G Augmented Triad Second Inversion
In a first inversion E augmented triad, what is the bass note?.
G augmented triad second inversion. Ab, C, E How would you alter this chord to create an F minor triad?. Answer (1 of 3) The Italian is the threetone “base model” In the French, scale degree 2 (relative to tonic) is added;. The Eb chord is made up of three notes – Eb, G, and B If you’re new to chords, the ‘’ means ‘augmented’ and the chord is also referred to as the ‘Ebaug chord’, ‘Ebaug triad’, ‘Eb augmented chord’, or ‘Eb augmented triad’ And you may notice that it’s the same as.
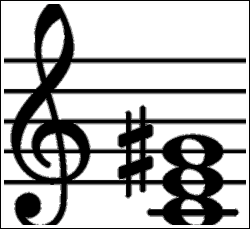
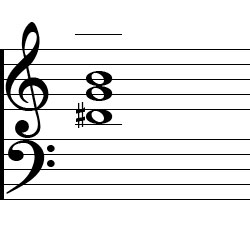
This step shows the G augmented 2nd inversion on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The G augmented 2nd inversion contains 3 notes D#, G, B These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef The figured bass symbols for this chord inversion are 6/4, so the chord is said to be in sixfour position Audio downloads. Constructed of two minor thirds This changes the outside interval from a perfect fifth to an augmented fifth inversion when a triad is reorganized so that the third of fifth is the lowest note first inversion when the third is the lowest note second inversion when the fifth is the lowest note C major triad C, E, G. The figured bass notation for this triad in 2nd inversion is 6/4, with the 6 placed above the 4 on a staff diagram Based on this numbering scheme, another name for this inversion would be G diminished triad in sixfour position.
The more notes there are in a chord, the more inversions are possible For example, the notes of the C dominant 7th chord are C, E, G and In root position, the notes of Cdom7 are CEG In its 1st inversion, it’s EGC In its 2nd inversion, it’s GCE In its 3rd inversion, it’s CEG Here’s an example of a minor chord. G major 2nd inversion This step shows the G major 2nd inversion on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The G major 2nd inversion contains 3 notes D, G, B These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef The figured bass symbols for this chord inversion are 6/4, so the chord is said to be in sixfour position. Three tones played simultaneously are called a triadTherefore a triad is a chordFive triads will be studied in this course They are the major triad, the minor triad, the augmented triad, the lowered fifth triad and the diminished triadThese triads are variations of the root note, third degree and fifth degree played simultaneously The major triad consists of the root note, third degree.
Not b, gflat, eflat What note is the seventh of an A dominant seventh chord?. Answer (1 of 16) There is always going to be a little confusion when questions like this one are asked of any musician, the nomenclature for chord language has often been adapted or I should say abused, to enable musicians with a limited knowledge of. From the choices given, select the note value(s) needed to complete the second measure in the example above One eighth note 2/8, 2/4, and 2/2 are very much related because they all share the same basic meter type.
Major triads Minor triads Diminished triads Augmented triads Chords Second Inversion Second inversion triads have the middle note as the root of the chord 2nd Inversion on 654 play notes play chord 2nd Inversion on 543 play notes play. Gsharp In a second inversion Eflat major triad, what is the bass note?. A second inversion triad inverts both of the original intervals and therefore contains a fourth and a sixth above the bass, thus the figuredbass signature 6 / 4 You will frequently encounter triads referred to by their interval content (“sixthree triad” instead of “firstinversion triad”).
Major triads Minor triads Diminished triads Augmented triads Chords Second Inversion Second inversion triads have the middle note as the root of the chord 2nd Inversion on 654 play notes play chord 2nd Inversion on 543 play notes play chord 2nd Inversion on 432. It's just a different inversion, giving a variation in how the chord sounds and fits in with the song Example C Major triad in inversions You can see here the C major chord, first in root position, 135 Then the 1st inversion, built from teh 3rd, and the 2nd inversion, built from the 5th. G augmented triad bass clefthis step shows the gsharp augmented 2nd inversion on the piano, treble clef and bass clef the gsharp augmented 2nd inversion contains 3 notes d##, g#, b# these note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef the figured bass symbols for this chord inversion are 6/4, so the chord is said to be.
This step shows the Gflat augmented 2nd inversion on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The Gflat augmented 2nd inversion contains 3 notes D, Gb, These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef The figured bass symbols for this chord inversion are 6/4, so the chord is said to be in sixfour position. Guitar Triads Interactive Tool The tool below shows you where the triads are located on the fretboard Click the start button , the tool will display the shapes of the four main types of triads major, minor, augmented, diminished, in all the possible positions and inversions Note all the shapes are shown with the note C as root, you can. Answer (1 of 9) I think calling it a C dim triad in 2nd inversion shows one of the inherent weaknesses with traditional harmonic analysis It obviously has the most important pitches of a V7/V, which are F sharp and C (it IS spelled with an F sharp, right?), which want to resolve to.
The tonic triad of B flat major in second inversion b the dominant triad of F sharp harmonic minor in root position c the supertonic triad of G flat major in first inversion d the leadingtone triad of B harmonic minor in root position e the subdominant triad of A flat major in second inversion 2 Write these triads using accidentals only a. For a 2nd inversion, take the first note of the 1st inversion above D#, and move it to the end of the chord So the second note of the 1st inversion note F## is now the note with the lowest pitch for the 2nd inversion Or put another way, the third note of the original triad (in root position) is now the note with the lowest pitch. G Chord Piano – Second Inversion Whenever you play a G chord on piano, and D# is the lowest note, that’s known as the second inversion It looks like this G Chord Piano – Second Inversion And here is the second inversion played in all places on a standard piano There are seven of these too And that’s about all for this post.
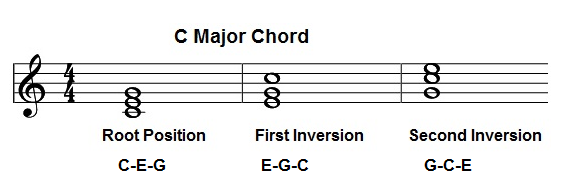
Second inversion major triad As you can probably guess, the second inversion of the major triad has the 5th in the bass The simplest C major chord in second inversion is made of G C E Mark Levine writes in The Jazz Theory Book that “triads sound strongest in. Triads and Inversions I N T R O D U C I N G T R I A D S A triad is a threenote chord built of two third intervals stacked on top of each other The three notes are called root, third and fifth from bottom to top In the chord below, the two third intervals are C to E and E to G A major triad has a major third on the bottom and a minor third on top The chord that occurs on the first step of. It's still the same chord!.
When you invert a triad, you do the same thing If you’re inverting a C major triad, you would take the C from the bottom and play it on the top, thus E, G, C That new arrangement of the notes is known as C major triad, first inversion. G#minor, 2nd Inversion 24 Notate the following triads, given the 3rd of the triad (4) a Major b Augmented C Minor d Diminished 25 Notate the following triads, given the 5th of the triad (4) a Minor b Diminished C Major d Augmented 26 Label the doubled note in each chord (5) 27 Name the ROOT, QUALITY, and INVERSION of each chord (5) 28. C sharp minor triad, first inversion C#m6 E flat augmented triad, root position Eb B diminished triad, second inversion Bo64 Seventh Chords A seventh chord symbol consists of a root (pitch class) quality (minor, major, majorminor, halfdiminished, or diminished) and inversion (root position, first, second, or third inversion).
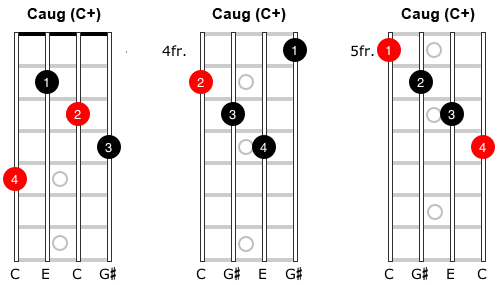
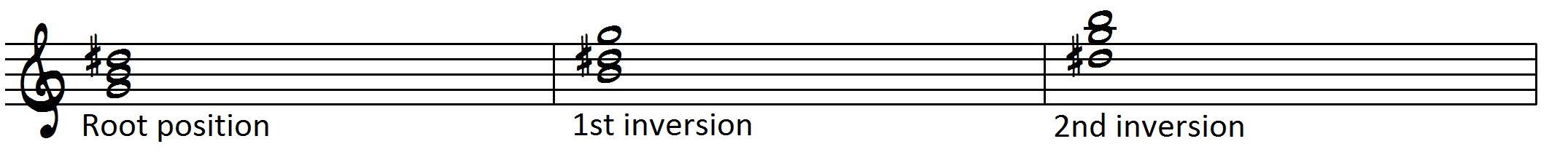
An Augmented Triad divides the octave into 3 equal parts Its interval makeup is Maj 3rd Maj 3rd (CEG#, EG#C, G#CE), and will, therefore, always create equal, repeating intervalic inversions of itself which can lead to certain redundancies The Augmented Triad is the only one of the four basic triad types not derived from the Major Scale It is, however, formed. If you’re new to chords, the ‘’ means ‘augmented’ and the chord is also referred to as the ‘Caug chord’, ‘Caug triad’, ‘C augmented chord’, or ‘C augmented triad’ And you may notice that it’s the same as the C Chord, but with a G# instead of G You can actually play a. By changing the order of those notes, you get inversions of the triad a) CEG = root position b) EGC = first inversion c) GEC = second inversion Figured bass numbers that represent the intervals above the bass note a) 5/3 = root position b) 6/3 (or just ‘6’) = first inversion c) 6/4 = second inversion.
Second inversion triad triad 5th is lowest pitch, labeled as 6/4 tertian A chord structure built of thirds 7th chord chord consisting of a root, 3rd, 5th, and 7th 4 write a melodic augmented 2nd and augmented 4th stylistic practices for second. How would you spell an augmented triad above this pitch?. In the German, this addition is replaced by \flat3 Their traditional names are pretty much nonsense — I prefer “Houyhnhnmnian,” “Trafalmadorian,” and “Eastasian,” myself Th.
Now, the augmented triad is what's called a symmetrical structure That means that mathematically, its notes are chosen in such a way that each inversion of the chord is exactly the same shape And because each chord is the same as its inversions, each inversion of the chord is also another augmented triad. C Major triad 1st inversion (E, G, C) becomes the spread triad G, E and C (spread triad 2nd inversion, meaning the 5th is in the bass) C Major triad 2nd inversion (G, C, E) becomes the spread triad C, G, and E (spread triad in root position). However, the easiest way to find augmented triads is to take a major triad and raise the fifth by one half step If you have a C major triad, spelled C, E, G, then a C augmented triad is spelled C, E, G# Stacking thirds, augmented triads are constructed with two major third intervals In a C augmented triad, C to E is a major third and E to.
SECOND INVERSION A triad is said to be in second inversion if the fifth of the chord is in the bass (the bottommost voice) Each quality triad may occur in second inversion In second inversion all triads will contain the interval of a 4th and a 6th above the bass Therefore, a first inversion chord is said to be in 6 4 position. Triads and sevenths are constructed in the same way, in that thirds are added to a base note For a triad, we’d take the base note, its third and its fifth For a seventh chord, we also take its seventh (which is again a third away from the last added note). The augmented triad, like the fullydiminished 7th, is a symmetrical chord As we saw with the diminished 7th, any inversion just forms a different augmented triad Use of the augmented chord will be discussed in the Progressions section Quartal A quartal voicing is composed of perfect 4th intervals.
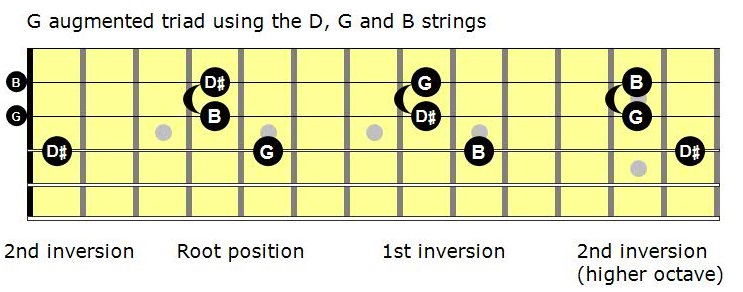
To find the second inversion of a triad, move the bass note of the first inversion to the top Taking the first inversion of G Major ( B , D , G ), we move B to the top Doing so, we find that the second inversion G Major chord is structured, from bottom to top, D , G , B. G What note is the seventh of an Aflat dominant seventh chord?. My method for mastering augmented triads My method is simple play the root position triad and both the 1st and 2nd inversions on all possible sets of strings So what are the possible sets of strings?.
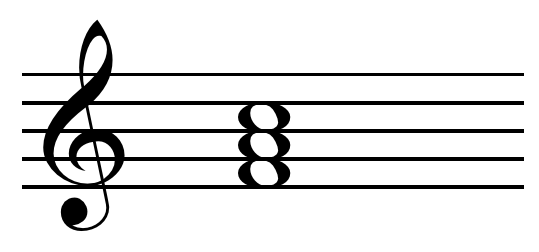
The G major 2nd inversion contains 3 notes D, G, B These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef The figured bass symbols for this chord inversion are 6/4, so the chord is said to be in sixfour position Bass Clef Treble Clef Lesson steps 1. The fullydiminished seventh chord consists of a diminished triad with a diminished seventh added above the root A deceptive cadence moves from V to vi at the end of a phrase. Sus4 with a #5 (augmented fifth) is the equivalent of a minor triad, second inversion If you play it, you'll hear what I mean It just sounds like a minor chord Sus2 with a #5 and b5 would probably be mostly used in jazz as well Those triads could suggest any number of chords, which makes them kinda cool.
Second inversion The fifth is in the bass, and above it are the root and the third This creates an interval of a sixth and a fourth above the bass note, and so is marked as ‘6/4’ or ‘Ic’ Second inversion is the most unstable chord position Inverted triads the first three chords played are C major root position, first inversion. What is an augmented triad?. The figured bass notation for this triad in 2nd inversion is 6/4, with the 6 placed above the 4 on a staff diagram Based on this numbering scheme, another name for this inversion would be G diminished triad in sixfour position.
The first set is E (low)ADThe second set is ADGThe third set is DGB and the 4th set is GBE (high) Let’s see what this looks like on the first set of strings.

5 2 Naming Triads

Basicmusictheory Com G Major Triad Chord

How To Play Triads On Guitar Jamieholroydguitar Com Jamie Holroyd Guitar
G Augmented Triad Second Inversion のギャラリー

G Chord Piano How To Play G Augmented Chords On Piano

Modern Music School
Chord Inversions Explained Chords In Their Root Position First And Second Inversions

Basicmusictheory Com D Augmented Triad Chord

The Ethereal Augmented Chord

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
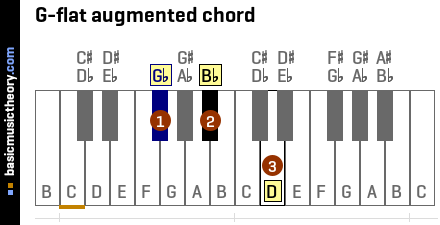
Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord

Inversions Of Diminished And Augmented Triads Musical U

G Chord Piano How To Play G Augmented Chords On Piano
1

Basicmusictheory Com G Minor Triad Chord

Naming Major Or Minor Triads In Music Theory Chord Inversions

Triads Music Theory Academy
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards

Augmented Triads On Guitar

Augmented Chords Open D Tuning

The Ethereal Augmented Chord

Basicmusictheory Com E Double Flat Augmented Triad Chord
/Triad_c_augmented.svg-583dbcb53df78c6f6a1f986e.png)
What Are Diminished And Augmented Triads

Integrated Aural Skills Ear Training Triads In Review
The Augmented Chord Music Theory For Mandolin Simplymandolin
Second Inversion Wikipedia

Augmented Triad Wikipedia

Basicmusictheory Com G Major Triad Chord

C5s1 Chords

Roman Numeral Analysis Wikipedia

The Definitive Easy Guide To Augmented Chords W Examples

What Is An Inversion What Is The Difference With Root Position

Basicmusictheory Com E Double Flat Augmented Triad Chord

Master Triads Daniel Nistico

How To Play Triads On Guitar Jamieholroydguitar Com Jamie Holroyd Guitar
13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form
Chapter 6 Classifying Chords With Strange Circles In Connectionist Representations Of Tonal Music On Au Press Digital Publications

The Augmented Scale Jens Larsen
1

15 Triads And Scales

Augmented Triad In Pathetique Sonata How Does It Function Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange
Solved Identify The Name And Quality Of The Given Triads 3 2 Notate The Following Triads In Root Position 9 G At Major 3 Identify Whether The Course Hero

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord

Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory
Solved Write The Following Triads In Root Position Amp Inversion Write A Bass Clef On The Staff Course Hero

The Augmented Chord Music Theory For Mandolin Simplymandolin

How To Name A Chord Do I Indicate De Bass Note
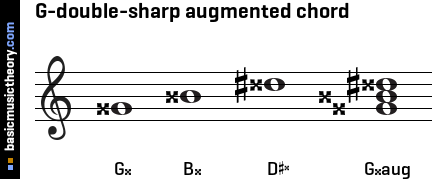
Basicmusictheory Com G Double Sharp Augmented Triad Chord

Scale 273 Augmented Triad

Basicmusictheory Com E Double Flat Augmented Triad Chord
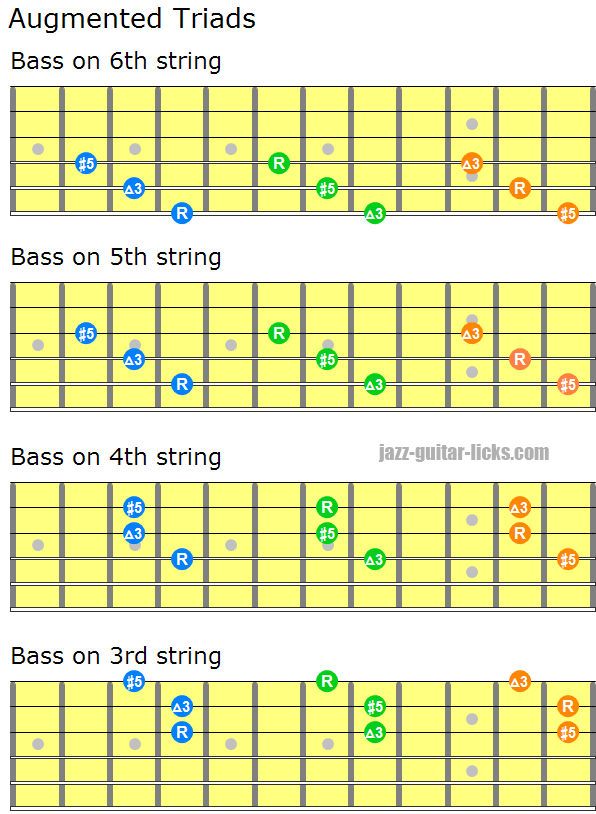
Augmented Triad Chords Guitar Diagrams And Voicing Charts
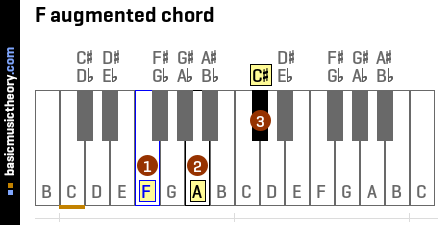
Basicmusictheory Com F Augmented Triad Chord

Augmented Options Open Music Theory

Augmented Triads The Nandi Method

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord

The Ethereal Augmented Chord

Basicmusictheory Com A Double Flat Augmented Triad Chord
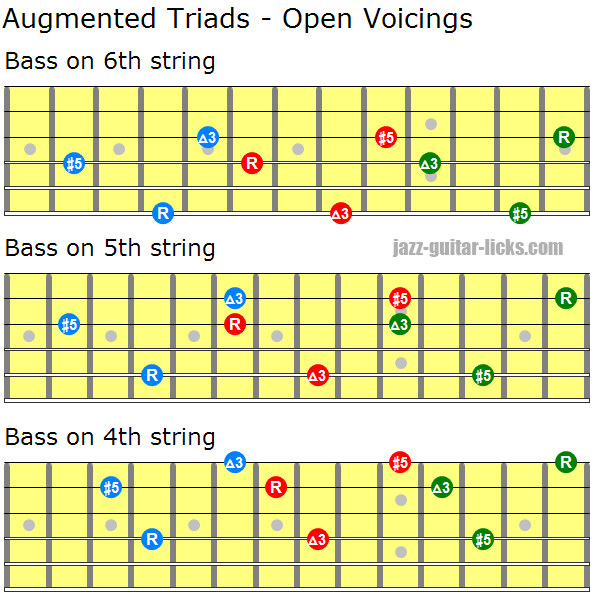
Augmented Triad Chords Guitar Diagrams And Voicing Charts

Augmented Triads On Guitar

Here S How Experienced Players Determine First Inversion Triads In A Second Or Less Hear And Play Music Learning Center

Week 2 The Augmented Triad Cheat Sheet Hear And Play Music Learning Center
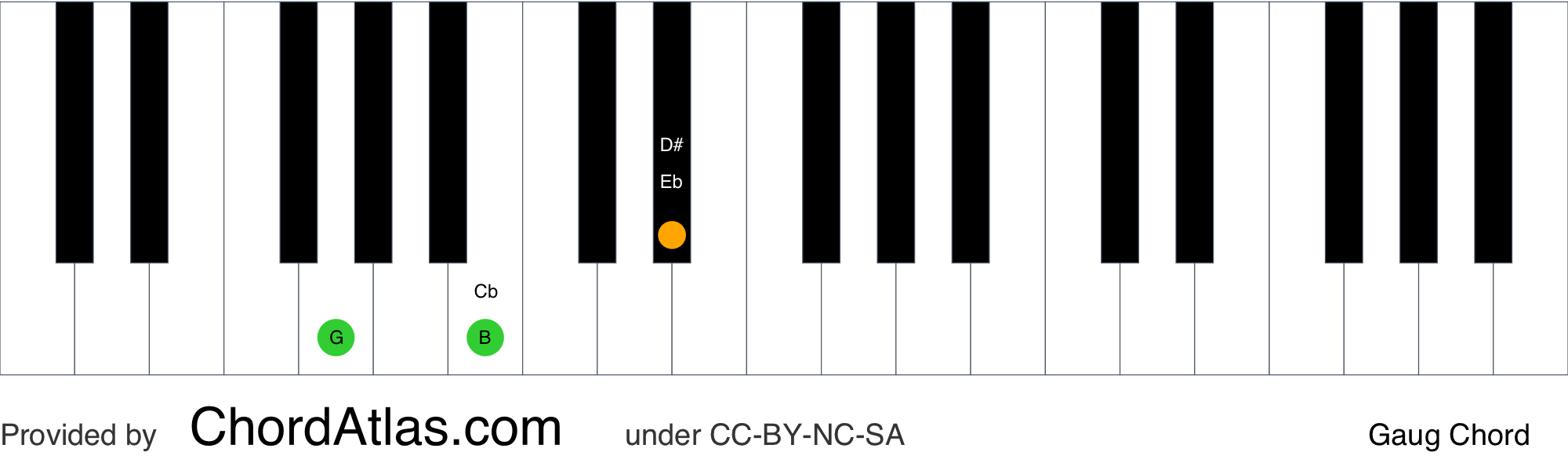
G Augmented Piano Chord Gaug Chordatlas
34 Other Chromatic Harmonies Fundamentals Function And Form

Basicmusictheory Com A Double Flat Augmented Triad Chord

G Chord Piano How To Play G Augmented Chords On Piano

Triad Quality And Inversions A Complete Guide Songsterr Blog

Augmented Triad Example Jens Larsen
1

Augmented Triads The Nandi Method
13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form
13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form

Triad Quality And Inversions A Complete Guide Songsterr Blog

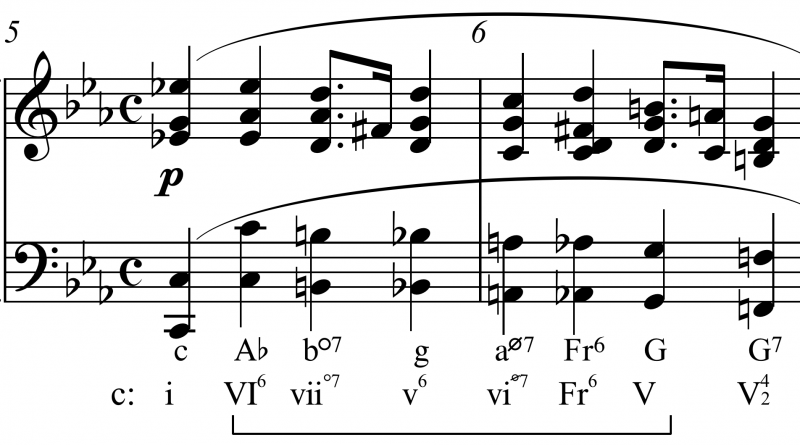
Example 1 Beethoven Bagatelle In C Major Op 119 No 8 Mm 1

Basicmusictheory Com G Major Triad Chord

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards

Basicmusictheory Com E Double Flat Augmented Triad Chord

Augmented Chords Open D Tuning
G Augmented Second Inversion Piano Chord
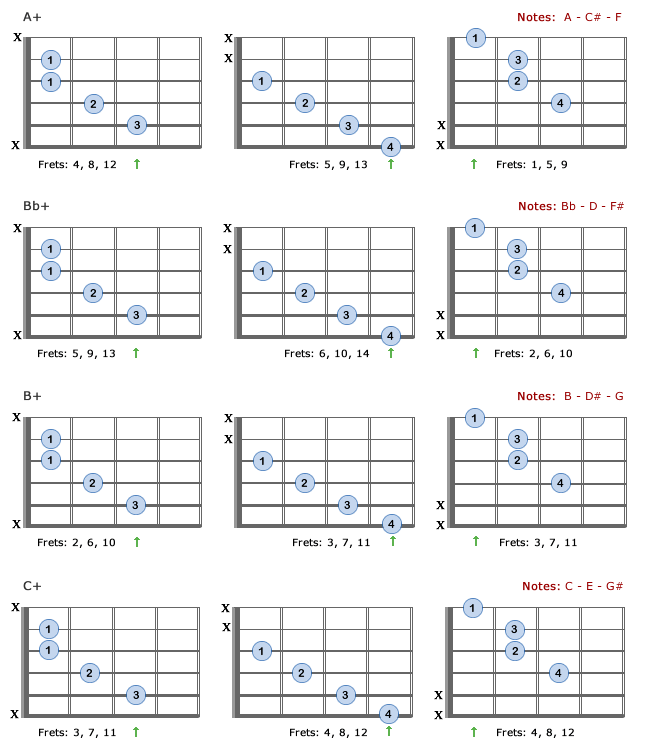
Augmented Chords For Guitar Theory Formulas Charts Bellandcomusic Com

Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord
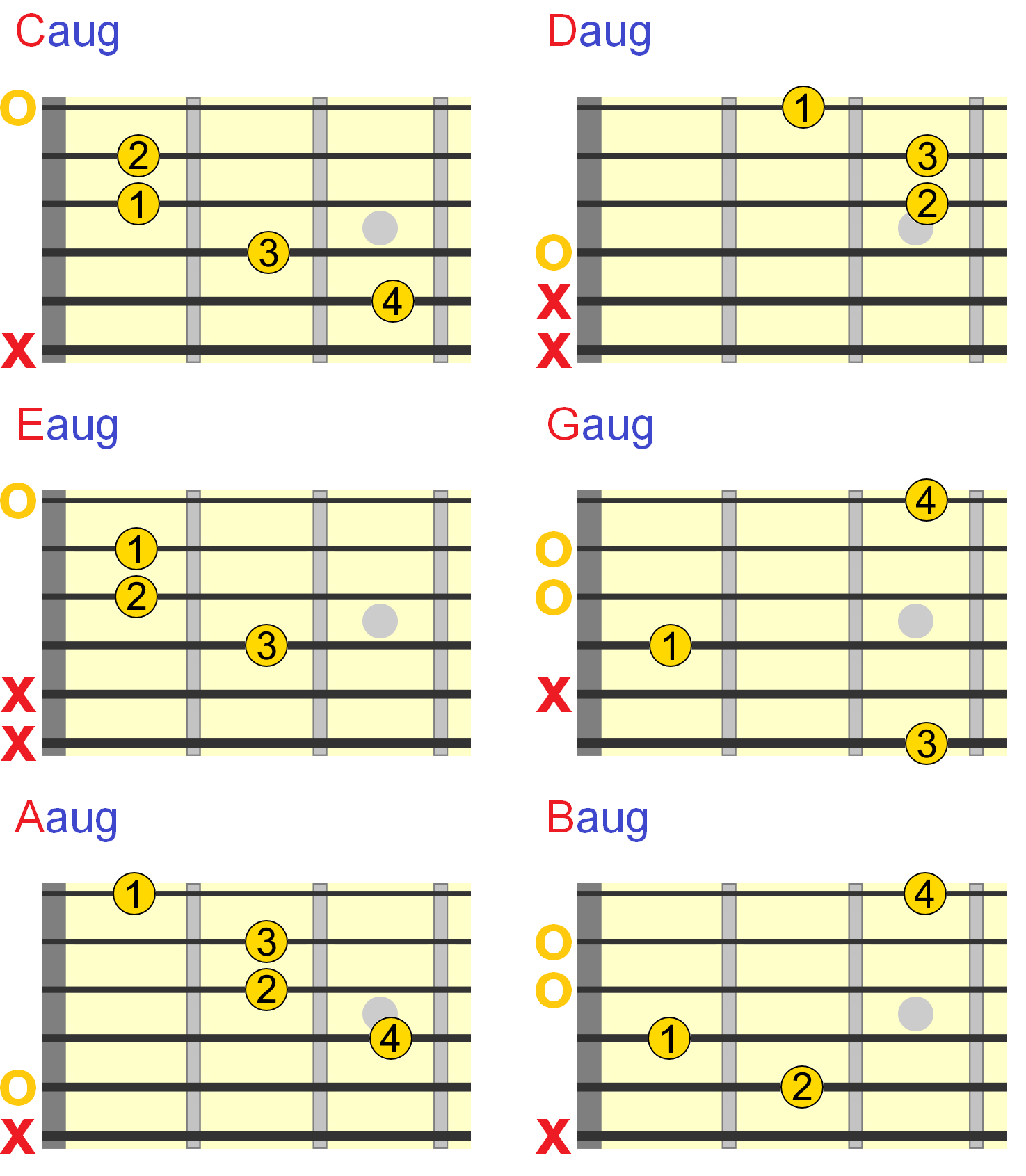
Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know

Section 6 3 Classical Chord Types Offtonic Theory
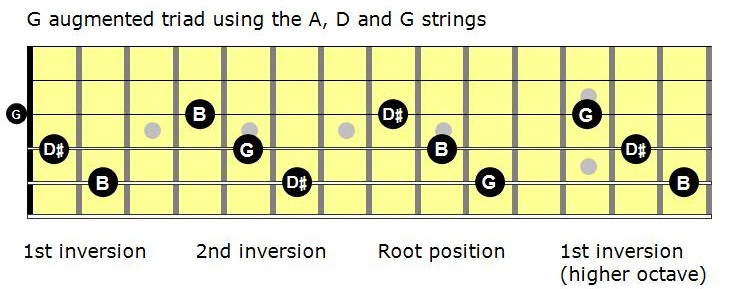
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards
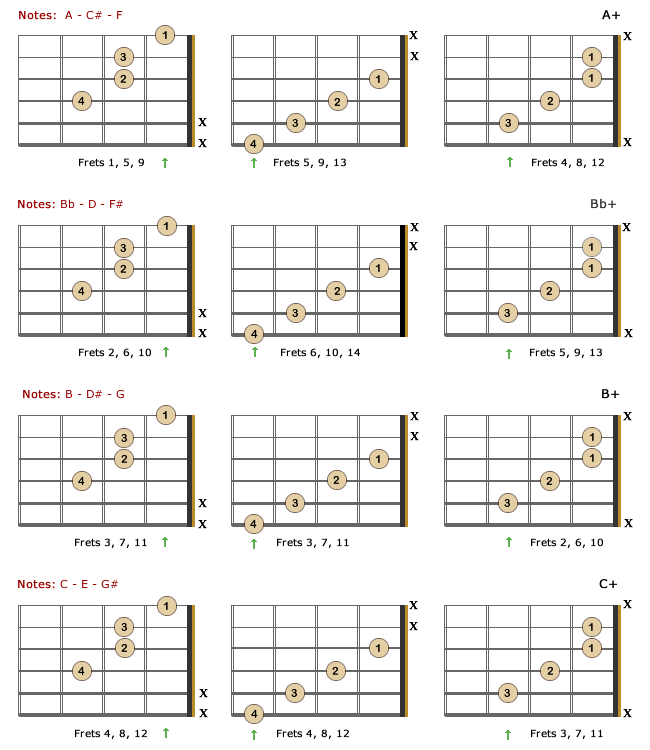
Augmented Chords For Guitar Theory Formulas Charts Bellandcomusic Com
Triad Chords Inversions Triads Music Chord Symbols
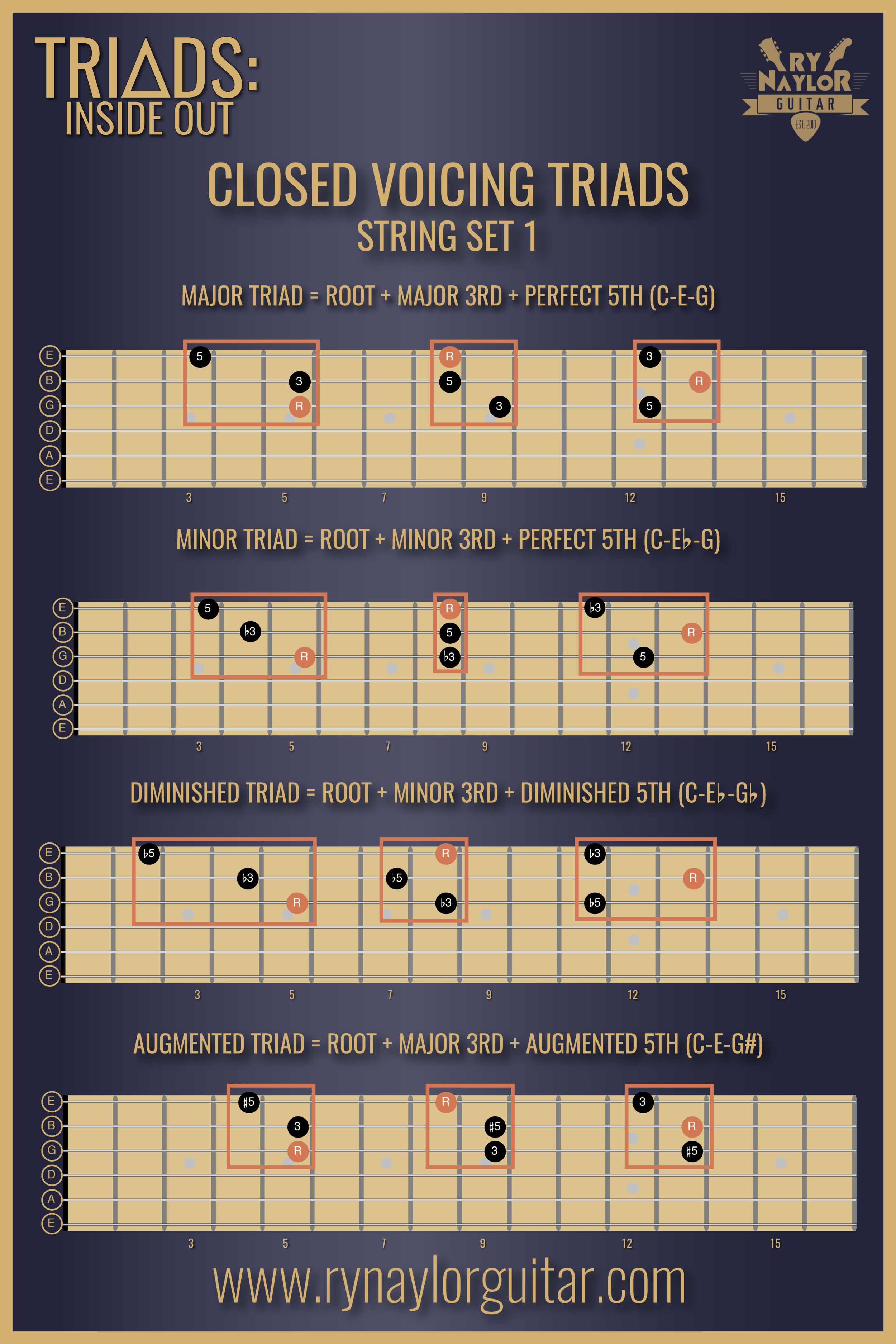
Part 1 Of Triads Inside Out Learning Your Closed Voicing Triad Inversions Ry Naylor Guitar

Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
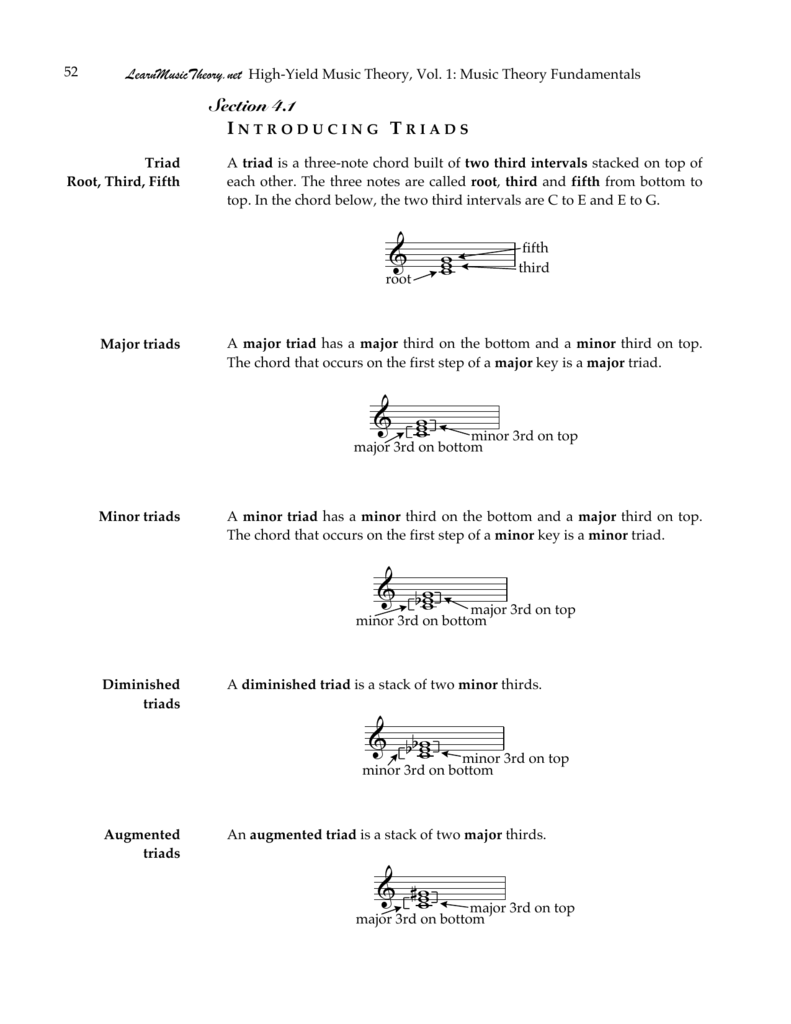
Introducing Triads Music Theory At Learnmusictheory Net

Basicmusictheory Com A Double Sharp Augmented Triad Chord

Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Minor Triad Chord

Click Here To A Pdf Of The Lesson

Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord

Rob Silver February 21
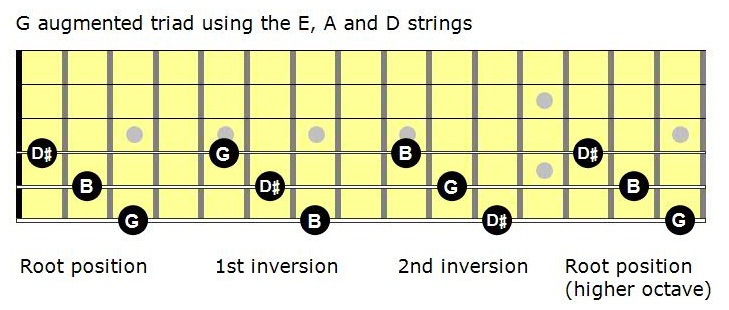
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards
3

The Ethereal Augmented Chord
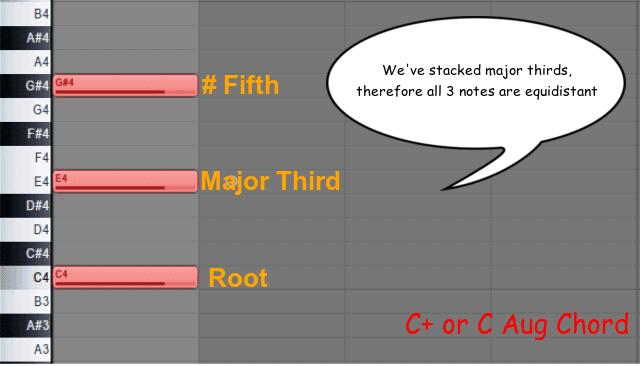
The Definitive Easy Guide To Augmented Chords W Examples

Augmented Sixth Chord Wikipedia
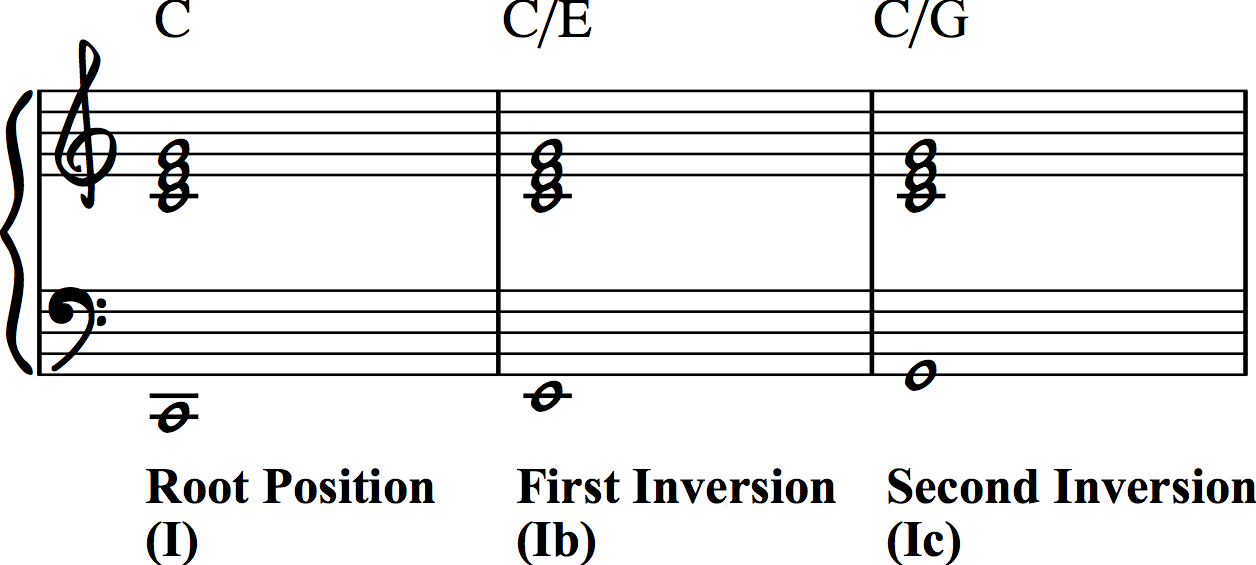
How To Write Interesting Chord Progressions Inversions Making Music Magazine

5 2 Naming Triads
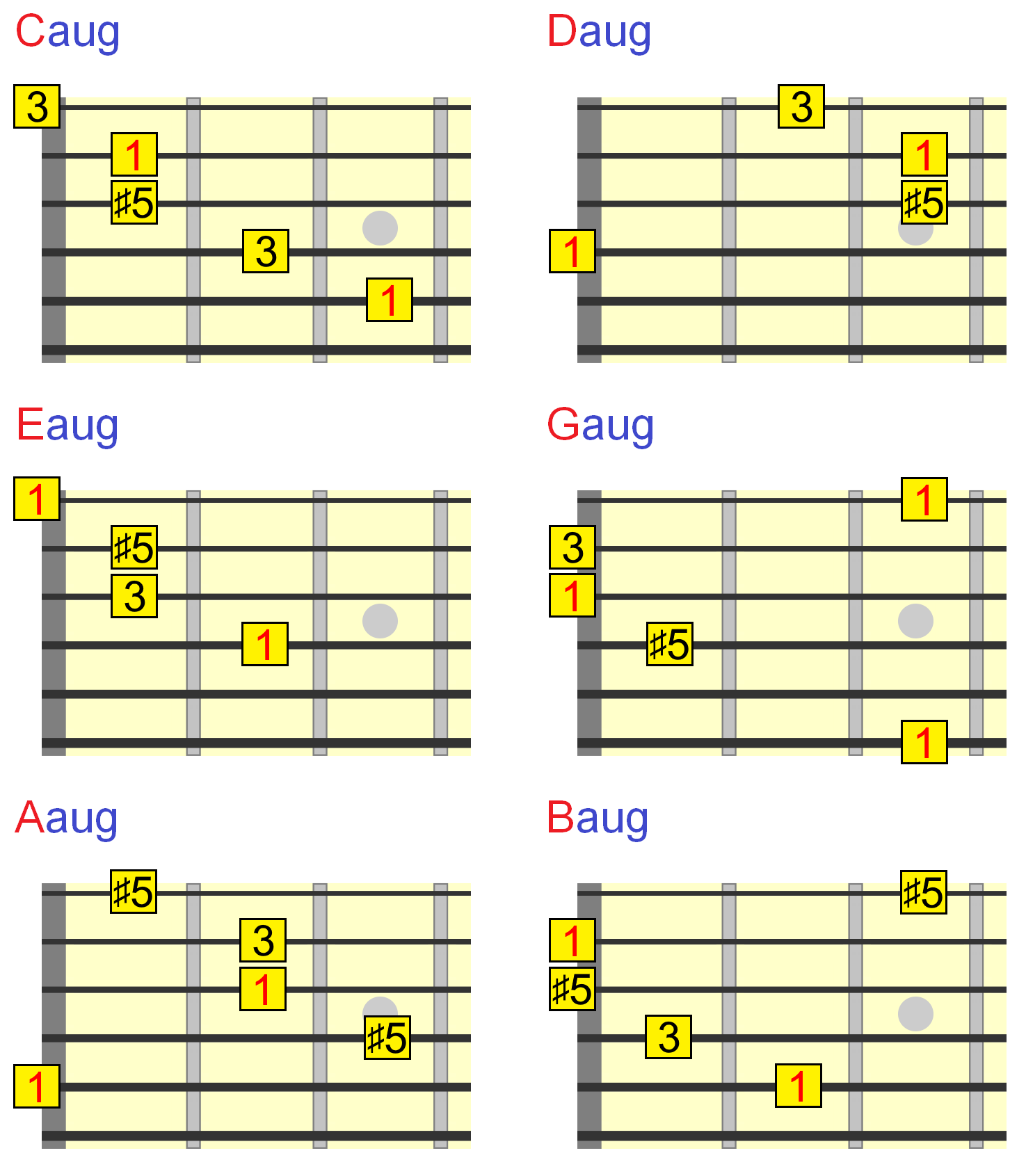
Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know
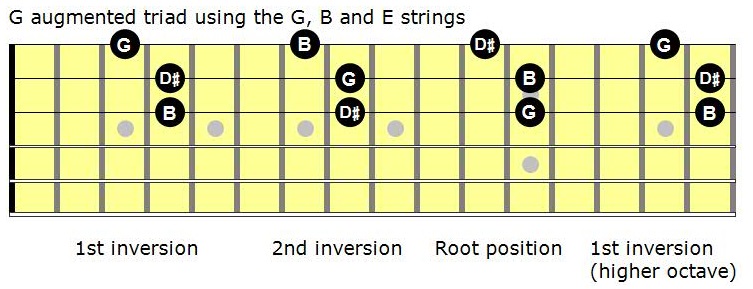
Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards

Augmented Triads The Nandi Method
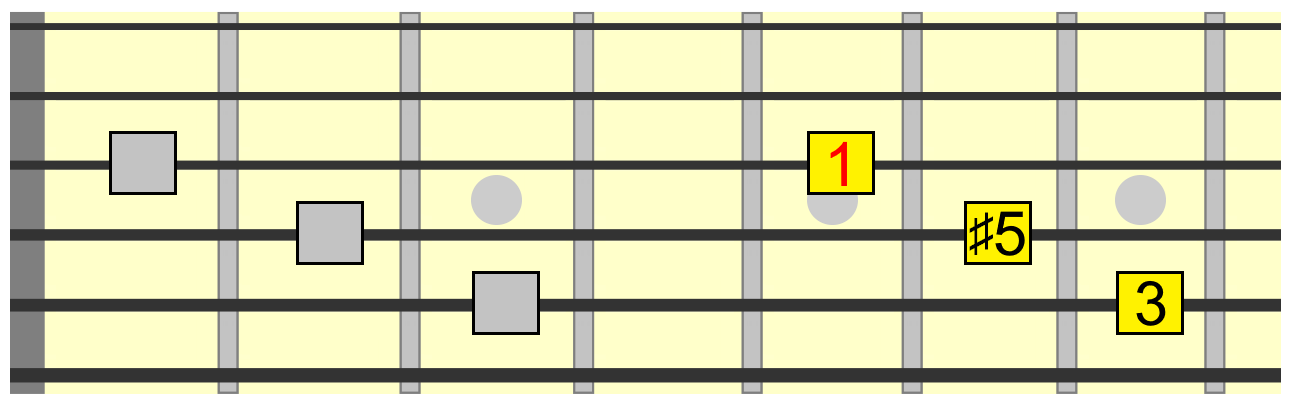
Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know




