Fx Y Zx2+y2+z2 Graph
Find the extreme values of f(x,y)=x 22y2 on the disk x2y ≤1 •Solution Compare the values of f at the critical points with values at the points on the boundary Since f x =2x and f y =4y, the only critical point is (0,0) We compare the value of f at that point with the.

Fx y zx2+y2+z2 graph. (e) Below is the graph of z = x2 y2 On the graph of the surface, sketch the traces that you found in parts (a) and (c) For problems 1213, nd an equation of the trace of the surface in the indicated plane Describe the graph of the trace 12 Surface 8x 2 y z2 = 9;. What is the surface area of the plane z=2x3y above the rectangle with 1. ³³ ³³f x y z dS f u v dA ur r r Formula 2 SURFACE INTEGRALS This should be compared with the formula for a line integral Observe also that ( , , ) ( ( )) '( ) b Ca.
Graph x^2y^2=1 x2 − y2 = −1 x 2 y 2 = 1 Find the standard form of the hyperbola Tap for more steps Flip the sign on each term of the equation so the term on the right side is positive − x 2 y 2 = 1 x 2 y 2 = 1 Simplify each term in the equation in order to set the right side equal to 1 1 The standard form of an. X r ( s ) z f (x,y) y f ( r (s ) ) The 2dim line integral is an area, since the curve arclength parametrization is used in the line integral computation Line integrals in space Example Evaluate the line integral of the function f (x,y,z) = xy y z along the curve r(t) = h2t,t,2 − 2ti in the interval t ∈ 0,1 Solution (r, straight line) Recall Z C. Where the two surfaces intersect z = x2 y2 = 8 − x2 − y2 So, 2x2 2y2 = 8 or x2 y2 = 4 = z, this is the curve at the intersection of the two surfaces Therefore, the boundary of projected region R in the x − y plane is given by the circle x2 y2 = 4 So R.
Z = k3 z = k2 z = k1 z = f(x,y) x y k2 k2 k3 k3 k1 Figure 163 Left Cross sections of the graph z = f(x,y) by horizontal planes z = ki, i = 1,2,3, are level curves f(x,y) = ki of the function f Right Contour map of the function f consists of level sets (curves) f(x,y) = ki The number ki indicates the value of f along each level curve. 2 Sec 51 Basics •First, develop for 2 RV (X and Y) •Two Main Cases I Both RV are discrete II Both RV are continuous I (p 185) Joint Probability Mass Function (pmf) of X. Graph y=x^2 Find the properties of the given parabola Tap for more steps Rewrite the equation in vertex form Tap for more steps Complete the square for The focus of a parabola can be found by adding to the ycoordinate if the parabola opens.
In order to use gradients, we introduce a new variable w = x2 2y2 3z2 Our surface is then the level surface w = 36 Therefore, the normal to surface is ∇ w = (2x, 4y, 6z) At the point P we have ∇ w P = (2, 8, 18) Using point normal form, the equation of the tangent plane is 2(x − 1) 8(y − 2) 18(z − 3) = 0, or. Example 5 X and Y are jointly continuous with joint pdf f(x,y) = (e−(xy) if 0 ≤ x, 0 ≤ y 0, otherwise Let Z = X/Y Find the pdf of Z The first thing we do is draw a picture of the support set (which in this case is the first. 2 Suppose that f R→ R3 and g R3 → Rare defined by f(t) = (t,t2,t3), g(x,y,z) = x2eyz, and h= g f R→ Ris their composition (a) Use the chain rule to compute h′(1) (b) Find h(t) and compute h′(1) directly Solution.
Graph the surface f (x,y,z) = c I have a function f (x,y,z) = x^2 y^2 z^2 and I'd like to graph the surface defined by the equation f (x,y,z) = 1 When I type "S x^2 y^2 z^2 = 1" into the input bar, this works perfectly;. Solution The given surface is the zero level surface of the function F(x;y;z) = x 2y xz 2y2z So, the normal vector to the tangent plane at the point P(1;1;1) is given by rF(1;1;1) We have rF(x;y;z) = h2xy z 2;x2 4yz;2xz 2yi=)rF(1;1;1) = h3;. ⇤ Iunderstandthedi↵erencebetweenthefunctionf(x,y)=z and the function F(x,y,z)=f(x,y)z ⇤ Icancalculaterf and rF ⇤ IcanuserF to define a tangent plane ⇤ Once I have a tangent plane, I can calculate the linear approximation Objectives Tangent lines are used to approximate complicated surfaces For example, 1 05 05 1 2 2 4 x y.
4 (Exercise 22) Find the minimum/maximum of f(x;y) = 2x2 3y2 4x 5 when x2 y2 16 We can look for extrema separately when x2 y2 < 16 and x2 y2 = 16 For the former, we have fx(x;y) = 4x 4 and fy(x;y) = 6y, so the only critical point is (1;0) with value f(1;0) = 7For the latter we use Lagrange multipliers with the constraint x2 y2 = 16 We get the equations. θ d θ d ϕ which is really hard to evaluate But we know that the normal vector to the sphere is r = ( x, y, z), hence, (2) ∬ S F r d S = ∬ S ( x 2, y 2, z 2) ⋅ ( x, y, z) d S = ∬ S ( x 3 y 3 z 3) d S = ∬ S ( x 3 y 3) d S ∬ S z 3 d S Can we say that the first summand evaluates to zero since S is symmetrical with respect to the x and yaxes?. If f (x, y, z) = x sin yz, (a) find the gradient of f and (b) find the directional derivative of f at (1, 3, 0) in the direction of v = i 2 j – k Solution (a) The gradient of f is ∇f (x, y, z) = 〈f x(x, y, z), f y(x, y, z), f z(x, y, z)〉 = 〈sin yz, xz cos yz, xy cos yz〉.
Compute the triple integral of f (x,y,z) = z in the region bounded by x > 0, z > 0, y > 3x, and 9 > y2 z2 Solution Sketch the integration region I The integration region is in the first octant I It is inside the cylinder y2 z2 = 9 I It is on one side of the plane 3x − y = 0 The plane has normal vector n = h3,−1,0i and contains (0,0,0)1 x z 3x y = 0 3. Open Middle PointSlope Exercise (2). Subject to the constraint 2x2 (y 1)2 18 Solution We check for the critical points in the interior f x = 2x;f y = 2(y1) =)(0;.
Graph of z = f(x,y) New Resources SSS Triangle Exploration;. 2 0 hx;y;z4i(r r ˆ)dˆd = Z 2ˇ 0 Z p 2 0 ˆ 2 p 2 ˆ5 8 dˆd = 2ˇ Z 2 0 ˆ2 2 p 2 ˆ5 8 dˆ = 1 3 1 6 = 1 6 1784 Use Stokes’ Theorem to evaluate ZZ S curlFdS when F(x;y;z) = x2y3zi sin(xyz)j xyzk, and Sis the part of the cone y2 = x2 z2 that lies between the planes y= 0 and y= 3, oriented in the direction of the positive yaxis. The graph of a function f(x;y) = 8 x2 y) So, one surface we could use is the part of the surface z= 8 x 2 yinside the cylinder x2 y = 1 (right picture) 4 x y z x y z Let’s call this surface Sand gure out how it should be oriented The original curve was parameterized.
Definition 2 The graph of a function f with the two variables x and y is the surface z = f(x,y) formed by the points (x,y,z) in xyzspace with (x,y) in the domain of the function and z = f(x,y) For a point (x,y) in the domain of the function, its value f(x,y) at (x,y) is determined by moving. 3;0i Thus, the equation of the tangent plane at (1;1;1) is 3(x 1) 3(y 1) = 0 =)x y= 0;. Use "x" as the variable like this Examples sin(x) 2x−3;.
Cos(x^2) (x−3)(x3) Zooming and Recentering You can clickanddrag to move the graph around If you just clickandrelease (without moving), then the spot you clicked on will be the new center To reset the zoom to the original click on the Reset button Using "a" Values. Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music. 1 f Z → Z, f(x) = 2x1 2 f R → R, f(x) = 2x1 3 f Z×Z → Z, f(x,y) = 2x2 y 4 f Z×Z∗ → Q, f(x,y) = x/y 5 f N → N × {0,1,2}, f(x) = (bx/3c,x − 3 bx/3c), where bxc = greatest integer less than or equal to x Solution 1 Onetoone It is not onto because the.
Let {eq}f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 {/eq} and let S be the level surface defined by f(x,y,z) = 4 (a) Find an equation for the plane tangent to S at {eq}P_{0}(1,1,2). Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music. 2 Gauss's Divergence Theorem Let F(x,y,z) be a vector field continuously differentiable in the solid, S S a 3D solid ∂S the boundary of S (a surface) n unit outer normal to the surface ∂S div F divergence of F Then ⇀ ⇀ ⇀ ˆ ∂S S.
Graph x^2=y^2z^2 Natural Language;. This tool graphs z = f (x,y) mathematical functions in 3D It is more of a tour than a tool All functions can be set different boundaries for x, y, and z, to maximize your viewing enjoyment This tool looks really great with a very high detail level, but you may find it more comfortable to use less detail if you want to spin the model. Plane z = 1 The trace in the z = 1 plane is the ellipse x2 y2 8 = 1.
Example 1 The graph of z = f ( x, y) as a surface in 3 space can be regarded as the level surface w = 0 of the function w ( x, y, z) = z − f ( x, y) Example 2 Spheres x 2 y 2 z 2 = r 2 can be interpreted as level surfaces w = r 2 of the function w = x 2 y 2 z 2. Z C f(x;y)ds = Z b a f(x(t);y(t))j!r0(t)jdt (53) = Z b a f(x(t);y(t)) s dx dt 2 dy dt dt Remark 391 We used aand bfor the limits of integration because they are the limits of the variable t Remark 392 Note that the line integral is with respect to arc length However, to compute it, we use the parametrization of the curve, whatever it is We. Solution The graph of f in R3 can be realized as the level surface (or hypersurface) S = {(x,y,z) ∈ R3 g(x,y,z) = 0}, g(x,y,z) = x2 y2 z −9 Our point is then (1,−2,4) on the level surface The general formula for the tangent plane T pS to a point p on.
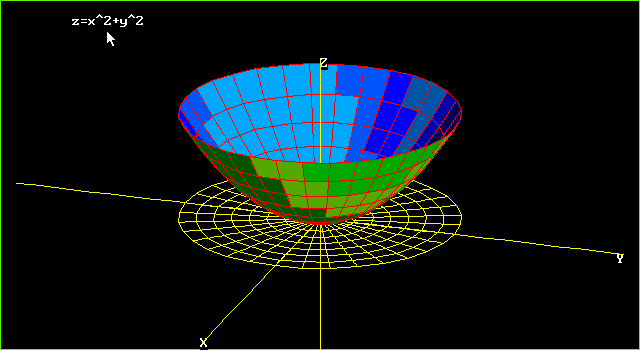
F is the set of all real numbers z z that has at least one ordered pair ( x, y) ∈ D ( x, y) ∈ D such that f ( x, y) = z f ( x, y) = z as shown in the following figure Figure 42 The domain of a function of two variables consists of ordered pairs ( x, y). First, remember that graphs of functions of two variables, z = f (x,y) z = f ( x, y) are surfaces in three dimensional space For example, here is the graph of z =2x2 2y2 −4 z = 2 x 2 2 y 2 − 4 This is an elliptic paraboloid and is an example of a quadric surface We saw several of these in the previous section. Here a, b × c, d denotes the Cartesian product of the two closed intervals a, b and c, d It consists of rectangular pairs (x, y) such that a ≤ x ≤ b and c ≤ y ≤ d The graph of f represents a surface above the xy plane with equation z = f(x, y) where.
Curves in R2 Three descriptions (1) Graph of a function f R !R (That is y= f(x)) Such curves must pass the vertical line test Example When we talk about the \curve" y= x2, we actually mean to say the graph of the function f(x) = x2That is, we mean the set. Answer (1 of 3) It's the equation of sphere The general equation of sphere looks like (xx_0)^2(yy_0)^2(zz_0)^2=a^2 Where (x_0,y_0,z_0) is the centre of the circle and a is the radious of the circle It's graph looks like Credits This 3D Graph is created @ code graphing calculator. Example 1 Find each of the directional derivatives D→u f (2,0) D u → f ( 2, 0) where f (x,y) = xexy y f ( x, y) = x e x y y and →u u → is the unit vector in the direction of θ = 2π 3 θ = 2 π 3 D→u f (x,y,z) D u → f ( x, y, z) where f (x,y,z) = x2zy3z2 −xyz f ( x, y, z) = x 2 z y 3 z 2 − x y z in the direction of →v.
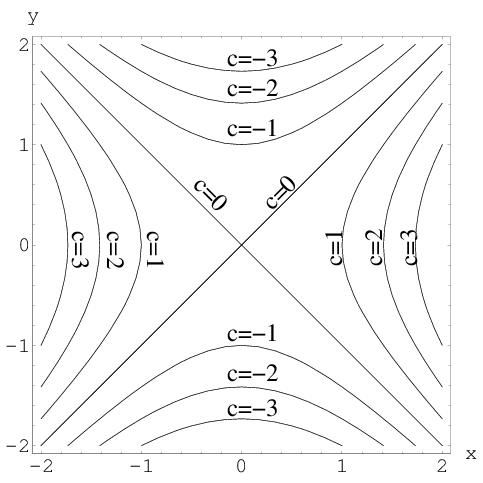
Divide y, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac{y}{2} Then add the square of \frac{y}{2} to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of the equation a perfect square. Let G be a smooth, twosided surface given by z = f(x,y), where (x,y) is in R and let n denote the upward unit normal on G If f has continuous firstorder partial derivatives and F = Mi Nj Pk is a continuous vector field, then the flux of F across G is given by flux F = ∫∫ G F·n dS = Mf∫∫ x Nf y Pdx dy R ⇀ ⇀ ⇀ ⇀ ^ ^ ^ ⇀ ⇀. The level curves of f(x,y) = x 2 y 2 are curves of the form x 2 y 2 =c for different choices of c These are circles of radius square root of c Several of them are shown below One can think of the level curve f(x,y)=c as the horizontal crosssection of the graph at height z=c When each level curve f(x,y)=c is plotted at a height of c units above the xyplane, we get the figure.
Chapter 11 which is the equation of a plane 112 Implicit Functions The totality of points (x,y) satisfying the equation F(x,y) = 0 forms a curveGiven a value of the independent variable x, evaluation of y, supposing one exists, may require the approximate solution of F(x,y) = 0 by numerical means, such as the method of bisections or the metod of successive linearizations. Now f(x,y) = x2 k2x2 = (p x2 k2x2)2 So the crosssection is the “same” parabola as in the xz and yz planes, namely, the height is always the distance from the origin squared This means that f(x,y) = x2 y2 can be formed by starting with z = x2 and rotating this curve around the z axis Finally, picking a value z = k, at whatpoints does f(x,y) = k?. S is defined as a sphere.
1) is a critical point The second derivative test f xx = 2;f yy = 2;f xy = 0 shows this a local minimum with. The graph of something like z = f(x;y) is a surface in threedimensional space Such graphs are usually quite di–cult to draw by hand Since z = f(x;y) is a function of two variables, if we want to difierentiate we have to decide whether we are difierentiating with. Steps to graph x^2 y^2 = 4.
A sphere is the graph of an equation of the form x 2 y 2 z 2 = p 2 for some real number p The radius of the sphere is p (see the figure below) Ellipsoids are the graphs of equations of the form ax 2 by 2 cz 2 = p 2, where a, b, and c are all positive.

Solved Functions Of Two Variables Display The Values Of The Chegg Com

Assignment Previewer Department Of Mathematics Ccny Pages 1 22 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
Level Set Examples Math Insight
Fx Y Zx2+y2+z2 Graph のギャラリー
Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits
What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora
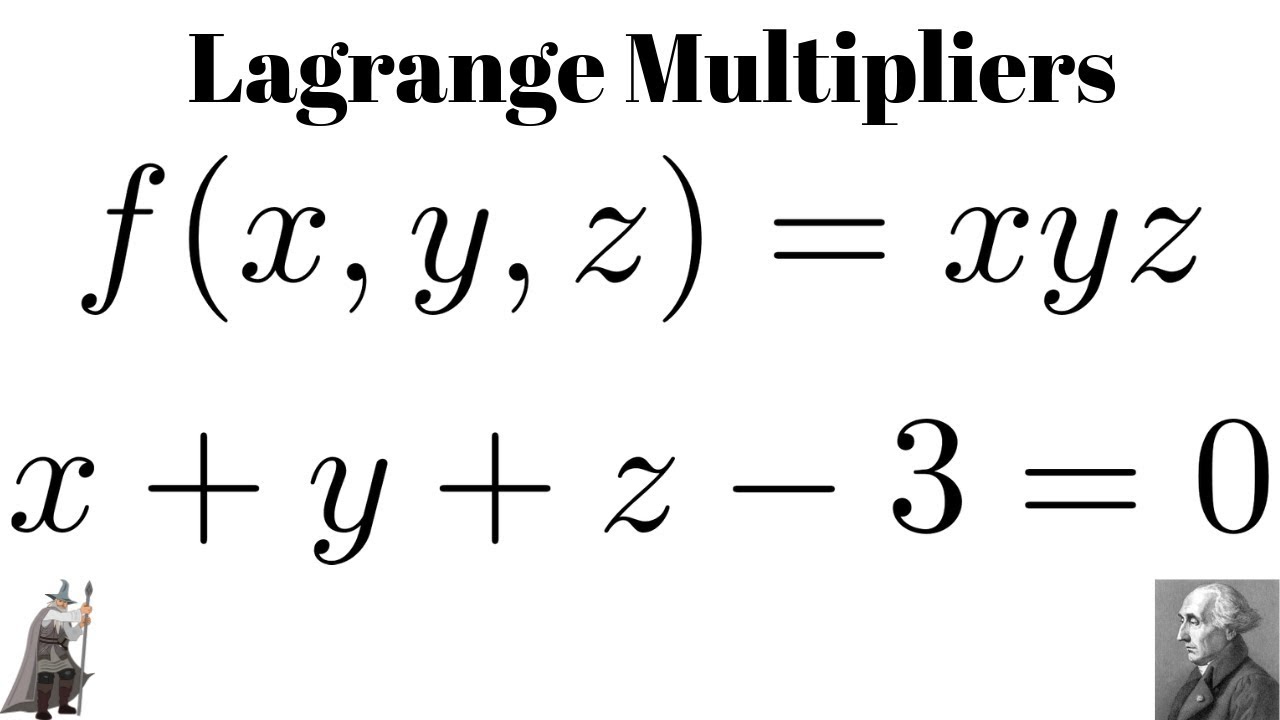
Lagrange Multipliers Maximum Of F X Y Z Xyz Subject To X Y Z 3 0 Youtube
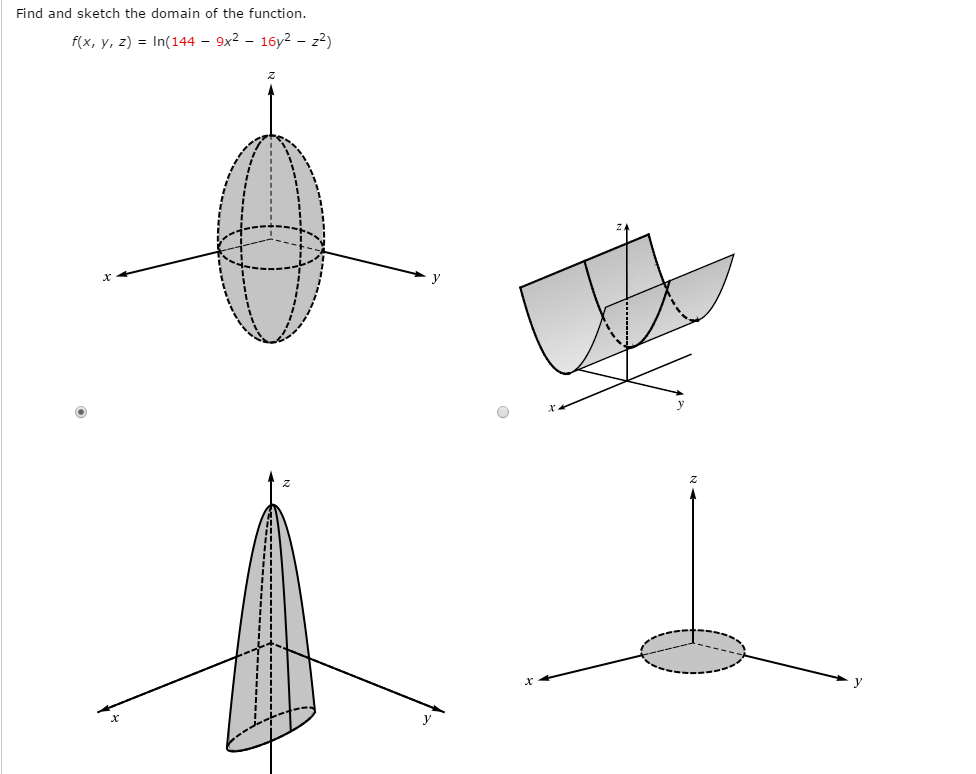
Solved Find The Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Z Chegg Com
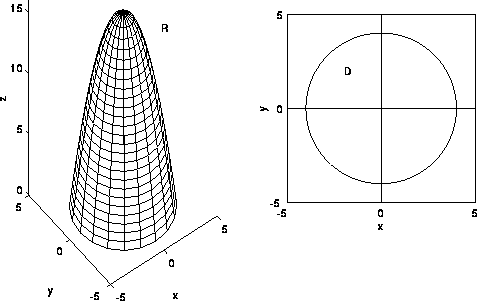
Triple Integrals In Cylindrical And Spherical Coordinates

28 Match The Equation Y X 2 Z 2 With Its Graph Labeled I Viii Toughstem

Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Z Ln 16 4x 2 4y 2 Z 2 Youtube

Matlab Tutorial
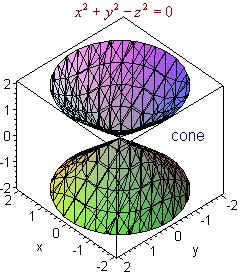
Surfaces
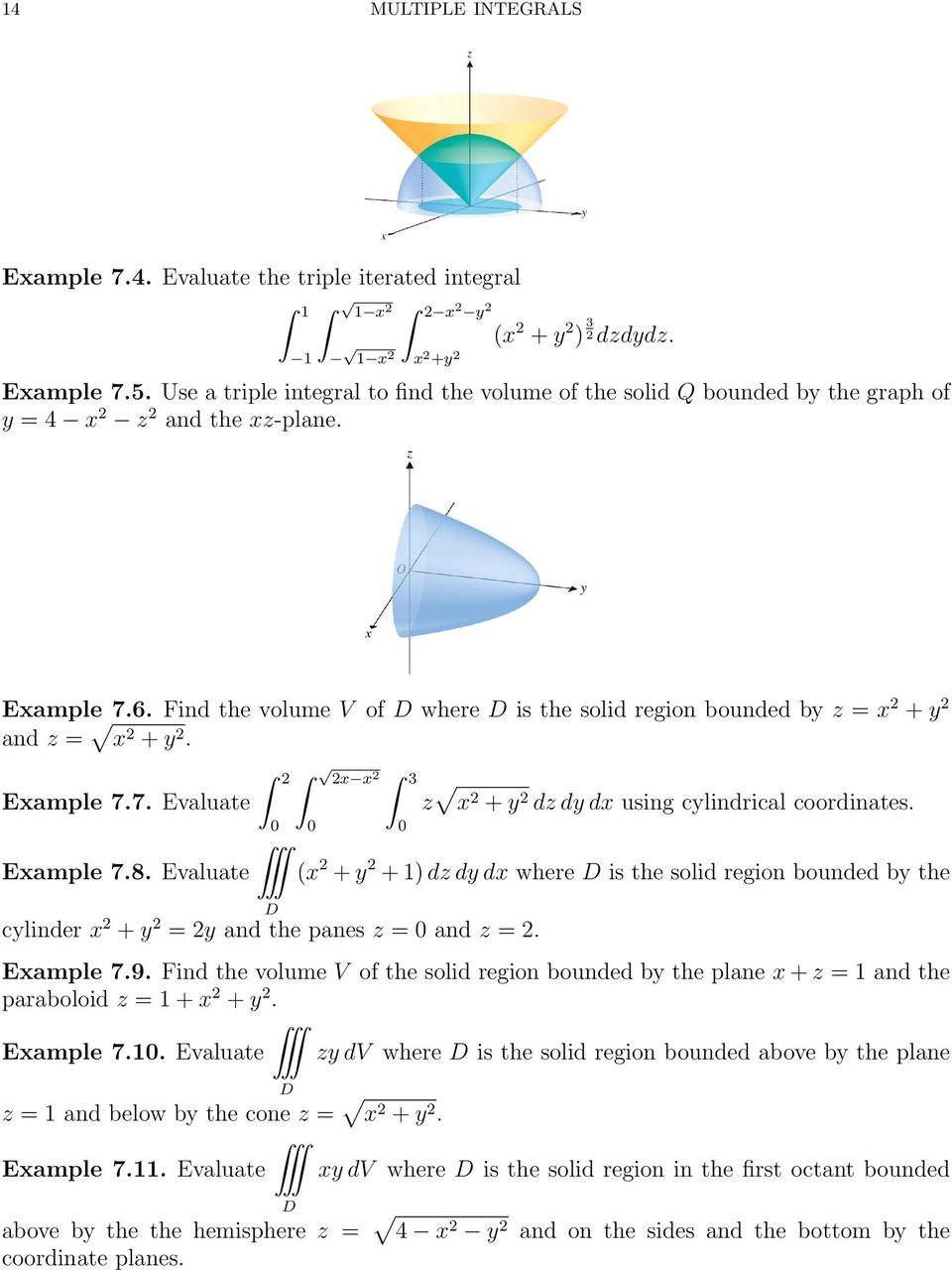
Multiple Integrals H 2 Y Are Continuous Functions On C D And Let F X Y Be A Function Defined On R Then Pdf Free Download

The Graph Of The X Y Z 0 Plane Download Scientific Diagram
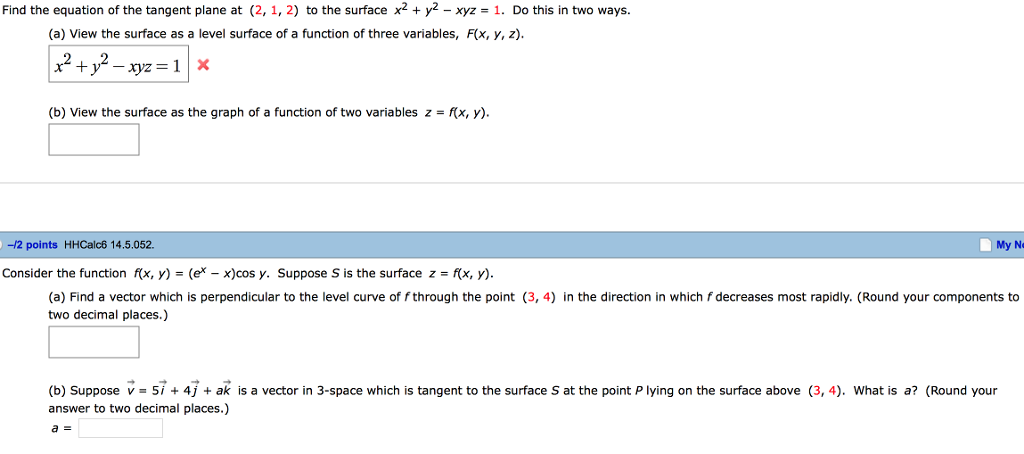
Solved Find The Equation Of The Tangent Plane At 2 1 2 Chegg Com

Describe The Level Surfaces Of The Function F X Y Z X 2 3y 2 5z 2 Study Com

Assignment Previewer Department Of Mathematics Ccny Pages 1 22 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Answered 14 F X Y Z X Y 4z X Y Bartleby
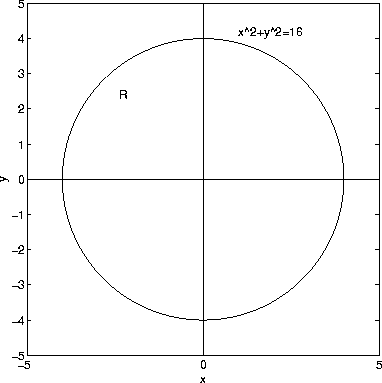
Surface Area
Math Drexel Edu
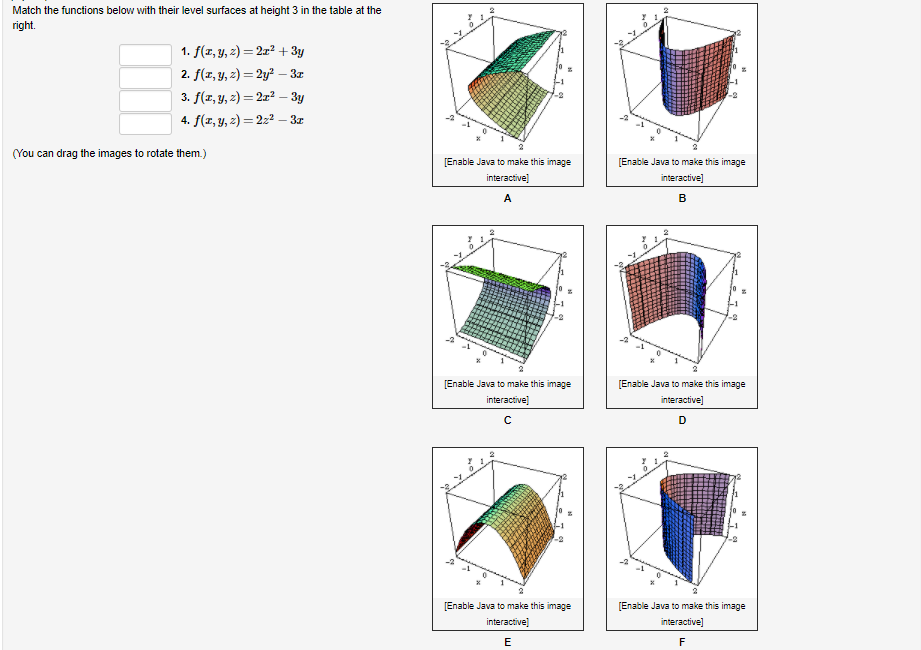
Solved Match The Functions Below With Their Level Surfaces Chegg Com

Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube
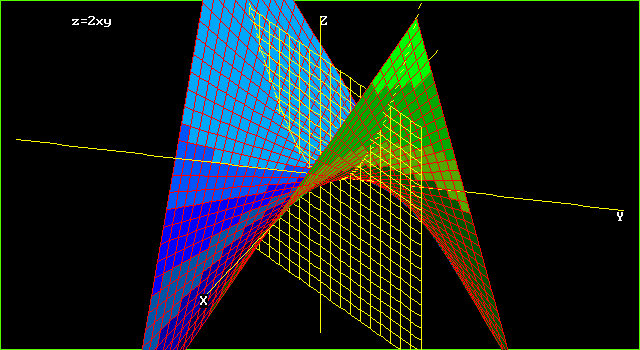
Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits

2 3 Tangent Plane To A Surface Mathematics Libretexts

Solved Finding An Equation Of A Tangent Plane In Exercises Chegg Com

Functions Of Several Variables 13 Copyright C Cengage Learning All Rights Reserved Ppt Download
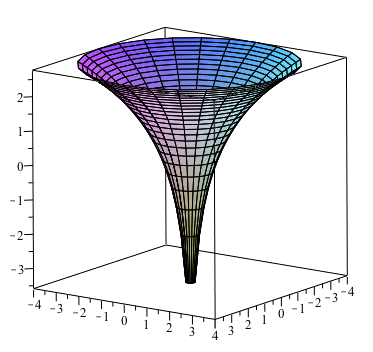
How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic
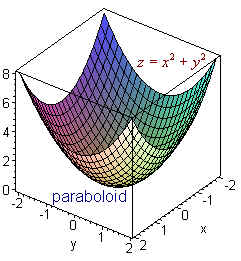
Surfaces
Math Drexel Edu

How Do I Reproduce This Heart Shaped Mesh In Matlab Stack Overflow
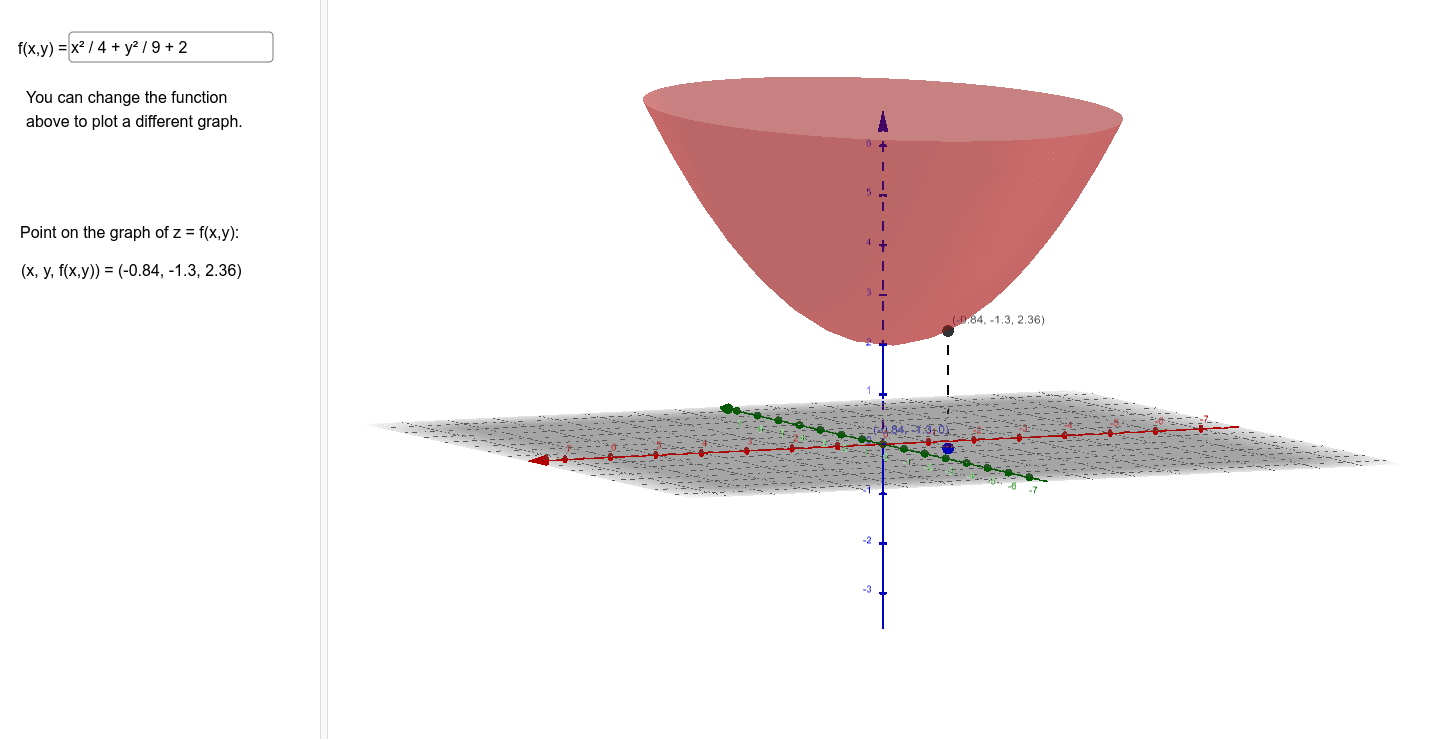
Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra
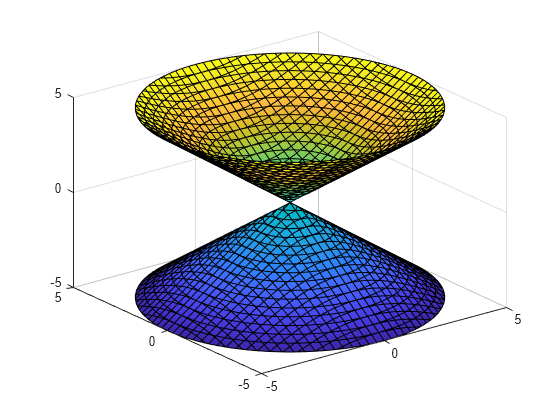
Plot 3 D Implicit Function Matlab Fimplicit3

How Do I Graph Z Sqrt X 2 Y 2 1 Without Using Graphing Devices Mathematics Stack Exchange
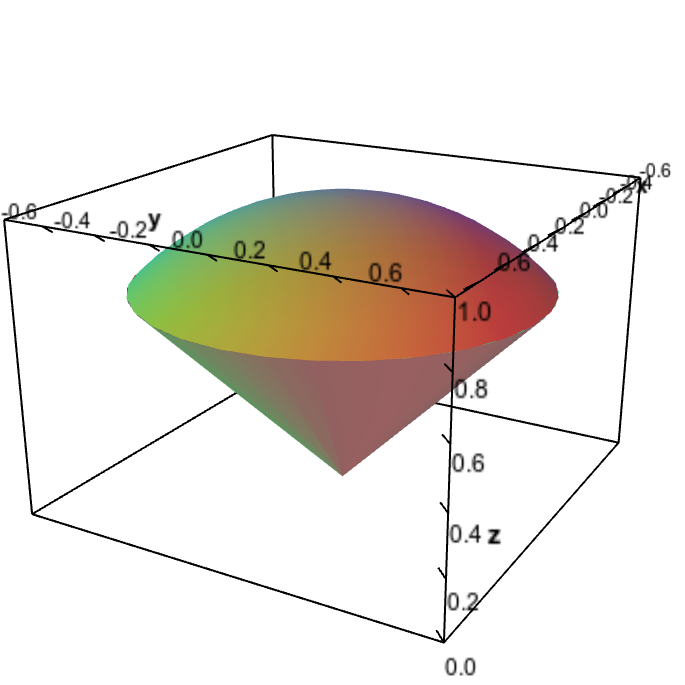
Triple Integral Examples Math Insight

1 Sketch The Surface Z X 2 Y 2 2 Sketch The Surface Z 2y 2 4x 2 Study Com

Matlab Tutorial
Help Geogebra Org
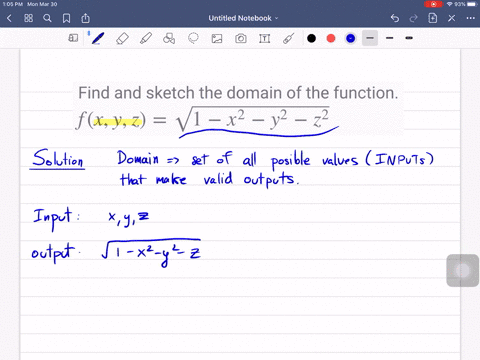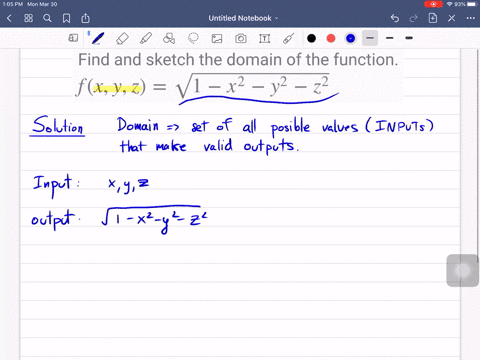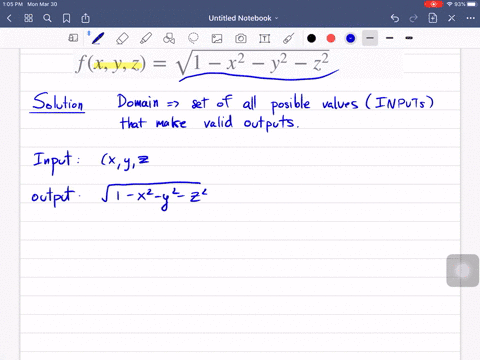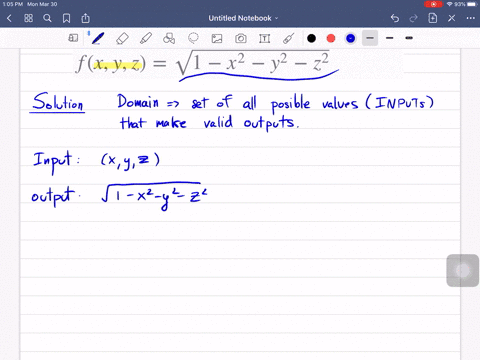
Solved Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Z Ln 16 4x 2 4y 2 Z 2
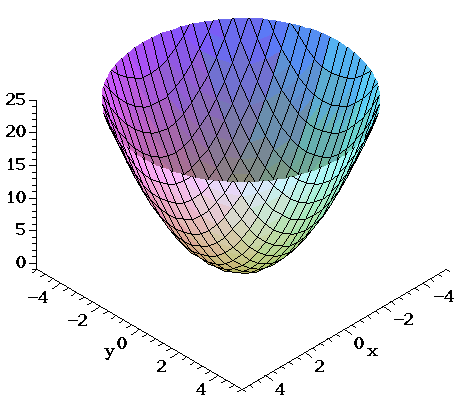
Surfaces Part 2
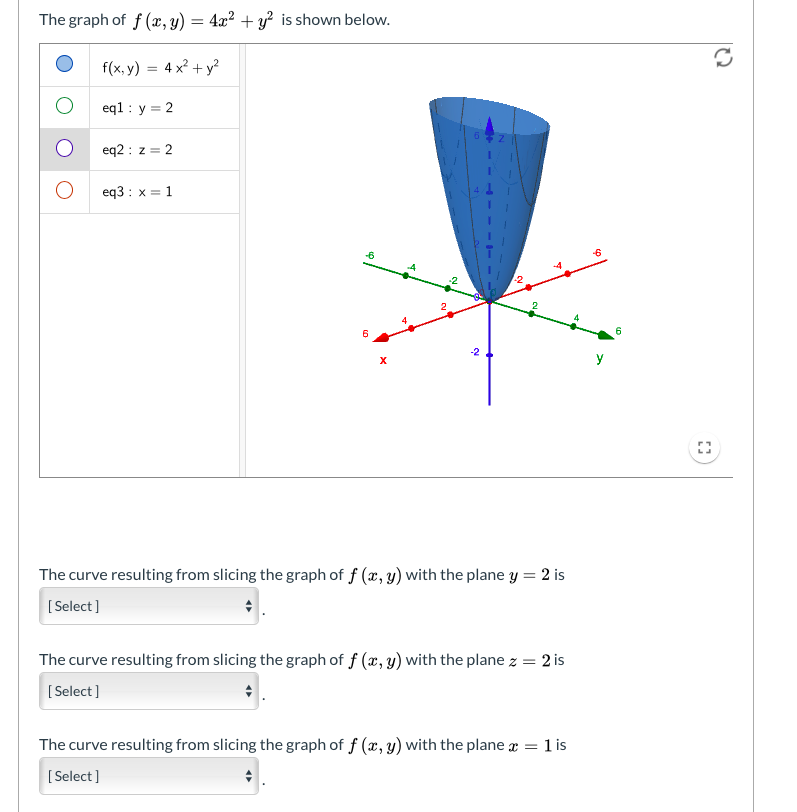
Solved The Graph Of F X Y 4 X2 Y2 Is Shown Below Chegg Com

F X Y X 2 Y Y Y F F X X 2xyx 2 3y Y Ln2 Z F X Y Cos Xy X Cos 2
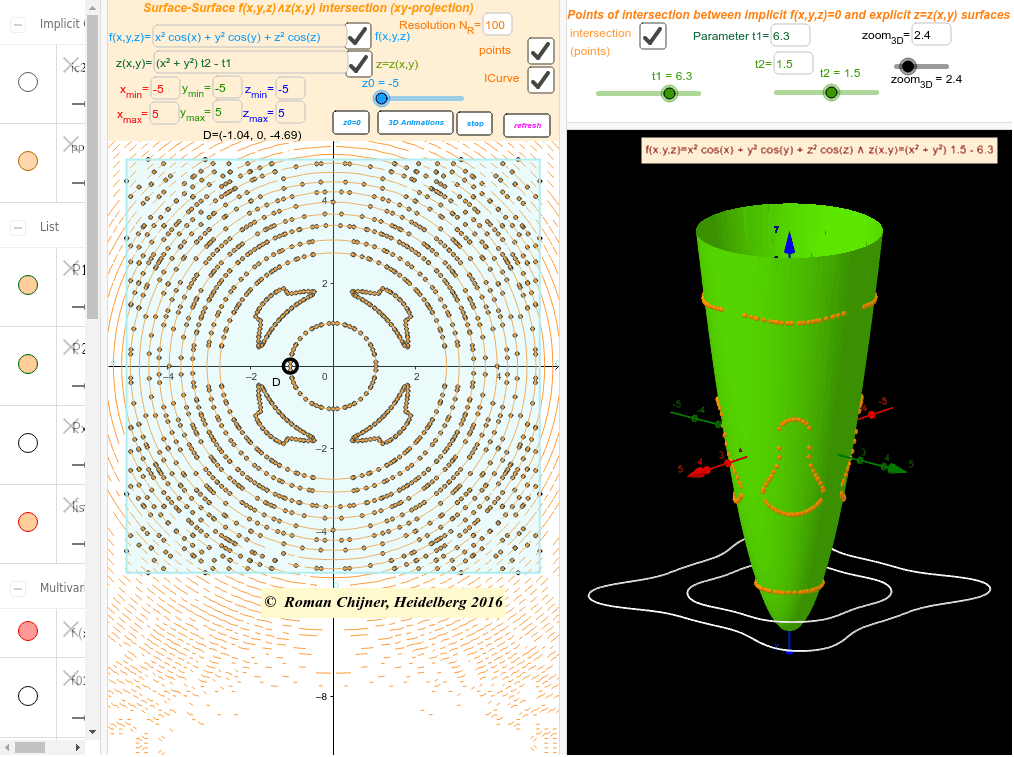
Points Of Intersection Between Implicit F X Y Z 0 And Explicit Z Z X Y Surfaces Geogebra
What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora

Quadratic Function Wikipedia

Solved Consider The Function F X Y Z Ln 2 X2 Y2 Chegg Com

Matlab Tutorial
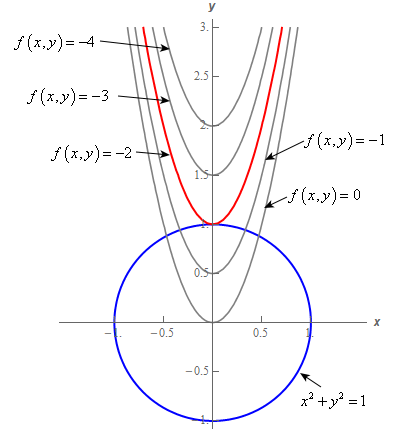
Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers

Assignment Previewer Department Of Mathematics Ccny Pages 1 22 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
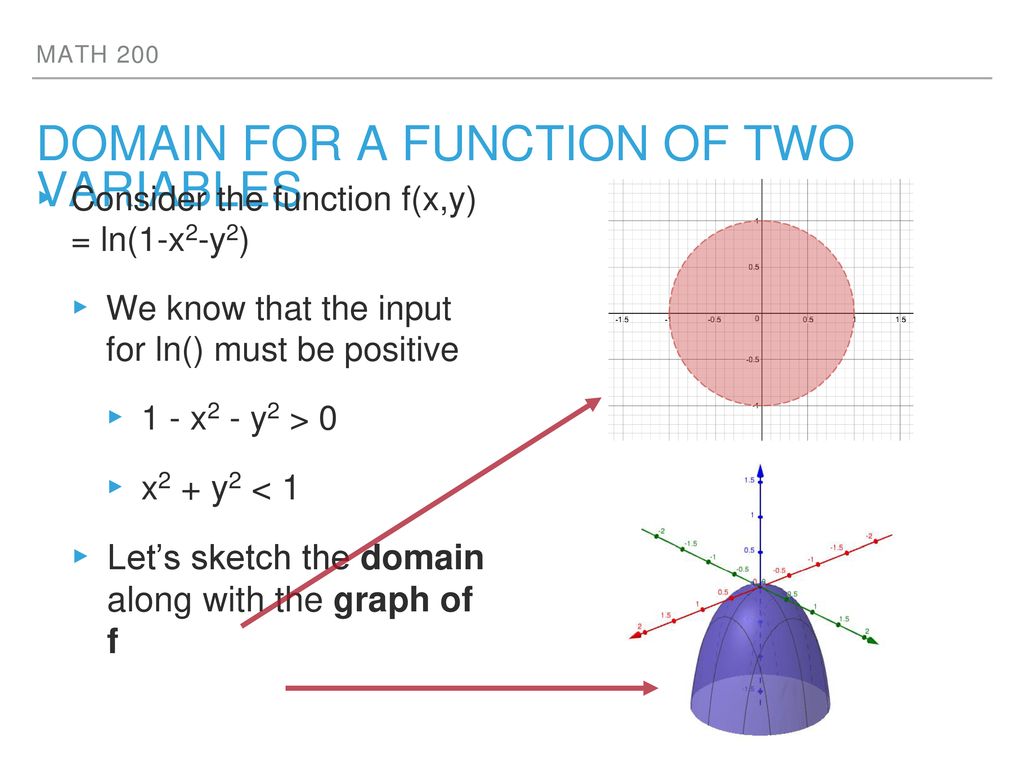
Functions Of Several Variables Ppt Download
Whitman Edu

Tangent Plane To X 2 Xy Y 2 Z 0 Youtube
Surface Area

Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download

Given F X Y 10 2x2 Y Find A The Equation Of The Tangent Plane To The Surface At The Point 2 Homeworklib
Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables And Surfaces

Matlab Tutorial

Graph Xyz With Vertices X 2 3 Y 3 2 And Z 4 3 And Its Image After The Translation X Brainly Com
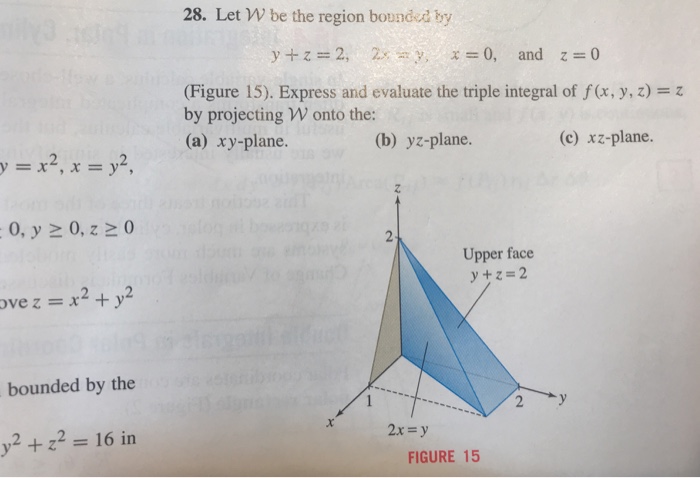
Solved 28 Let W Be The Region Bounded By Y Z 2 2x Y X 0 Chegg Com
1

How Do I Graph Z Sqrt X 2 Y 2 1 Without Using Graphing Devices Mathematics Stack Exchange

Calculate The Double Integral Over S Of F X Y Z Ds For Y 7 Z 2 0 Less Than Or Equal To X Less Than Or Equal To 7 0 Less

Describe The Level Surfaces Of The Function F X Y Z X 2 3y 2 5z 2 Study Com

Graphs And Level Curves
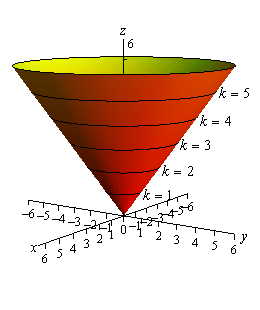
Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables
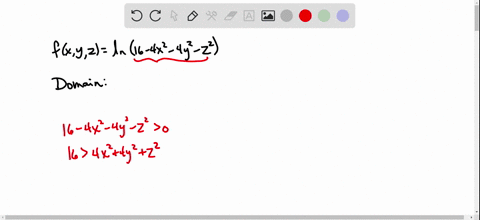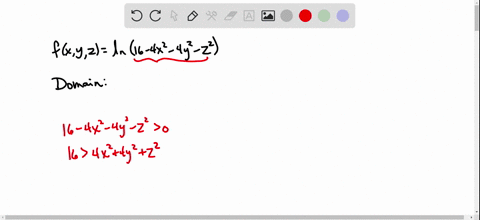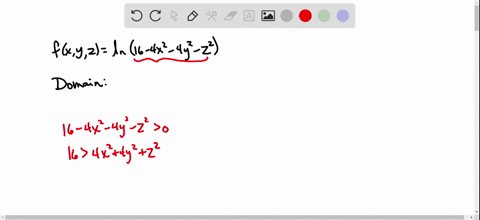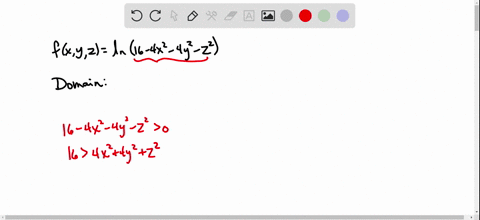
Solved Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Z Ln 16 4x 2 4y 2 Z 2
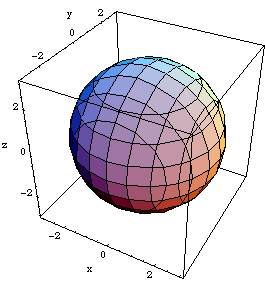
Level Surfaces Nb

28 Match The Equation Y X 2 Z 2 With Its Graph Labeled I Viii Toughstem

Matlab Tutorial
X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1

Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download

Copyright C Cengage Learning All Rights Reserved Partial Derivatives Ppt Download
Help Geogebra Org
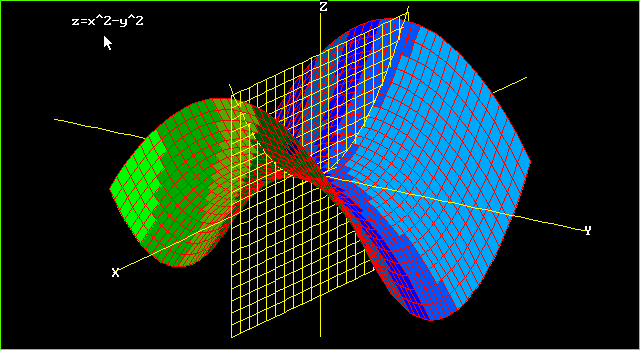
Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits

13 1 Functions Of Multiple Variables Mathematics Libretexts

Solved Find The Extreme Values Of F X Y Z X 2 Y Z 1 On The Intersection Of The Plane Z 1 With The Sphere X 2 Y 2 Z 2 10
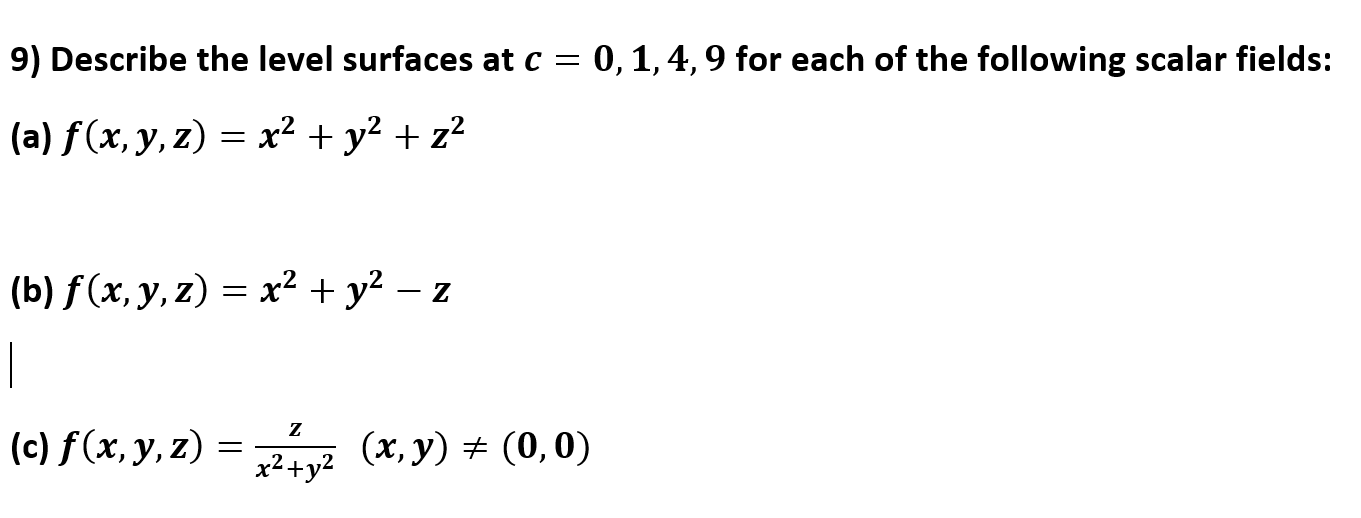
Answered 9 Describe The Level Surfaces At C Bartleby

Homework 14 5

6 7 Maxima Minima Problems Mathematics Libretexts

Graphs And Level Curves
Sketching Surfaces In 3d
Surfaces Part 2

Vector Calculus Chapter 9 5 9 9 Ch9 5 9 9 2 Contents 9 5 Directional Derivatives 9 5 Directional Derivatives 9 6 Tangent Planes And Normal Lines Ppt Download
16 8 Lagrange Multipliers
Math Ucsd Edu
1
How Do You Find The Equations For The Tangent Plane To The Surface X 2 2z 2 Y 2 Through 1 3 2 Socratic
Points Of Intersection Between Implicit F X Y Z 0 And Explicit Z Z X Y Surfaces Geogebra

14 1 Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Libretexts
1

Solved Evaluate The Surface Integral F Ds For The Given Chegg Com

Graphs And Level Curves
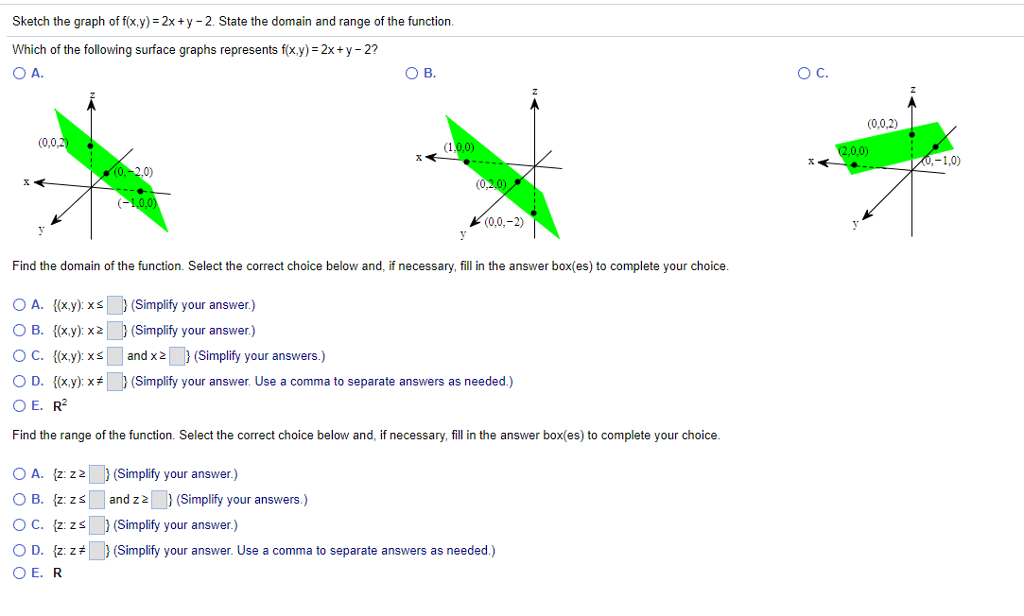
Solved Sketch The Graph Of F X Y 2x Y 2 State The Domain Chegg Com
Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra
3d Surface Plotter Academo Org Free Interactive Education
Level Surfaces

Answered 9 M A Y Z Xyz Xyz P 2 1 1 U Bartleby

Level Surfaces In Matlab
Lagrange Multipliers Minimum Of F X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Subject To X Y Z 9 0 Youtube

1 Point Match The Functions Below With Their Level Surfaces At Height 3 In The Table At The Right 1 F X Y Z 22 3x 2 F X Y Z 2y 3x 3 F X Y Z 2y 3z 2
Level Surfaces
Xyz 3 D Mesh Surface Plotter
Level Sets Math Insight

Factorising Cyclic Expression X 2 Y Z Y 2 Z X Z 2 X Y Youtube
How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic




