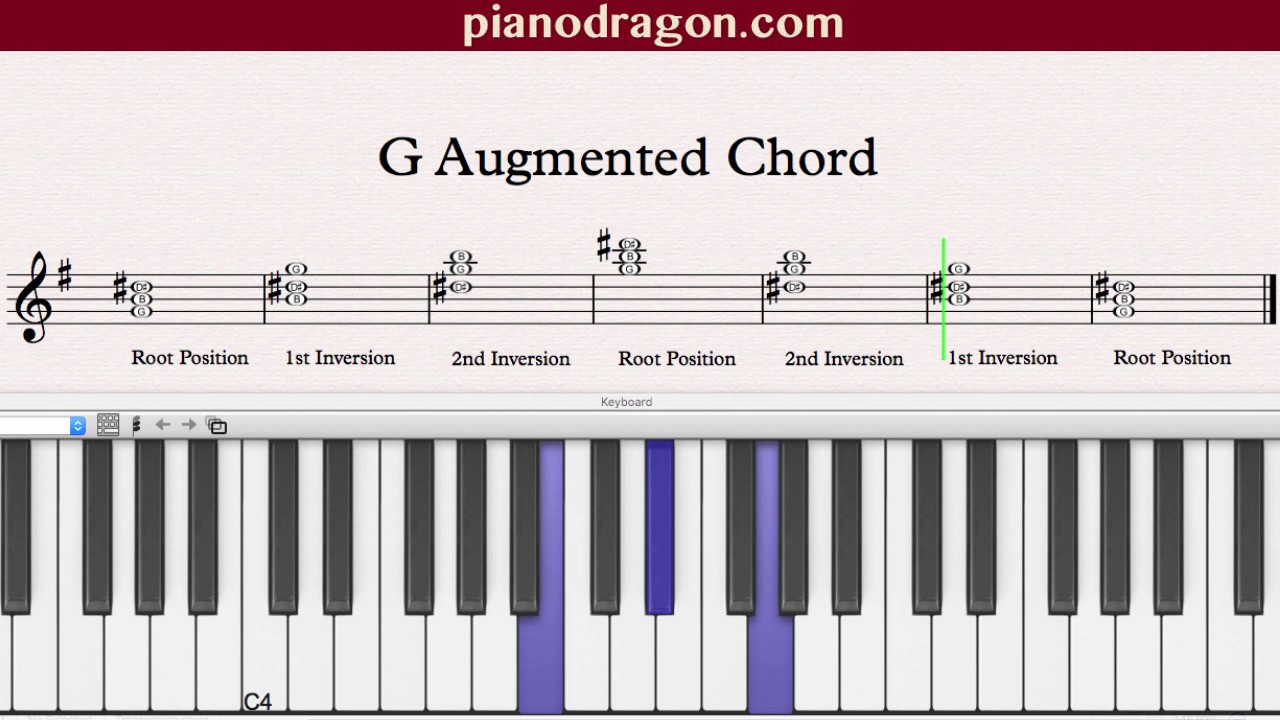
G Augmented Triad In Root Position
E flat augmented triad, root position Eb B diminished triad, second inversion Bo64 Seventh Chords A seventh chord symbol consists of a root (pitch class) quality (minor, major, majorminor, halfdiminished, or diminished) and inversion (root position, first, second, or third inversion).

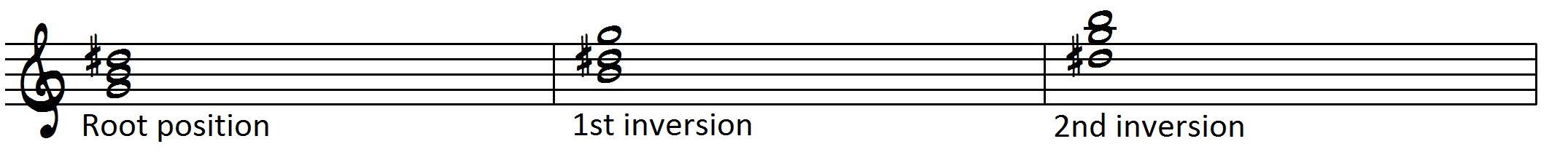
G augmented triad in root position. By changing the order of those notes, you get inversions of the triad a) CEG = root position b) EGC = first inversion c) GEC = second inversion Figured bass numbers that represent the intervals above the bass note a) 5/3 = root position b) 6/3 (or just ‘6’) = first inversion c) 6/4 = second inversion. So here's the F augmented root position arpeggio I just want to point out that the last root, F, can be moved to the B string if you want to make it a little easier Okay, here's the A augmented arpeggio, or the first "inversion" of the F augmented arpeggio, if you will And here's the G# augmented arpeggio Great, so practice these arpeggios. Augmented Triad The augmented triad has a major third on both the bottom and top Triad Inversions Triads can appear in three inversions The inversion is determined by the lowest note of the chord In root position the root is the the lowest note In first inversion the third is the the lowest note In second inversion the fifth is the lowest note.
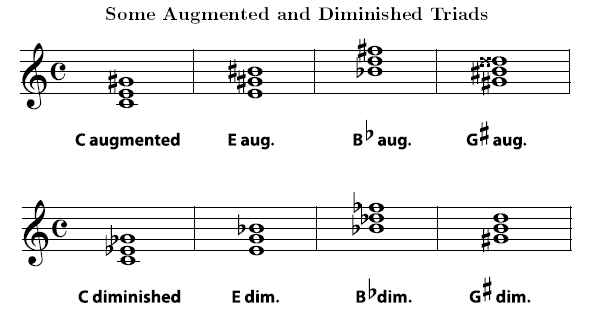
A NAMING TRIADS diminished chord is built from two minor thirds, which add up to a diminished fth Listen closely to an augmented triad 13 and a diminished triad14 Example 23 Some Augmented and Diminished Triads Figure 27 Exercise 23 (Solution on p 13) Write the augmented triad for each root given Figure 28 Exercise 24 (Solution on p. If it's minor, it's a minor triad, if the fifth is diminished, the triad is diminished, if the fifth is augmented the triad is augmented You'll still need to rearrange the notes into stacked thirds root position to figure them out Let's practice identifying a few, I. How would you alter this chord to create a G augmented triad?.
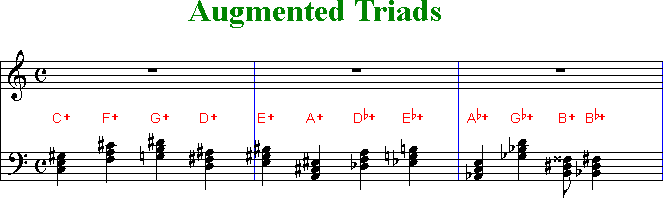
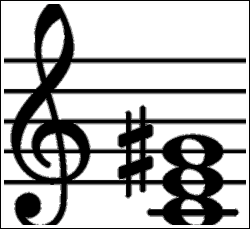
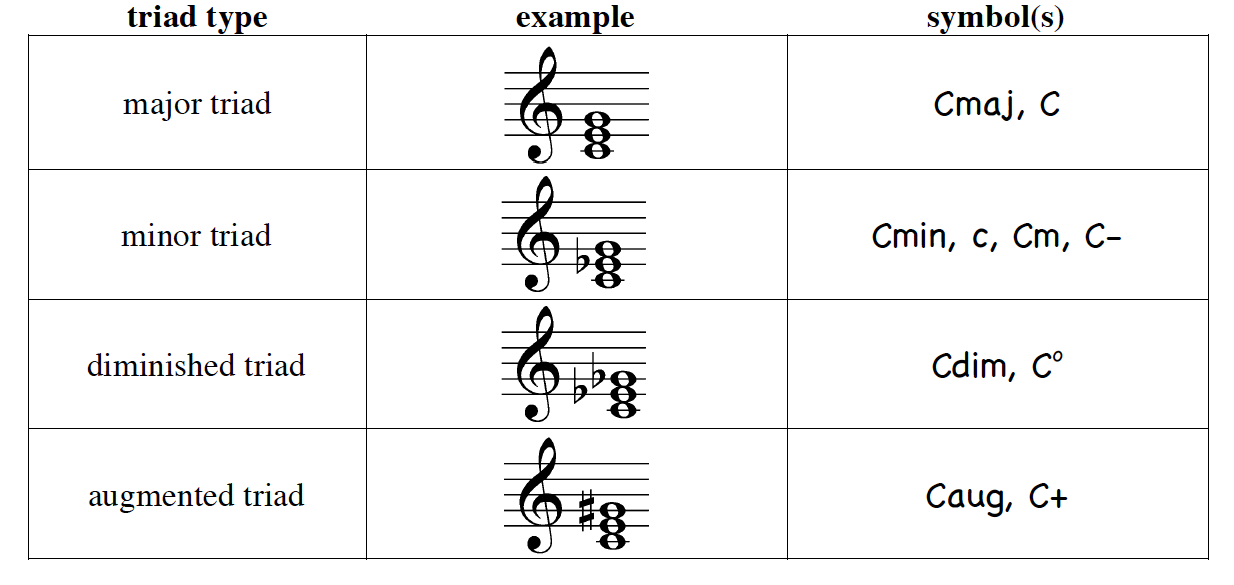
The Work Remember that a major triad is made of three notes, the root, the third, and the fifth, and an augmented triad is the same, but with the fifth augmented, or raised by a half step Example 1 shows the notes in a G major triad (G B D) and Example 2 shows the notes in a Gaug triad (G B D#). G augmented triad bass clef so the chord is said to be in sixfour position1 Gsharp augmented chord This step shows the Gsharp augmented triad chord in root position on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The Gsharp augmented chord contains 3 notes G#, B#, D## The chord spelling / formula relative to the G# major scaleis 1 3 #5 Gsharp. Called triads Using C as a starting point, the notes, and formulas for the chords are Major C E G, Root 3 5 Minor C Eb G, R b3 5 Diminished C Eb Gb, R b3 b5 Augmented C E G# R 3 #5 Major Chord Minor Chord Diminished Chord Augmented Chord Let’s actually look at the guitar (and the crowd cheers) If you’re normal (not a.
Interactive Chord Finder The intervals that compose the G chord are Root, Major Third, and Augmented Fifth Different notations for the G Augmented Fifth chord G Augmented Fifth G Augmented Triad G 5 G #5 Gaug The notes of the Gaug chord are G, B, and D#. The formula for an augmented triad Formula Root3rd#5 We are going to use the key of G for our examples, so using this formula, the notes in a G augmented triad would be GBD# Let’s take a look at what an augmented triad looks like notated in root position, 1st inversion and 2nd inversion. The Eb chord is made up of three notes – Eb, G, and B If you’re new to chords, the ‘’ means ‘augmented’ and the chord is also referred to as the ‘Ebaug chord’, ‘Ebaug triad’, ‘Eb augmented chord’, or ‘Eb augmented triad’ And you may notice that it’s the same as.
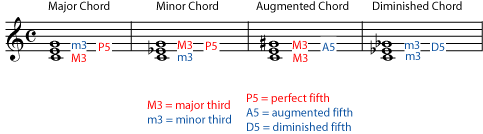
A much bigger difference in the chord's sound comes from the intervals between the rootposition notes of the chord For example, if the B in one of the chords above was changed to a B flat, you would still have a G triad, but the chord would now sound very differentSo chords are named according to the intervals between the notes when the chord is in root position. Building augmented Triads An augmented chord is a major triad with a raised 5th So a normal C major CEG becomes the augmented or raised CEG#. Naming major or minor triads – Chord Inversions in Music Theory The name of a chord depends on the intervals between its notes when the chord is in root position The position that a chord is in does make a difference in how it sounds, but it is a fairly small difference Listen to a G major chord in three different positions.
In other words, we typically don't use a triad name and a sixth/seventh name together (like 'A flat major major 7 sharp 11') The one exception is the name 'Minor Major 7' where both the triad and the seventh are named G7 The chord root here is 'G' The minus sign is found in the second column, so the triad type is minor. Root position A major triad has a major third on the bottom and a minor third on top True How would you alter this chord to create a D diminished triad?. Triads in Root Position The chords in Figure 51 are written in root position, which is the most basic way to write a triad In root position, the root, which is the note that names the chord, is the lowest note The third of the chord is written a third higher than the root, and the fifth of the chord is written a fifth higher than the root (which is also a third higher than the third of the chord).
The G major triad would be G B D Minor Triads Minor triads are constructed in the same fashion as major triads, only based off the minor scale Take the 1st, 3rd, and 5th notes of the scale and you end up with the minor triad Augmented Triads Augmented triads have a cool sound, very mysterious An augmented triad is a major third on top. The root and quality will tell you what three pitch classes belong to the triad For example, C tells you the root is C, and the quality is augmented Since the quality is augmented, there is a major third above the root (E) and an augmented fifth above the root (Gsharp). The figured bass notation for a triad in root position is 5/3, with the 5 placed above the 3 on a staff diagram These numbers represent the interval between the lowest note of the chord and the note in question So another name for this chord would be G augmented triad in fivethree position.
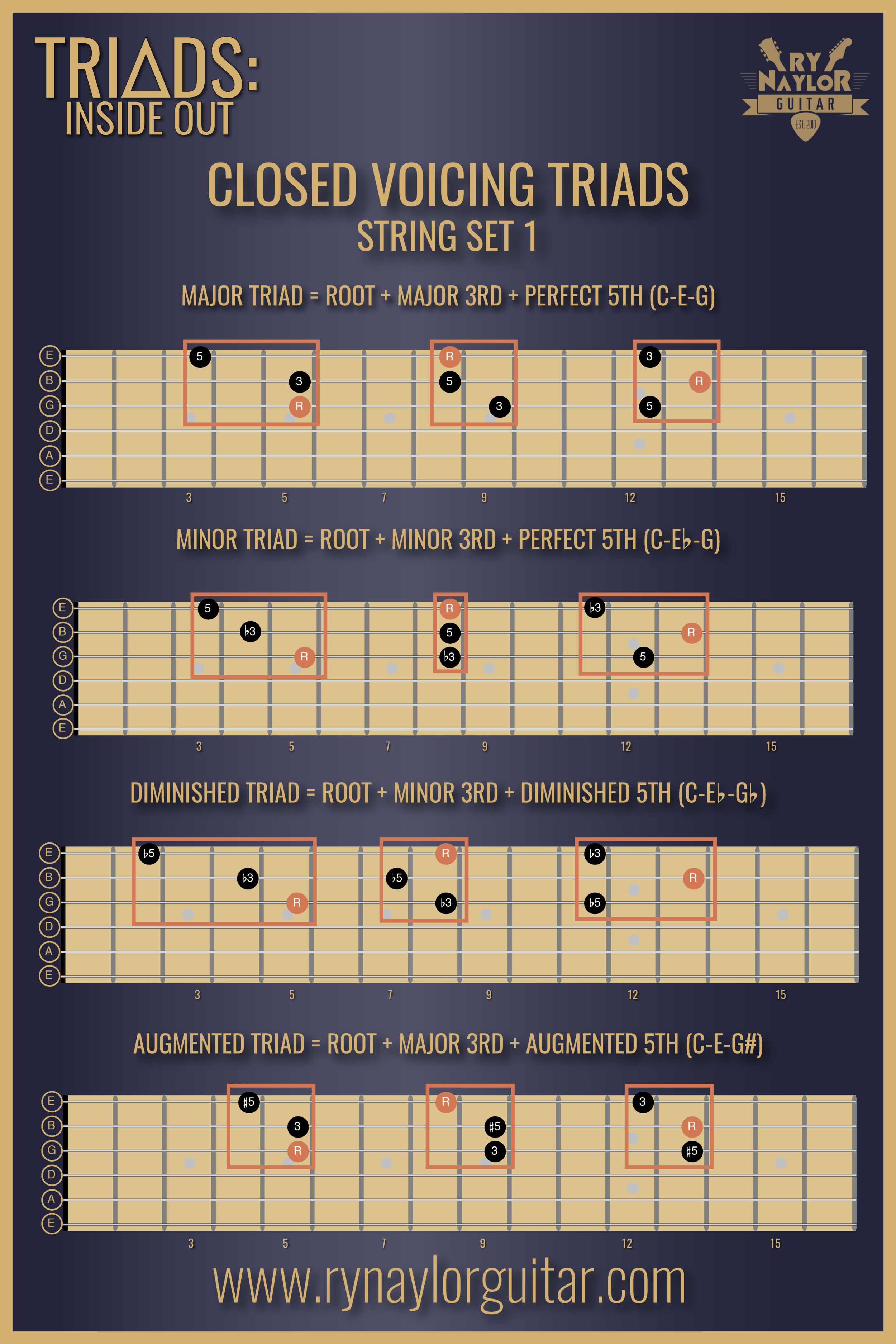
Root position 3 half steps 4 half steps And considering the second way, you have to take the first, the minor or flat third, and fifth intervals from a major scale #3 Augmented Triads An augmented triad is like having a stack of major intervals and four intervals between each interval. The first tone of the triad when it is shifted to root position is known as its root For example, the root of G#, B, E is E and the root of C, D#, G is C Given a triad, help Bob find its root, type, and inversion If the given triad is augmented, assume it is in root position Input Specification 3 lines with a valid tone on each line. If you play strings 5, 4 and 3 of the open C chord you are playing a triad The Root note, C, is the lowest in pitch and so this is called a Root Position triad When the notes are played within the same octave (as close as they possibly can be to one another) it is said to be in a closed voicing.
Write a triad in root position using each root given If you need some sta paper for exercises you can print this PDF le 8 Figure 12 12 First and Second Inversions Any other chord that has the samenamed notes as a root position chord is considered to be essentially the same chord in a. Answer (1 of 2) It is basically the 1st (root), the 3rd, and the 5th notes of a scale For example, in the C Major scale, which goes C D E F G A B C, the 3 notes in. Diminished triads root (1), minor 3rd (b3) and diminished 5th (b5) 1 b3 b5 Augmented triads root (1), major 3rd (3) and augmented 5th (#5) 1 3 #5 Note In the video, we didn't use augmented triads, because they don't exist in the particular scale we were harmonizing That doesn't mean you can't try using them in places.
Of the four triad qualities, augmented triads are outliers since they cannot be constructed using only diatonic pitches and will therefore always require at least one accidental Major, minor, and diminished triads, on the other hand, can be constructed using only white (natural) keys on a piano and appear in every major or minor key The position of a triad is determined by the bass voice. For a chord to be built in thirds, it just means that in its most basic position, what we call Root Position, each note is separated by the interval of a third*C, E, G is a root position triad, because C and E are a third apart from each other and E and G are a third apart from each other. Major triads Minor triads Diminished triads Augmented triads G;.
So, in this case, G is considered the "root" of the chord Then we take the 3rd and 5th notes of the G major scale, which are B and D This gives you the major triad!. Lower the fifth The bottom note of this triad is called the How would you spell an augmented triad above this pitch?. G augmented chord This step shows the G augmented triad chord in root position on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The G augmented chord contains 3 notes G, B, D# The chord spelling / formula relative to the G major scale is 1 3 #5 G augmented chord note names Note no Note interval Spelling / formula.
TRIADS On the given lines, name the intervals (eg m3) in each type of rootposition triad (the first one has been done for you) Major triad Minor triad Augmented triad Diminished triad In a rootposition triad, the _____ is the lowest note Inversion symbol In a firstinversion triad, the _____ is the lowest note Inversion symbol. I made all voicings for the triads be in root position That is, the root note of each triad was voiced (located) in the bass (The root note was the lowest note of the chord) For example when I presented a C major triad, I voiced it as such C, E, G the root, the 3rd, and then the 5th. Then you simply flat the 3rd (lower one halfstep) to make it a minor triad Now, let's look at building it by intervals Again, take the G root.
In music theory, this triad chord as it stands is said to be in root position because the root of the chord note G, is the note with the lowest pitch of all the triad notes The note order of this triad can also be changed, so that the root is no longer the lowest note, in which case the triad is no longer in root position , and will be called an inverted triad chord instead. Whenever you play a G chord on piano, and G is the lowest note, that’s known as root position It looks like this G Chord Piano – Root Position There are six places on a standard piano where you can play a G chord in root position If you have a piano close by, try playing each one. Root position major triad Root position simply means that the root is in the bass (the lowest note) So that G major chord stated above is in root position The simplest form of root position is stacking 1 3 5, but as long as the root is in the bass, you can add any number of roots, thirds, and fifth above it and remain in root position!.
Three tones played simultaneously are called a triadTherefore a triad is a chordFive triads will be studied in this course They are the major triad, the minor triad, the augmented triad, the lowered fifth triad and the diminished triadThese triads are variations of the root note, third degree and fifth degree played simultaneously The major triad consists of the root note, third degree. When the notes are arranged in this order, from bottom to top, we have a G Major triad in root position A G Major triad First Inversion A first inversion triad exists when the third is in the bass Going back to the example of G Major, a first inversion triad would have, from bottom to top, B, D, and G. In music theory, this triad chord as it stands is said to be in root position because the root of the chord note G, is the note with the lowest pitch of all the triad notes The note order of this triad can also be changed, so that the root is no longer the lowest note, in which case the triad is no longer in root position , and will be called an inverted triad chord instead.
Lower the fifth A major triad has a major third on the bottom and a minor third on top Not counting root position, how many inversions are there for seventh chords?. Root Position Root position triads have the lowest note as the root of the chord Root on 654 play notes play chord Root on 543 play notes play chord Root on 432 play notes play chord Root on. Below are triads in root position (or 5/3 position) \cadenzaOn \meterOff 1 1 First inversion (sixth chord, 6/3) A triad is in first inversion when the third is in the bass The fifth and root are vertically stacked "on top" of the third.
Invert each root position triad to the requested inversion (4) 23 Notate triads according to the specified root, quality, and inversion (4) a Dflat Major, 1st Inversion b F Augmented, Root Position c A minor, Root Position d G#minor, 2nd Inversion 24 Notate the following triads, given the 3rd of the triad (4) a Major b Augmented C. Raise the fifth How would you alter this chord to create an E diminished triad?.
1
Music Secrets Of Chords

Triad Quality And Inversions A Complete Guide Songsterr Blog
G Augmented Triad In Root Position のギャラリー
Naming Major Or Minor Triads In Music Theory Chord Inversions

Basicmusictheory Com C Flat Augmented Triad Chord
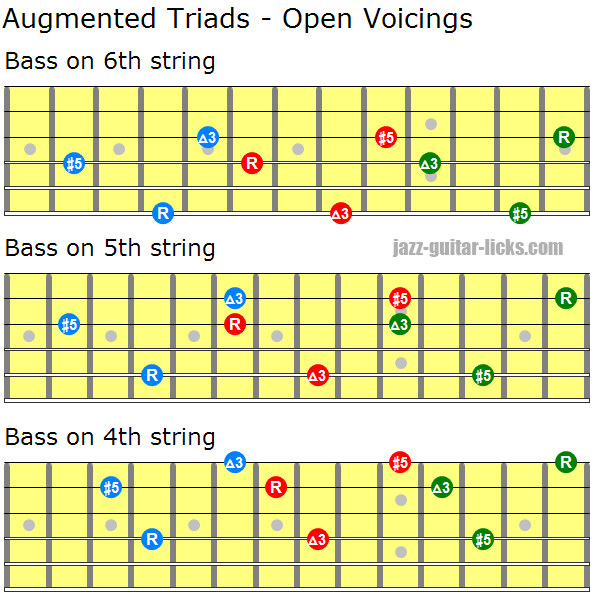
Augmented Triad Chords Guitar Diagrams And Voicing Charts

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form

Click Here To A Pdf Of The Lesson

Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory

What S A Diminished Triad What Is An Agmented 3 Notes Chords

6 Ways To Play G Augmented Chord By Chord Acoustic Guitar
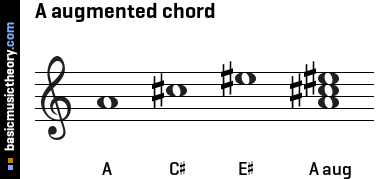
Basicmusictheory Com A Augmented Triad Chord

Augmented And Diminished Chords Open Textbooks For Hong Kong

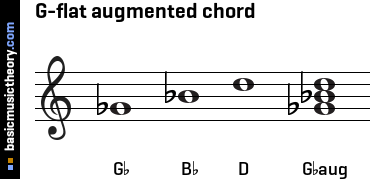
Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord
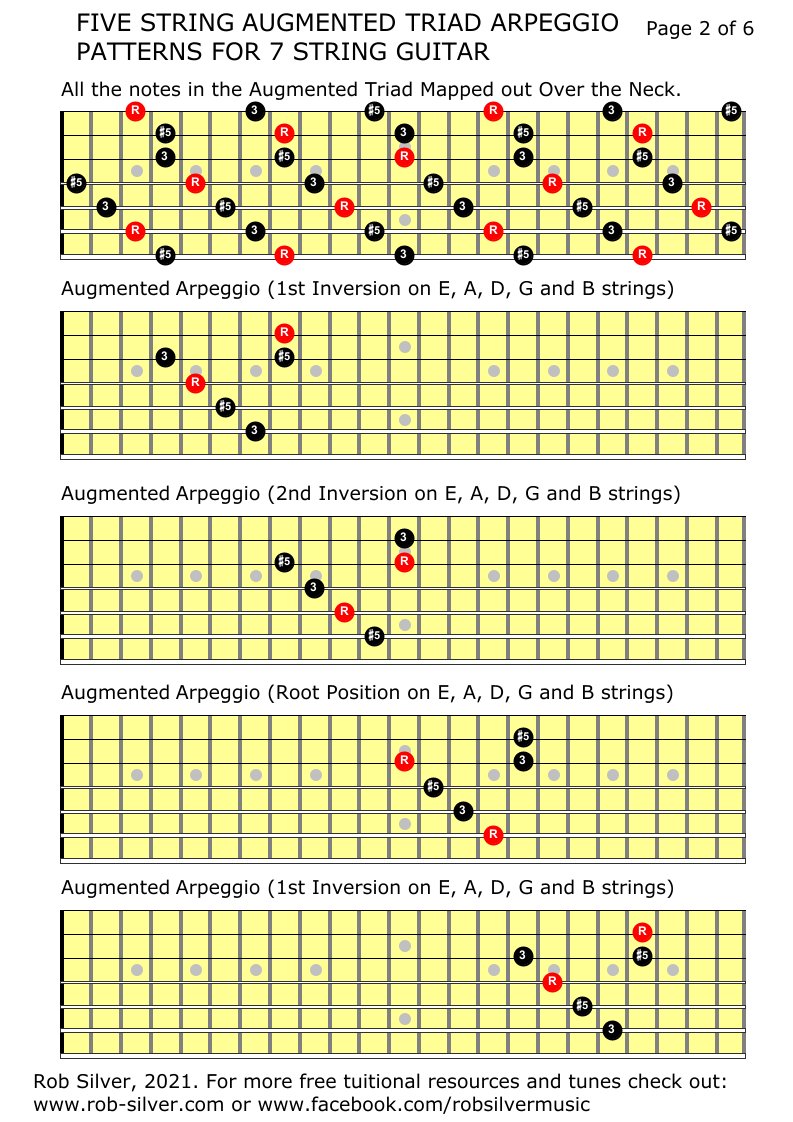
Rob Silver Five String Augmented Triad Arpeggios For 7 String Guitar All String And All Inversions
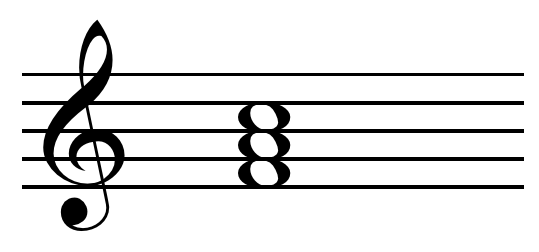
Root Position Wikipedia
/Triad_c_augmented.svg-583dbcb53df78c6f6a1f986e.png)
What Are Diminished And Augmented Triads
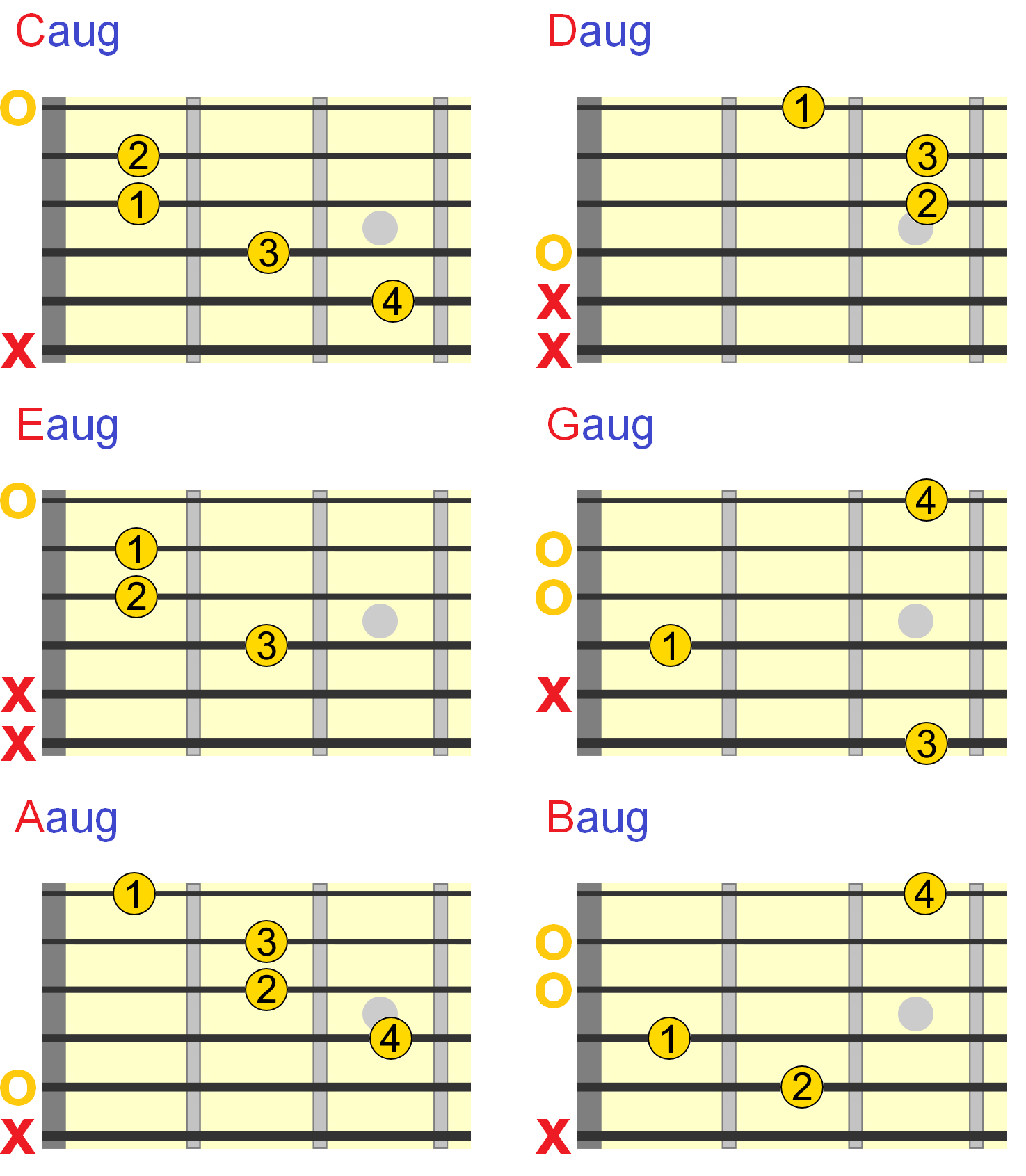
Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know

C5s1 Chords

Triads The International Institute Of Bassists

Guitar Triads Pdf Musical Notation Melody
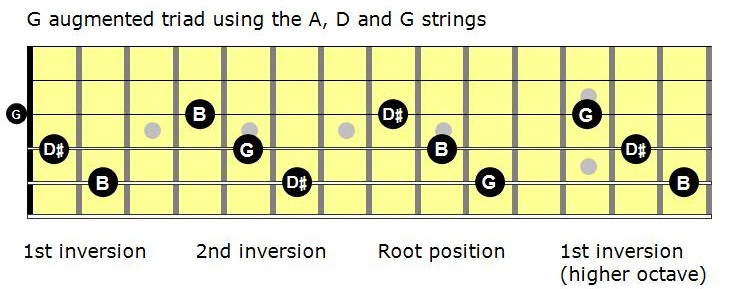
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards
Part 1 Of Triads Inside Out Learning Your Closed Voicing Triad Inversions Ry Naylor Guitar
1

Triads Music Theory Academy
Solved Write The Following Triads In Root Position Amp Inversion Write A Bass Clef On The Staff Course Hero
13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form
G Augmented Chord Youtube
Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord
13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards

How To Play Triads On Guitar Jamieholroydguitar Com Jamie Holroyd Guitar

Learn 5 Ways To Play A Augmented Chord By Chord Acoustic Guitar

Augmented Chords Open D Tuning

G Ab Augmented Triad Closed Positions Guitar Scientist

Augmented Chords Open D Tuning
The Augmented Chord Music Theory For Mandolin Simplymandolin
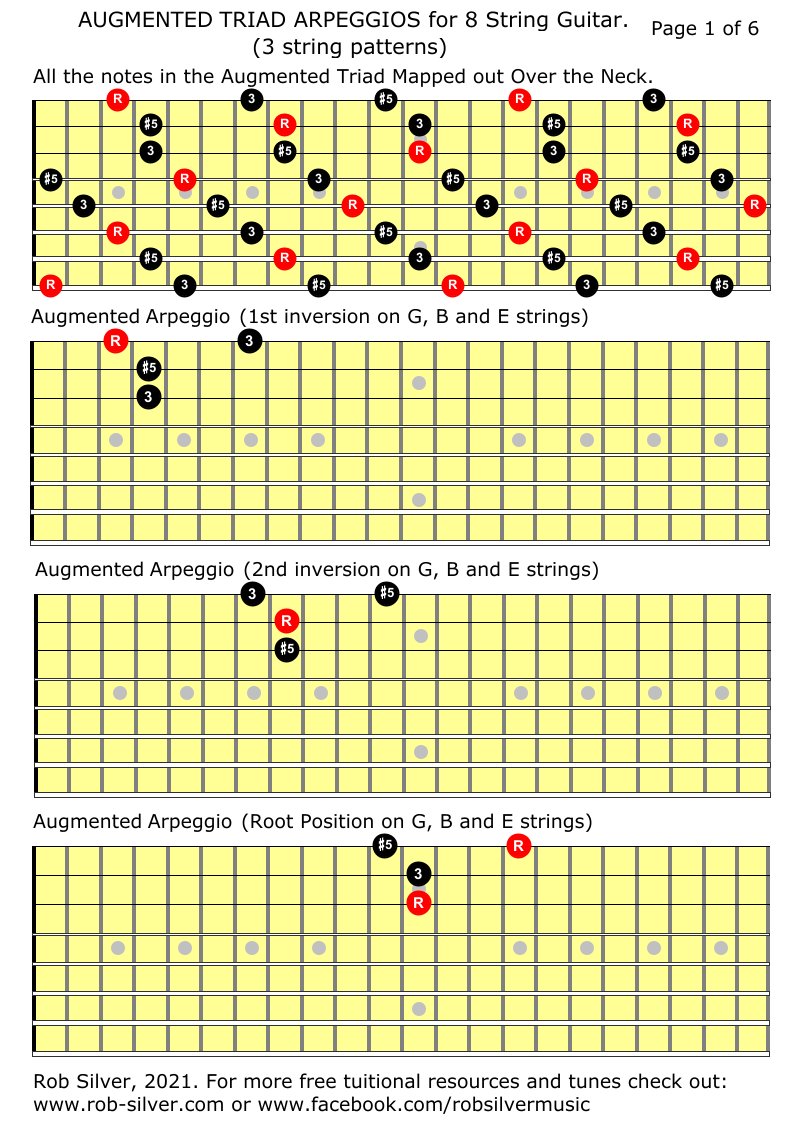
Rob Silver Three String Augmented Triad Arpeggios For 8 String Guitar All Strings And All Inversions

Integrated Aural Skills Ear Training Triads In Review

5 2 Naming Triads

Augmented Triads On Guitar
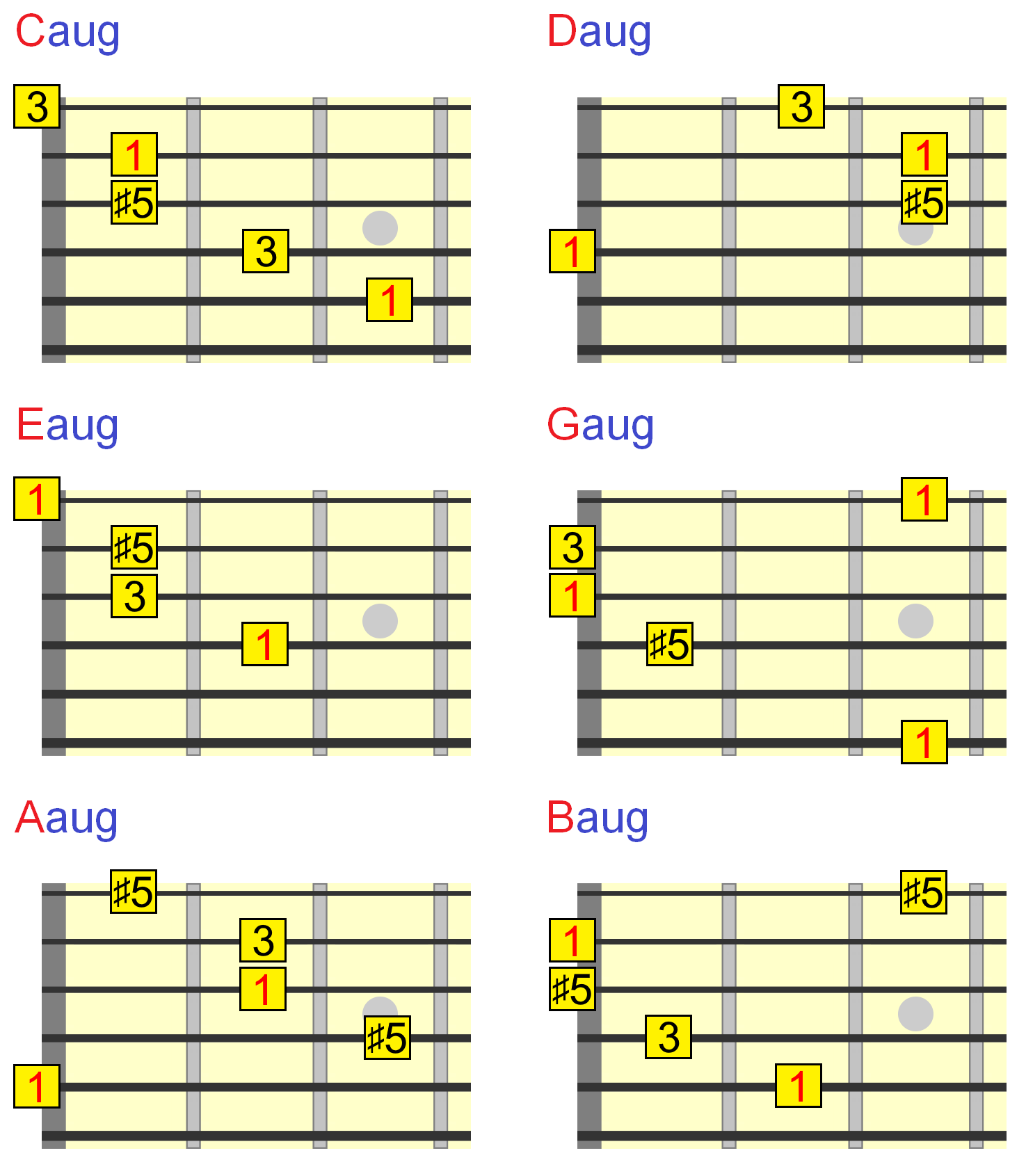
Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know

Augmented Triads

G Chord Piano How To Play G Augmented Chords On Piano
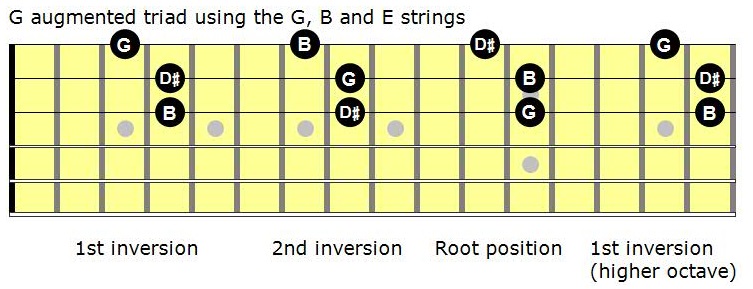
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards

G Chord Piano How To Play G Augmented Chords On Piano

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord

Three Major Triads In Root Position In The Key Of G Normally It Would Download Scientific Diagram

5 2 Naming Triads

コレクション G Augmented Chord Guitar シモネタ
The Augmented Chord Music Theory For Mandolin Simplymandolin

Augmented Triads On Guitar

Triad Jens Larsen

Capybara Guitar Posts Facebook
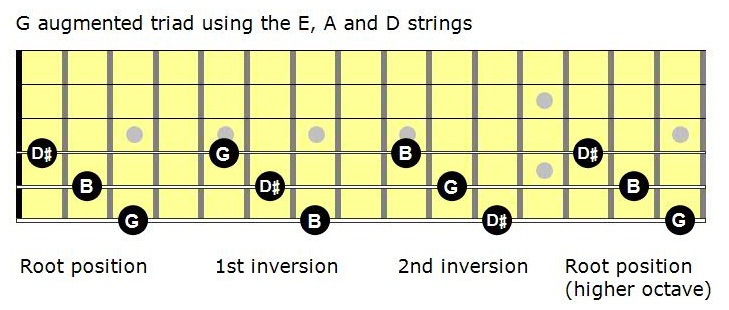
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards
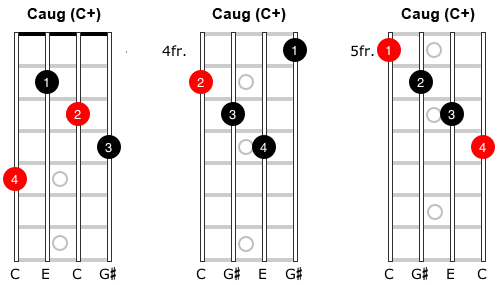
C Augmented Guitar Chord Gtrlib Chords

Augmented Triads The Nandi Method

6 Ways To Play G Augmented Chord By Chord Acoustic Guitar

G Chord Piano How To Play G Augmented Chords On Piano
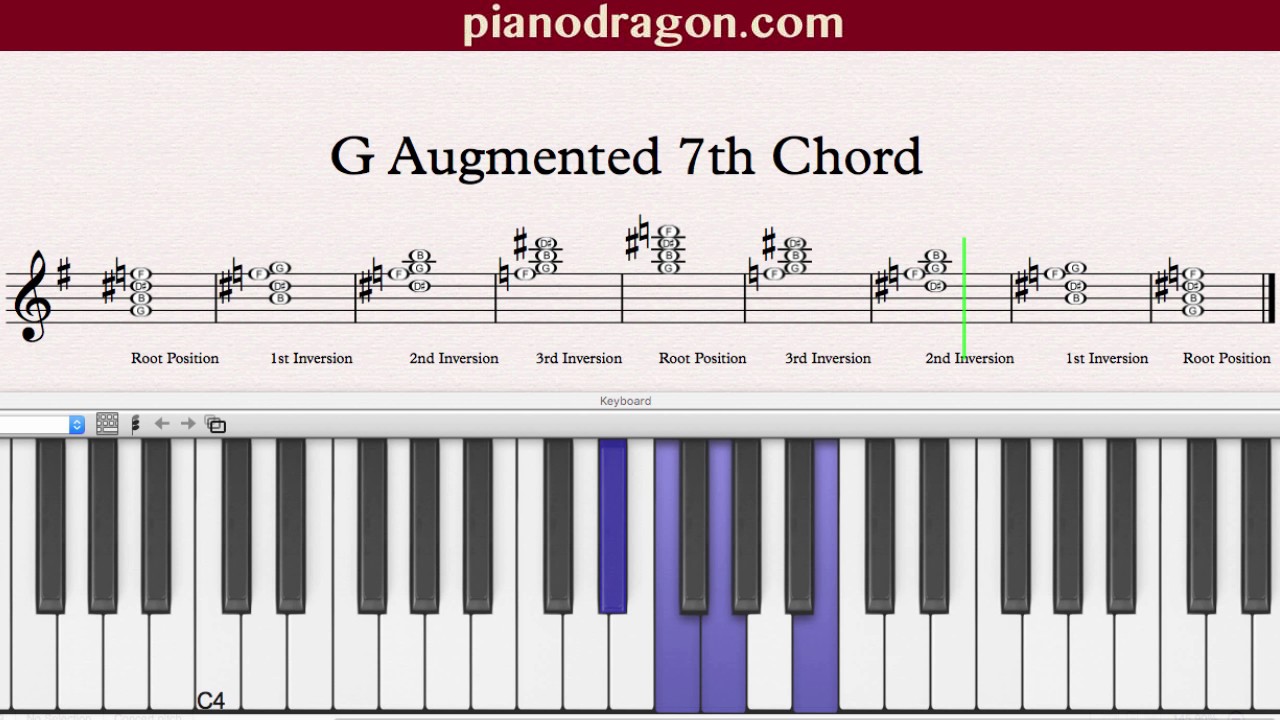
G Augmented 7th Chord Youtube
Augmented And Diminished Chords Open Textbooks For Hong Kong

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
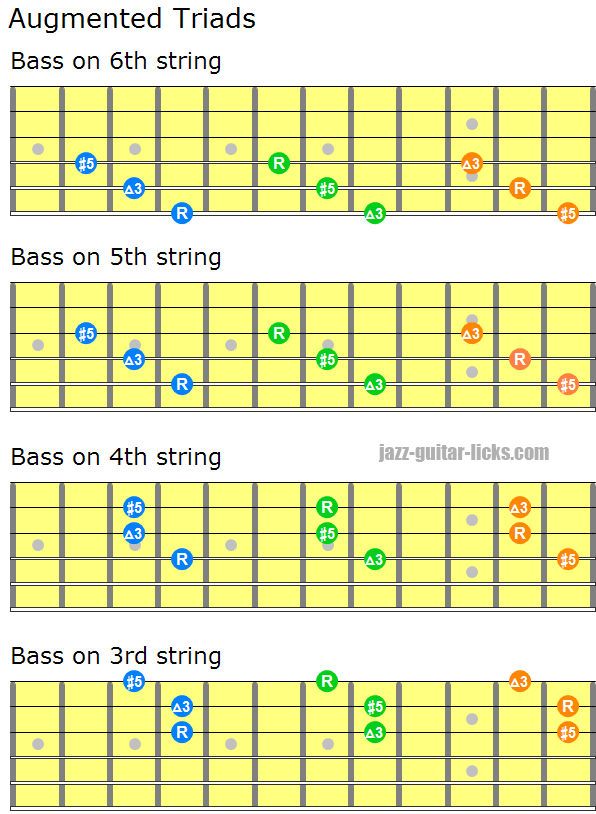
Augmented Triad Chords Guitar Diagrams And Voicing Charts

13 Ear Training Basic Triads Music Student 101
1
Unit 13 Music 110 Fundamentals Of Theory

Augmented Triads The Nandi Method

G Sharp Augmented Chord On The Guitar G Diagrams Finger Positions Theory
34 Other Chromatic Harmonies Fundamentals Function And Form

Basicmusictheory Com F Flat Augmented Triad Chord

Basicmusictheory Com G Major Triad Chord
G Flat Augmented Guitar Chord Gtrlib Chords
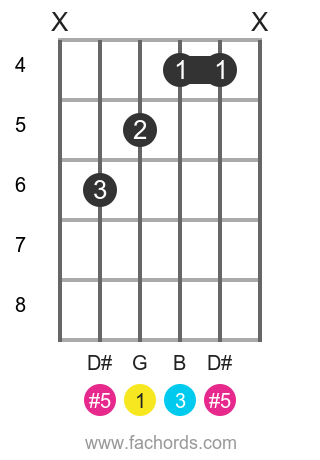
Play G Aug Chord On Guitar
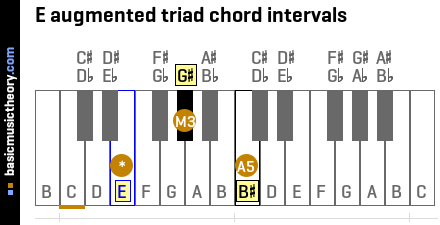
Basicmusictheory Com E Augmented Triad Chord

13 Ear Training Basic Triads Music Student 101

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord

Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory

Root Position Triad Quality Youtube

How To Play G Augmented Mandolin Chords

5 2 Naming Triads

How To Play Triads On Guitar Jamieholroydguitar Com Jamie Holroyd Guitar

Naming Major Or Minor Triads In Music Theory Chord Inversions
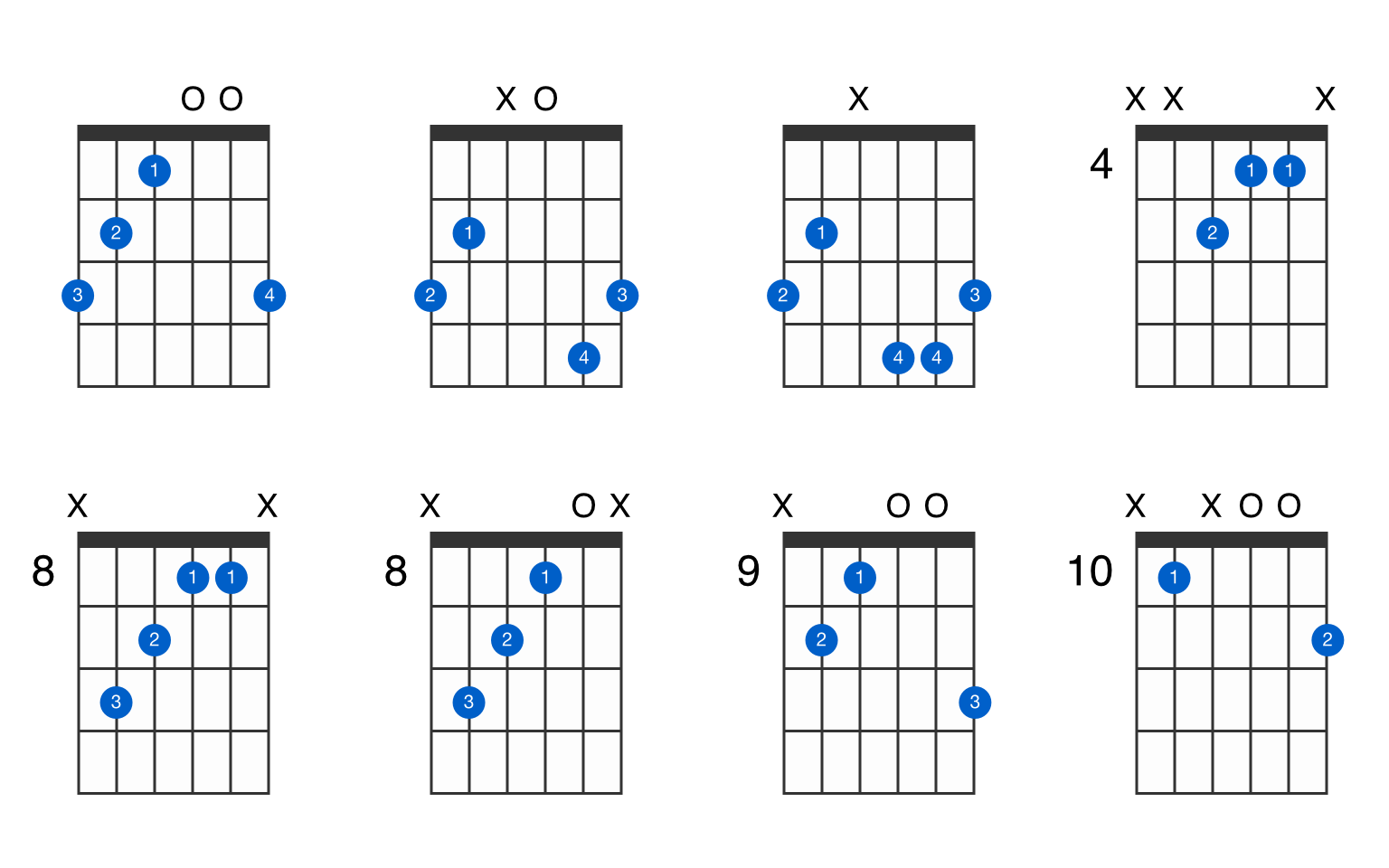
G Augmented Guitar Chord Gtrlib Chords

What Is An Inversion What Is The Difference With Root Position
1
Solved 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Course Hero

Basicmusictheory Com A Augmented Triad Chord
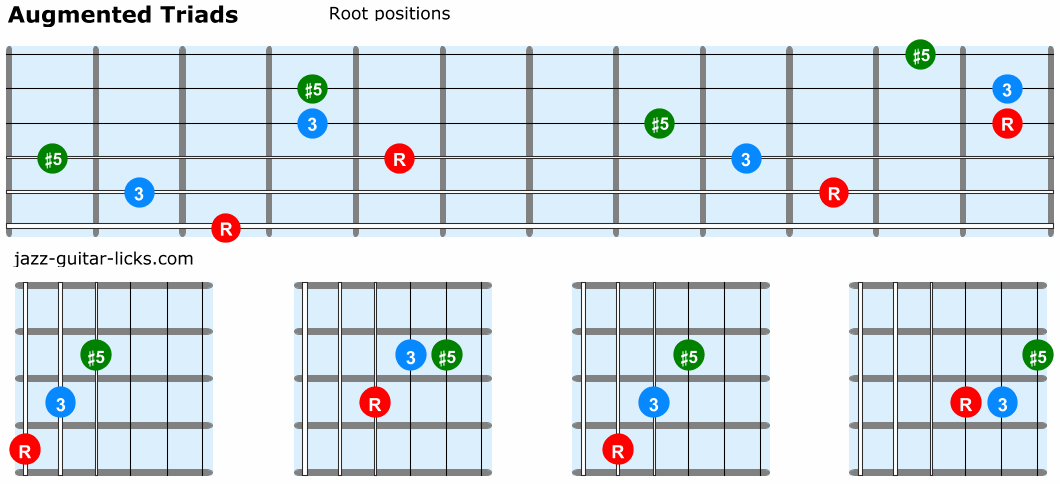
Triad Chords 84 Guitar Shapes Lesson With Pdf

5 2 Naming Triads

Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory

B Augmented Triad Closed Positions Guitar Scientist
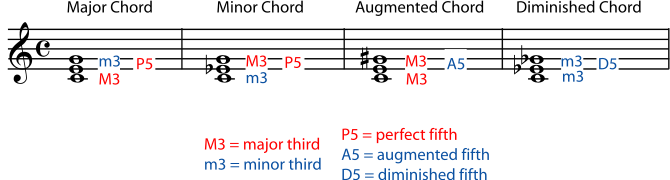
5 2 Naming Triads

Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory
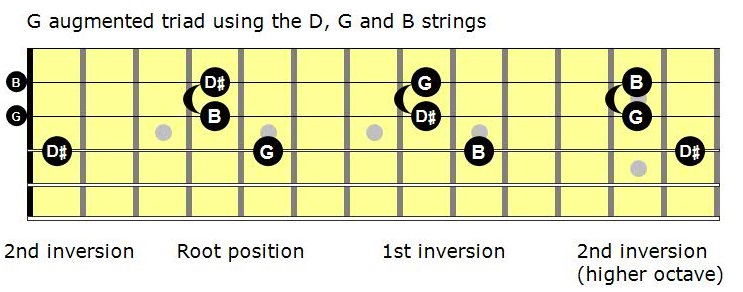
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards

Rob Silver Left Handed Augmented Triad Arpeggios 2 3 4 5 And 6 String Options In All Inversions And On All Strings

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord

Augmented Options Open Music Theory

Basicmusictheory Com D Augmented Triad Chord
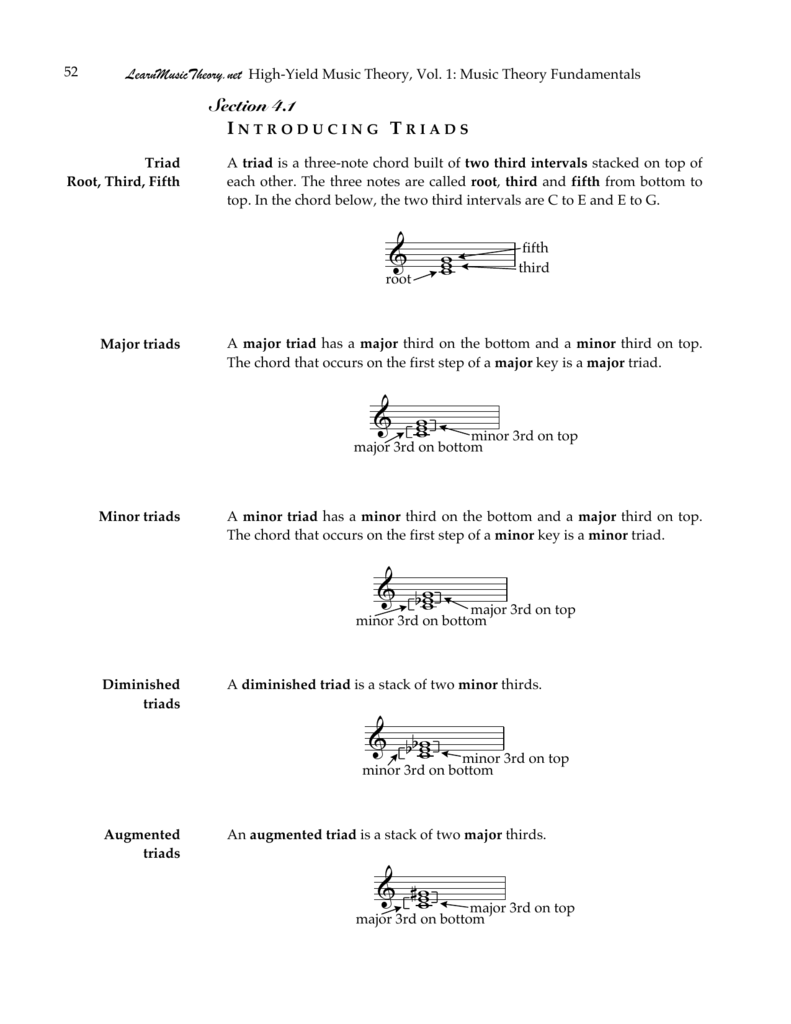
Introducing Triads Music Theory At Learnmusictheory Net
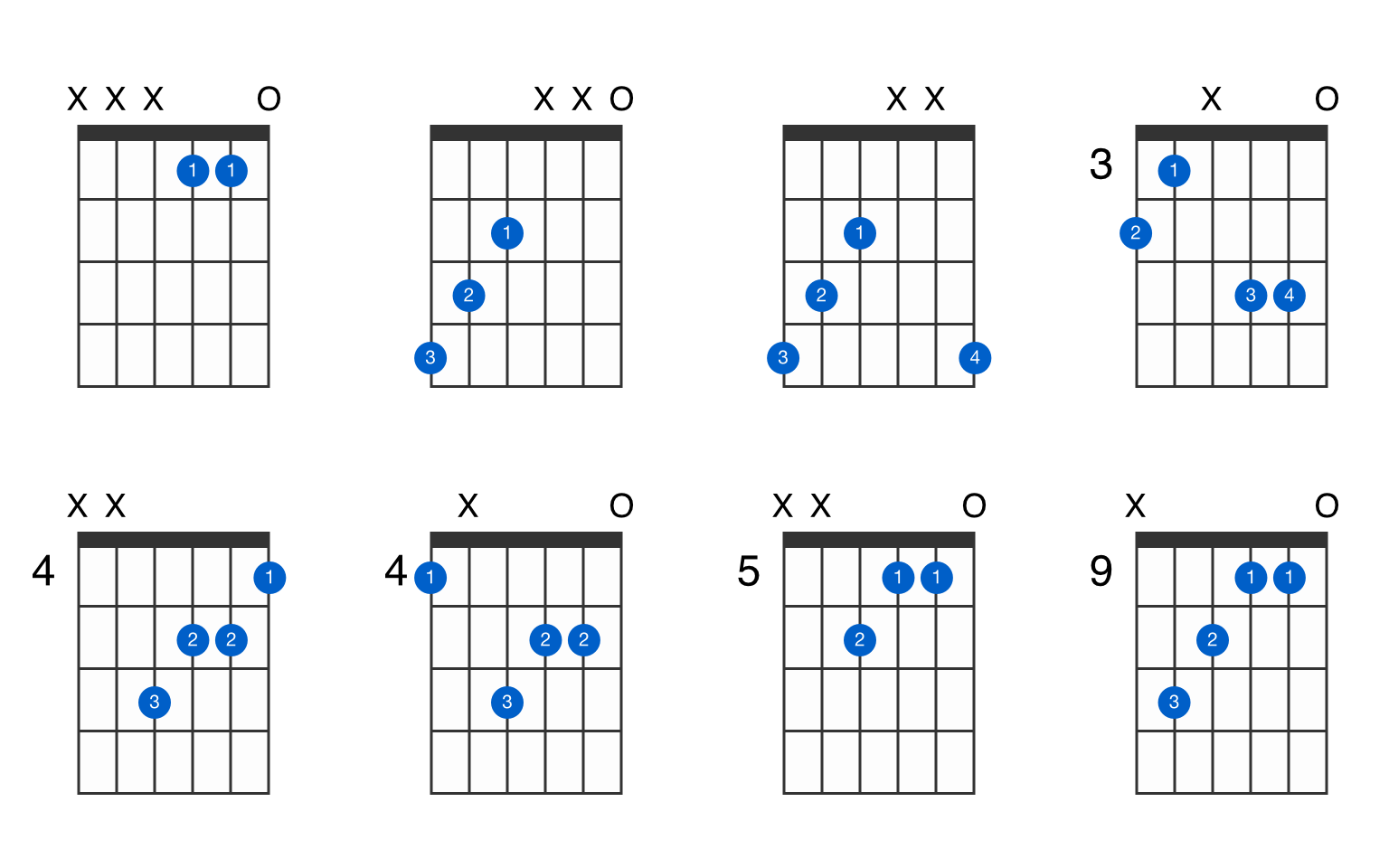
G Sharp Augmented Guitar Chord Gtrlib Chords
Basicmusictheory Com E Augmented Triad Chord

G Chord Piano How To Play G Augmented Chords On Piano

Rob Silver Chords 3 And 4 String Augmented Triads On All Strings In All Inversions




