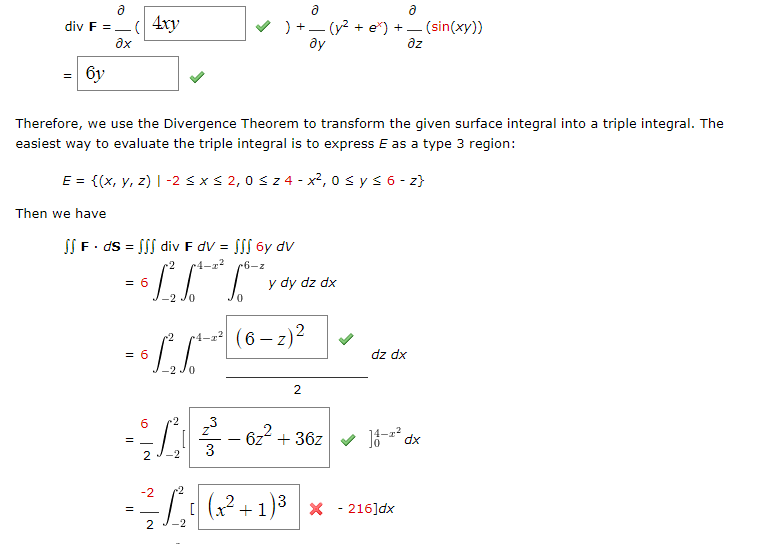
Solved Evaluate F Ds Where F X Y Z 4xyi Y2 Chegg Com

Module 2 Pdf Partial Differential Equation Equations

The Decision Of Three Methods Of The Solutions Dx P Dy Q Dz R Mathematics Stack Exchange

Chapter 1 Maths 3

Chapter 1 Maths 3

Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations
Document
Solved Solve The Pde Using Lagrange Methode Z Xp Yq Y 2 X 2 Y Z Yz P Z X Zx Q X Y Xy Course Hero
1
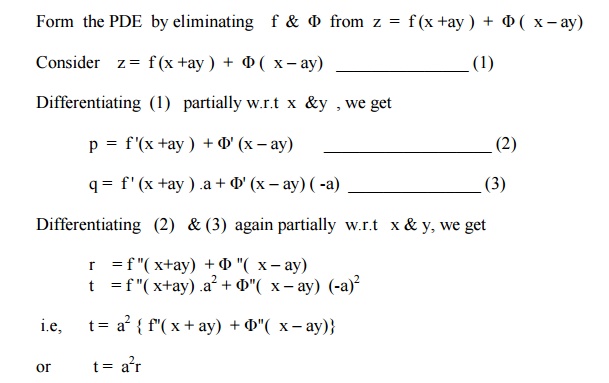
Formation Of Partial Differential Equations

Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
2

Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download

1 First Order Ordinary Differential Equations Pdf Free Download

Unit 1 Pdf Partial Differential Equation Equations
2
2
2

Ode Pde Laplace Transforms And Vector Analysis Unit

Solved Partial Differential Equations Pde Find And P X Z Chegg Com
How To Solve Partial Differential Equation P Cos X Y Q Sin X Y Z Quora

Ode Pde Laplace Transforms And Vector Analysis Unit

Solved Partial Differential Equations 2 Form The Partial Chegg Com

Solution Of First Order Linear Pde Pdf Partial Differential Equation Differential Calculus

Sma 2371 Pde Notes
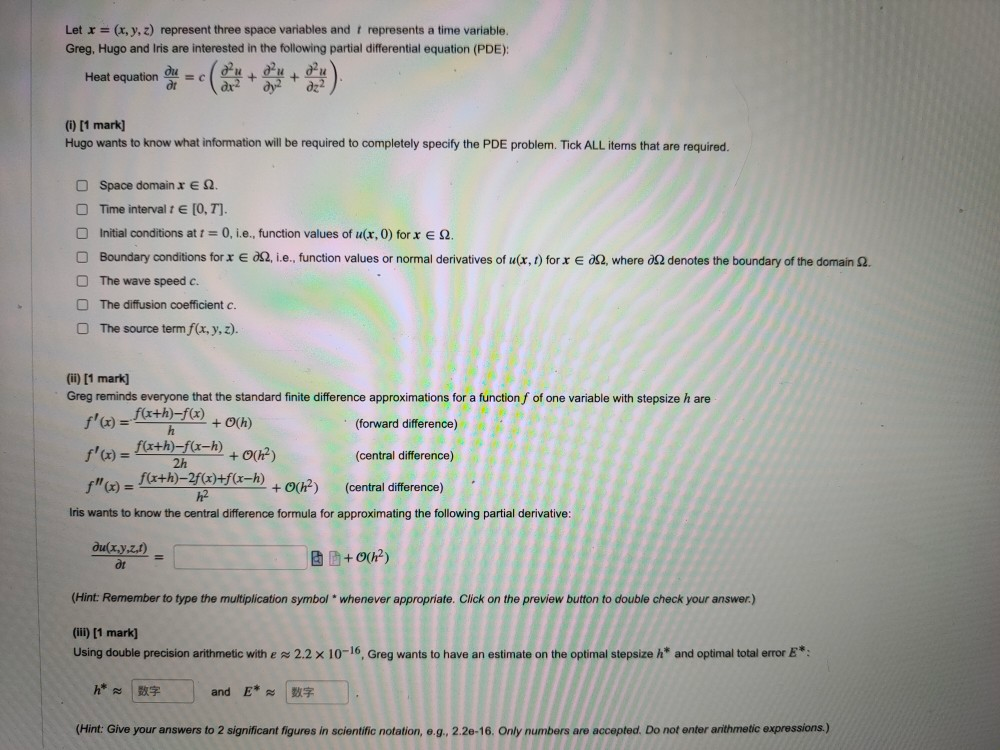
Solved Let X X Y Z Represent Three Space Variables And Chegg Com

Partial Differential Equations Eliminate Arbitrary Functions Z Y 2 2f 1 X Log Y Youtube
Partial Differential Equations
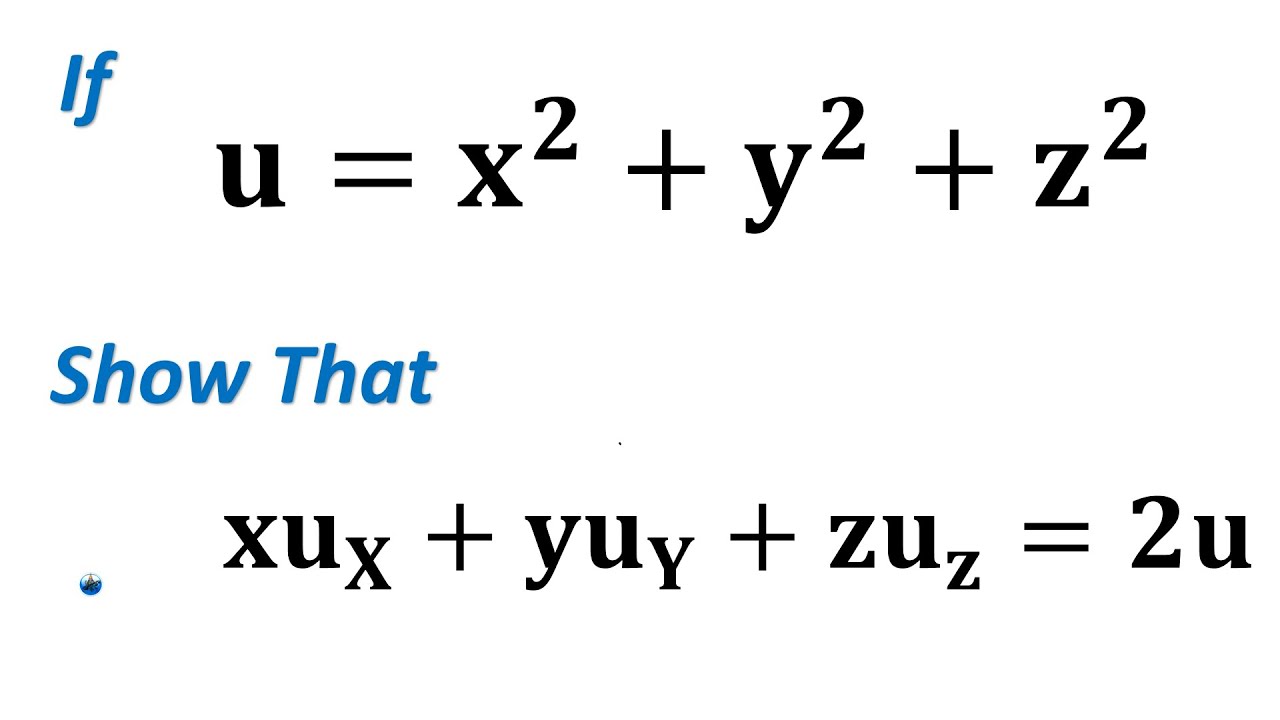
Show That Xux Yuy Zuz 2u If U X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Partial Derivatives Solved Example Youtube

8 Partial Differential Equations Differential Equations Dev Guis

Form The Partial Differential Equation From X A 2 Y B 2 Z 2 Cot 2 A Infintynotes




