Fx+y+z X2+y2+z20
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge.
Fx+y+z x2+y2+z20. 2 for twice differentiable functions, show ∇2f(x) 0 3 show that f is obtained from simple convex functions by operations that preserve convexity • nonnegative weighted sum • composition with affine function • pointwise maximum and supremum • composition • minimization • perspective Convex functions 3–13 Positive weighted sum & composition with affine function nonnegative. X→2±0 f 4(x) → 18 Durch f 4(−1) = 9, f 4(1) = 15 und f 4(2) = 18, ist die Funktion folglich stetig fortsetzbar (e) f 5 x → cos(3x) sin(2x) L¨osungshinweise hierzu Zun¨achst sei bemerkt, dass sin(2x) = 0 f¨ur x = kπ mit k ∈ Z Folglich ist D 5 = Rr kπ 2 k ∈ Z Wir wissen cos(3x) ist 2 3 πperiodisch und sin(2x) ist πperiodisch Somit ist f 5 eine 2πperiodische. F(x;y;z) = x2 y2 (z 1)2 auf dem Ellipsoid S= f(x;y;z) 2R3 x2 (y 2) 2 (z 3) 2 = 1g Hinweis Diese Aufgabe l asst sich wie in dem Beispiel der Vorlesung vom 181 diskutieren Dazu eliminiere man geeignet eine Variable in der Funktion und bestimme den De nitionsbereich Alternativ l asst.
Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. C) Geben Sie den Scheitelpunkt der Parabel f an!. 0 = (z y) (zx yx) = ( x)(z y) Dabei kann nicht x= y= zgelten, da sonst x= y= z= 5.
Z!0 f( z) f(0) z = lim z!0 z z = x i y x i y Here we used z= x i y Now, z!0 means both xand yhave to go to 0 There are lots of ways to do this For example, if we let zgo to 0 along the xaxis then, y= 0 while xgoes to 0 In this case, we would have f0(0) = lim x!0 x x = 1 On the other hand, if we let zgo to 0 along the positive yaxis then f0(0) = lim y!0 i y i y = 1 1 2 ANALYTIC. Despite the fact that the same variables appear in every term, this expression does not factorize into one term There is no common factor, and no common bracket EAch term can be factored by differemce of squares xy(x^2y^2) yz(y^2z^2) zx(z^2x^2) =xy(xy)(xy) yz(yz)(yz) zx(zx)(zx) The only other option would be to multiply out the brackets and try a. A= f(x;y) 2R2 jx 0gund B= f(x;y) 2R2 jx= 0gsind abgeschlossen,aberAnB= f(x;y) 2R 2 jx>0gistoffen (c) KorrektSei~xeinbeliebigerPunktinA\BDaAoffenist,gibtesein.
0 ’ ˇ 2;. Aufgabe Gegeben sei das Gebiet D= {(x,y) y. Wenigstens eine der Zahlen und von 0 verschieden ist Multiplizieren wir die ersten drei Gleichungen mit x, ybzw z, so folgt xyz= x (xy xz) = y (xyyz) = z (xz yz) und daraus wiederum 0 = (y x) (yz xz) = ( z)(y x);.
(x;y;z) 2R3 jz= x2 y2;0 z 4, H= n (x;y;z) 2R3 jz= p 1 x2 y2;1 z 5 o, K= n (x;y;z) 2R3 jz= p x2 y2;0 z 4 o a)Alle drei Flaschen haben Höhe 4 vom Boden der Flasche aus gemessen Welche fasstammeistenWasser,wennmansiebiszumRandfüllt?. B) Für welche Werte von t liegt Q(t;. Abbildungen f X !Y, wobei X und Y strukturierte Mengen sind (wie zB Vektorr aume oder metrische R aume), spielen eine zentrale Rolle in der Mathematik In der Analysis sind Abbildungen mit besonderen Eigenschaften wie etwa "stetig" oder "di erenzierbar" von vorrangigem Interesse Bei der Eigenschaft, dass eine Abbildung "stetig in einem Punkt x0" ist, geht es darum, der Idee,.
F(2) = 2, P liegt nicht auf G f f(t) = 7, t 2 = 9, t = 3, t = 3 S(0 2) Berechnen Sie die Funktionswerte f(3) und f(2 t) für die Funktion y = f(x) = (x – 2) 2 – 4 f(3. 2⋅cos x 2 y , P 2, 1, z0 Aufgabe 7 f x,y = x2 − y2 ⋅sin y, P 1, 2 Aufgabe 8 f x,y = x3 2cos y, P −2, 3 2 3A Ma 2 – Lubov Vassilevskaya Gleichung der Tangentialebene Lösung 3 Tangentialebene im Punkt P (0, 1, 1) Abb 31 Graphische Darstellung der Funktion z = f (x, y) als Fläche im 3DRaum 31 Ma 2 – Lubov Vassilevskaya f x,y = x2 y2 ⋅e−x z= −x 2 y− 1. = 1 i 2 2C mit f(z 0 h) = f(z 0) h h o(jhj) fürh!0;.
Aus f1(x;y;z) = 0 erh¨alt man x2 = 22 z ¡ y2, aus f2(x;y;z) = 0 weiter y2 = ¡z3 ¡ x, und setzt man das ein, ergibt sich x2 ¡x¡z3 ¡z ¡22 = 0 Als L¨osung der quadratischen Gleichung erh ¨alt man x = ’1(z) = ¡ 1 2 r 1 4 z3 z 22 (nur der positive Zweig der Wurzel kommt in Betracht, da f¨ur z = ¡2 ja x = 4 > 0 sein soll) und. Answer (1 of 11) x^2y^2z^2xyyzzx= 0 \implies \frac{1}{2} 2x^22y^22z^2 2xy 2xz 2yz = 0 \implies (xy)^2 (yz)^2 (zx)^2 = 0 Sum of three nonnegative terms can be zero only if each term is zero \implies x= y = z. 22 Limits and continuity The absolute value measures the distance between two complex numbers Thus, z 1 and z 2 are close when jz 1 z 2jis smallWe can then de ne the limit of a complex function f(z) as follows we write.
(1x)−2k−1 2 Zz ‡ f(k) ·0 (x) = f(k1)(x) = (−1)k (2k)!. Z 1 0 1 √ 1−x2 dx Z 1 0 Z √ 1−y2 0 1 p (1−x2)(1−y2) dxdy 12 ?. Abb L2 Graphische Darstellung der Funktion f (x, y) 2 2 2 W = 0, 2 Definitionsbereich einer Funktion f = f (x, y) Lösung 63b Ma 2 – Lubov Vassilevskaya Abb L3 Graphische Darstellung der Funktion f (x, y) Definitionsbereich einer Funktion f = f (x, y) Lösung 63c Ma 2 – Lubov Vassilevskaya f x, y = 9− x2 − y2 3, D f = { x, y ∈ ℝ2 x2 y2 9} 3 3 6 Abb L211.
Z ∞ −∞ f(x,y)dydx = Z 1 0 Z 2 0 (cx2 xy 3)dydx = 2c 3 1 3, so c = 1 (b) Draw a picture of the support set (a 1by2 rectangle), and intersect it with the set {(x,y) x y ≥ 1}, which is the region above the line y = 1 − x See figure above, right To compute the probability, we double integrate the joint density over this subset of the support set P(X Y ≥ 1) = Z 1 0 Z 2. A= f(x;y2R2 jjfj= 1g= f(x;y) 2R2 jx 0;. 42 Conditional Distributions and Independence Definition 421 Let (X,Y) be a discrete bivariate random vector with joint pmf f(x,y) andmarginal pmfs fX(x) and fY (y)For any x such that P(X = x) = fX(x) > 0, the conditional pmf of Y given that X = x is the function of y denoted by f(yx) and defined by f(yx) = P(Y = yX = x) = f(x,y) fX(x) For any y such that P(Y = y) = fY (y) > 0, the.
Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. Welche Form haben die Höhenlinien der Funktion f(x,y) = x 2 y 2 4> Kreis wegen x 2 y 2 Da eventuell eine ähnliche Frage dran kommt, möchte ich nun gerne die Gleichungen für andere Formen wissen, wenn sie den existieren Eine Glocke wäre eventuell auch noch interessant. When x = 0 this becomes f = y2, a parabola in the yz plane;.
X 2 y2 = 4 ;. 2変数関数z=f(x,y)=ax 2 by 2 ( a>b>0)のグラフ すなわち、z=ax 2 by 2 を満たす(x,y,z) を全て集めた集合 {(x,y,z) z=ax 2 by 2}は、 以下のようになる。 このグラフを、楕円放物面と呼ぶ。 例:2変数関数z=5x 2 y 2 のグラフ. Dafuer aber ihre maximalen relativen Abweichungen x = 2, y = 1, z = 2 x=2, y=1, z=2 x= 2,y = 1,z = 2 Vielleicht machst Du Dir mal klar, worum es ueberhaupt geht Du sollst eine Abschaetzung von ,z)−f (x,y,z)∣ unter den gegebenen Voraussetzungen machen Dabei unterscheidet sich.
Erreichbare Punktzahl Prof Dr Moritz Kaßmann Fakultät für Mathematik Sommersemester 15 Universität Bielefeld Übungsaufgaben zu Analysis 2. Y′(x)=1 2 x−y 4, f¨ur x−y 4> 0, y(0)=1 Substitution z =x−y 4liefert z ′ = 1−y′ =1−1− 2 z dz dx =− 2 z eine separierbare Dgl 5 dz dx =− 2 z =⇒ z ·dz = −2·dx Z zdz = − Z 2dx =⇒ z2 2 = −2x˜c =⇒ z(x)=± √ c−4x Die L¨osung ist nat urlich nur f¨ ¨ur c − 4x > 0 definiert Rucktrans¨ formation ergibt die allgemeine L¨osung y(x)=x4∓ √ c. Z = 0 Point (0;0) z = 1 Circle x 2 y = 1 z = 2 Circle x 2 y = 2 z = 3 Circle x2 y2 = 3 (b) Sketch all the traces that you found in part (a) on the same coordinate axes (c) Compute equations for the traces in the y = 0, y = 1, y = 2, and y = 3 planes Plane Trace y = 0 Parabola z = x2 y = 1 Parabola z = x2 1 y = 2 Parabola z = x2 4 y = 3 Parabola z = x2 9 (d) Sketch all the traces.
Let {eq}f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 {/eq} and let S be the level surface defined by f(x,y,z) = 4 (a) Find an equation for the plane tangent to S at {eq}P_{0}(1,1,2). Let f(x,y)=1/(x^2y^2) for (x,y)\neq 0 Determine whether f is integrable over U0 and over \mathbb{R}^2\bar{U};. F 2 (x)) = f 1 (x) (y 1 – y 0), dh y ist Lösung von (**) b) Zu zeigen Ist y eine beliebige Lösung von (**), so ist y 1 = y y 0 eine Lösung von (*) In der Tat y 1‘ = y‘ y 0‘ = f 1 (x) y f 1 (x) y 0 f 2 (x) = f 1 (x) (y y 0) f 2 (x) Beispiel 5 y‘ = 4y 6x 2 (*) Die homogene DGL y‘ = 4y hat Lösungsgesamtheit.
F¨ur ( x,y,z) ∈ A gilt 0 6 z 6 1, und die zweite A definierende Ungleichung liefert die Bedingung r 2 6 (1−z) 2 Die Menge A ist also charakterisiert durch. #grad f(x,y,z) = (6xy)hati(3x^23y^2z^2)hatj(2y^3z)hatk# Evaluate at the point #(1,2,1)# #grad f(1,2,1) = (6(1)(2))hati(3(1)^23(2)^2(1)^2)hatj(2(2)^3(1))hatk# Simplify #grad f(1,2,1) = 12hati9hatj16hatk# Answer link Related questions How do I determine the molecular shape of a molecule?. Aufgabe 2 (Implizite Funktionen) f(x;y;z) = xex ysiny zlnz= 0 ist bei (1;ˇ;e) nach allen Variablen au osbar F ur y= h(x;z), bzw z= g(x;y) berechne man h0(1;e),bzw g0(1;ˇ) L osungsvorschlag Eien formelm aˇige Au osung nach einer Variablen zB yist uns nicht m oglich f x= (x 1)ex)f x(1;ˇ;e) = 2e6= 0 f y= siny ycosy)f y(1;ˇ;e) = ˇ6= 0 f z= (1 lnz) )f z(1;ˇ;e) = 2 6= 0)gradf(1.
When y = 0 we get the “same” parabola f = x2 in the xz plane Now consider the line y = kx If we simply replace y by kx we get f(x,y) = (1 k2)x2 which is a parabola, but it does not really “represent” the crosssection along y = kx, because the crosssection has the line y = kx where the horizontal axis should be In 14. Divide y, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac{y}{2} Then add the square of \frac{y}{2} to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of the equation a perfect square. Begruendung Loesung Fuer (x;y) 6= 0 ist fals komposition stetiger Funktionen wieder stetig Fuer (0;0) waehle man zB x n= 1 n, y n= 1 n2 und zeige so (7) f(x n;y n) = 6 n2 1 n6 2 1 n 4 6 1 n = 6 1 2 6 !n!1 3 4 6= 0 Da wir Nullfolgen.
7) auf dem Graphen von f?. (1x)−1/2 = f0(x) k → k 1 Wir vermuten nun, dass die Darstellung fur ¨ k gilt, und wollen zeigen, dass sie dann auch fur¨ k1 gilt, also die Ableitung von f(k) tats¨achlich der Formel f ¨ur f(k1) entspricht Geg f(k)(x) = −(−1)k (2k −2)!. Xf(x;y) @ xf(0;0)j 2 x y (4) Gegeben ist f R2!R mit (6) f(x;y) = (6x 2y3 2x46y2 (x;y) 6= (0 ;0) 0 (x;y) = (0;0) L osung zu Kapitel 5 und 6 3 Ist fstetig?.
3) in der xzEbene (y = 0) , quadratische Parabel z = 4x2 in der yzEbene 0)(x = , quadratische Parabel z = y2 Niveaulinien z = c Ellipsen 1 2 4 2 = c x y c Die Funktion beschreibt ein elliptisches Paraboloid 4) a) a t t a xy axy t axy t Substituti on x y = = = → → sin lim sin( ) lim ( , ) (0,0) 0 b) lim 0 0 2 sin lim lim 0 0 0 1 = = − = y→ x→ x y y→ x y x g, 2 2 lim 2. Lösung Wir berechnen jeweils zuerst das Volumen zwischen der Flaschenoberfläche und der xyEbene Beachte, dass das das Volumen. 3 For each solution ( x,y,z,,µ), find f(x,y,z) and compare the values you get The largest value corresponds to maximums, the smallest value corresponds to minimums 5 Examples Example 51 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraints xy z =0and x2 2z2 =1 f(x,y,z.
So in the case when x,y,z not equal to 0 we get 1 If we consider the case when one of the terms can be 0, then the answer would be 3 So the answer to this question wi Continue Reading Consider the given equation Multiply both the numerator and denominator of the first term by x, second term by y, third term by z Doing that we get Now consider x 2 = y z Adding x on both. Jeder direkt proportionale Zusammenhang zwischen zwei Größen x und y kann durch eine spezielle lineare Funktion mit der Gleichung y = f ( x ) = m x ( m x ≠ 0 ) beschrieben werdenDefinitonsbereich und Wertevorrat (Wertebereich) von f ist die Menge der reellen Zahlen ℝ Der Graph von f ist eine Gerade, die durch den Koordinatenursprung O verläuft. F’y = h(x,y) (2 Partielle Abl) einer Funktion immer identisch sind F’xy = g’y = h’x = F’yx Beispiel 1532, S8 Zum Bestimmen von F(x,y) G(x,y) (h(x,y)∫ y G'(x,y))dy = c So kommt man darauf x yy y I F(x,y) = F'c(y)=g(x,y)dxc(y)= G(x,y)c(y) II diese Funktion nach y ableiten F'=G'(x,y)c'(y)=h(x,y) III umgeformt ergibt sich c'(y) = h(x,y) G'(,) IV Integrieren ergibt.
0 = xyxzyz 3 2 (xyz) = 8 3 10 ;. Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge. 2 cs309 G W Cox – Spring 10 The University Of Alabama in Hunt sville Computer Science The Duality Principle “A Boolean expression that is always true is still true if.
162 Line Integrals We have so far integrated "over'' intervals, areas, and volumes with single, double, and triple integrals We now investigate integration over or "along'' a curve—"line integrals'' are really "curve integrals'' As with other integrals, a geometric example may be easiest to understand Consider the function f = x y and. @f @x (z 0)h 1 @f @y (z 0)h 2 = 1 2 @f @x (z 0) i @f @y (z 0) (h 1 ih 2) 1 2 @f @x (z 0) i @f @y (z 0) (h 1 ih 2) = @f @z (z 0)h @f @z (z 0)h gilt,ergibtsichschließlich,wiegewünscht, f(z 0 h) = f(z 0) @f @z (z 0)h @f @z (z 0)h o(jhj) fürh!0 “(”Existierenumgekehrtfürz 0 2 Zahlen = 1 i 2;. Gegeben ist die Funktion y = f(x) = x 2 – 2 a) Prüfen Sie ob P(2 18) auf dem Graphen liegt!.
(1x)−2k1 2 Dazu bestimmen wir die. Z= 0 und z= p x y2 begrenzt wird und fur den x;y 0 gilt L osung Der K orper Bist das Prisma uber dem Viertelkreis mit dem Radius 2 im 1 Quadran ten, bez uglich zbegrenzt durch 0 z p x2 y2 Als B0in Zylinderkoordinaten x= rcos’;y= rsin’;z= z l aˇt er sich beschreiben als Normalbereich 0 r 2 ;. Xycoordinates x = x0 su1,y = y0 su2, and the value of z = f(x,y) at the point s on the saxis is F(s) = f(x0 su1,y0 su2) (1) We call z = F(s) the cross section through (x0,y0) of z = f(x,y) in the direction of u ˆ x = x0 su1 y = y0 su2 Tangent line of slope F0(0) = Duf(x0,y0) FIGURE 1 FIGURE 2 327 p 328 (3/23/08) Section 145, Directional derivatives and gradient vectors If (x0.
What is the lewis structure for co2?. 0 = (z x) (zy xy) = ( y)(z x);.
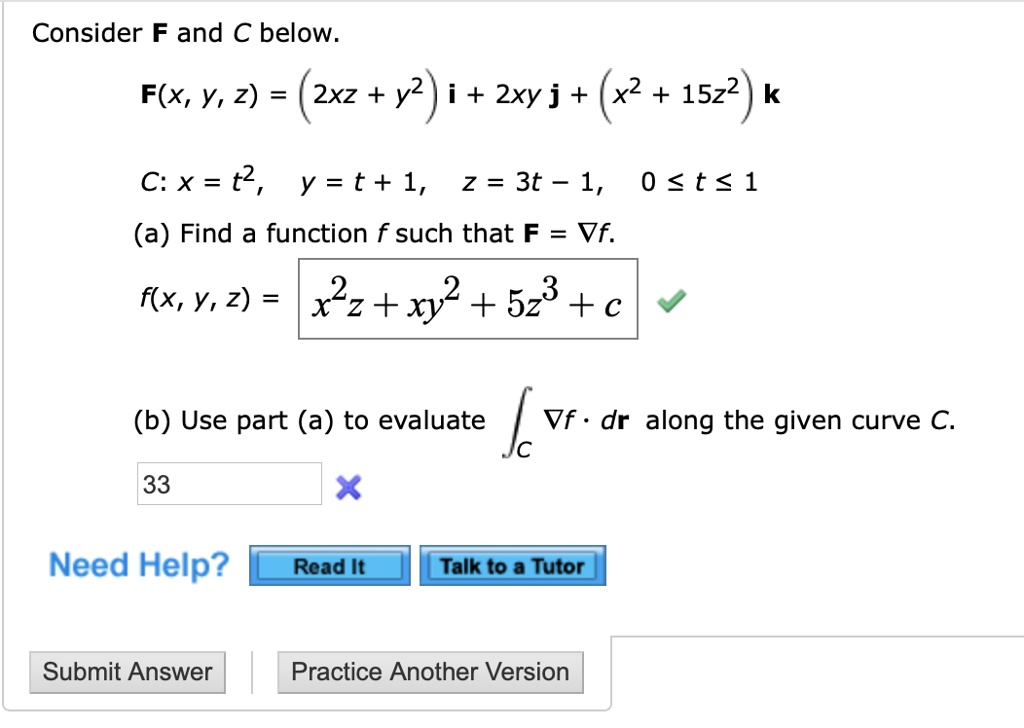
Solved Consider F And C Below F X Y 2 2xz Y2 I Zxy J X2 1522 K C X T2 Y T 1 Z 3t 1 0
Math Ntu Edu Tw
Supermath Info
Fx+y+z X2+y2+z20 のギャラリー
Math Drexel Edu
People Math Harvard Edu
Solved Solve Yz 2 X 2 Yz Dx Zx 2 Y 2 Xz Dy Xy 2 Z 2 Xy Dz 0 Subject Differential Equation And Integral Equation Course Hero
Www2 Math Binghamton Edu
Surface Area
Triple Integrals In Cylindrical And Spherical Coordinates
Math Hawaii Edu
Solved Form Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function F Ax By Cz X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Also Find Order And Degree Of The Course Hero
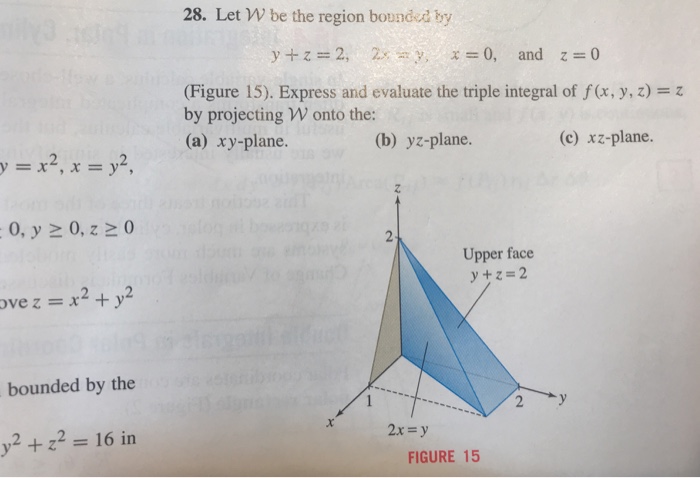
Solved 28 Let W Be The Region Bounded By Y Z 2 2x Y X 0 Chegg Com

Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu

If X 2 Y 2 Z 2 2 X Y Z 3 Find The Value Of 2x 3y 4z Youtube
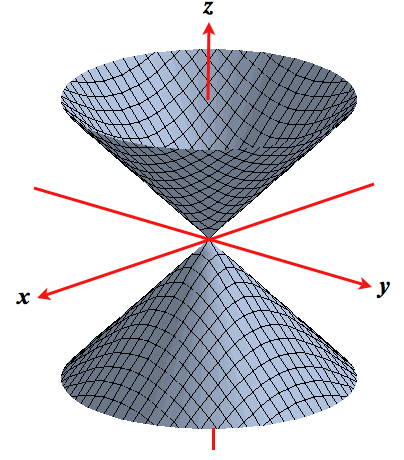
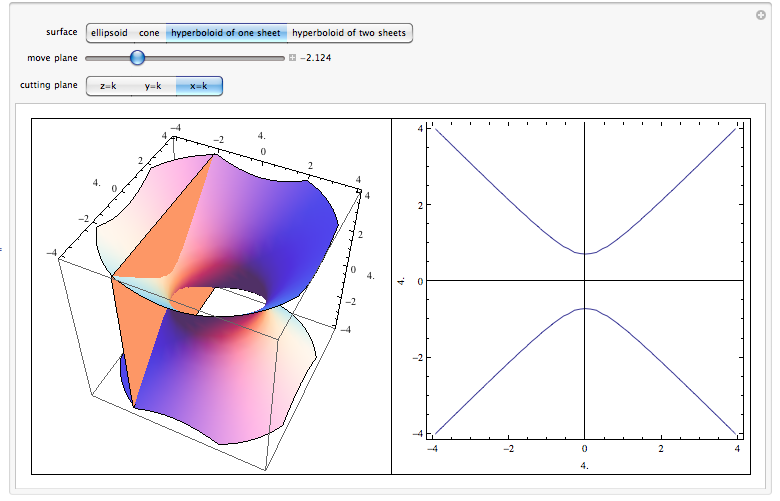
Level Surfaces
Using Properties Of Determinants Prove That X 2 1 Xy Xz Xy Y 2 1 Yz Xz Yz Z 2 1 1 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu

Intersection Of X Y Z 0 And X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
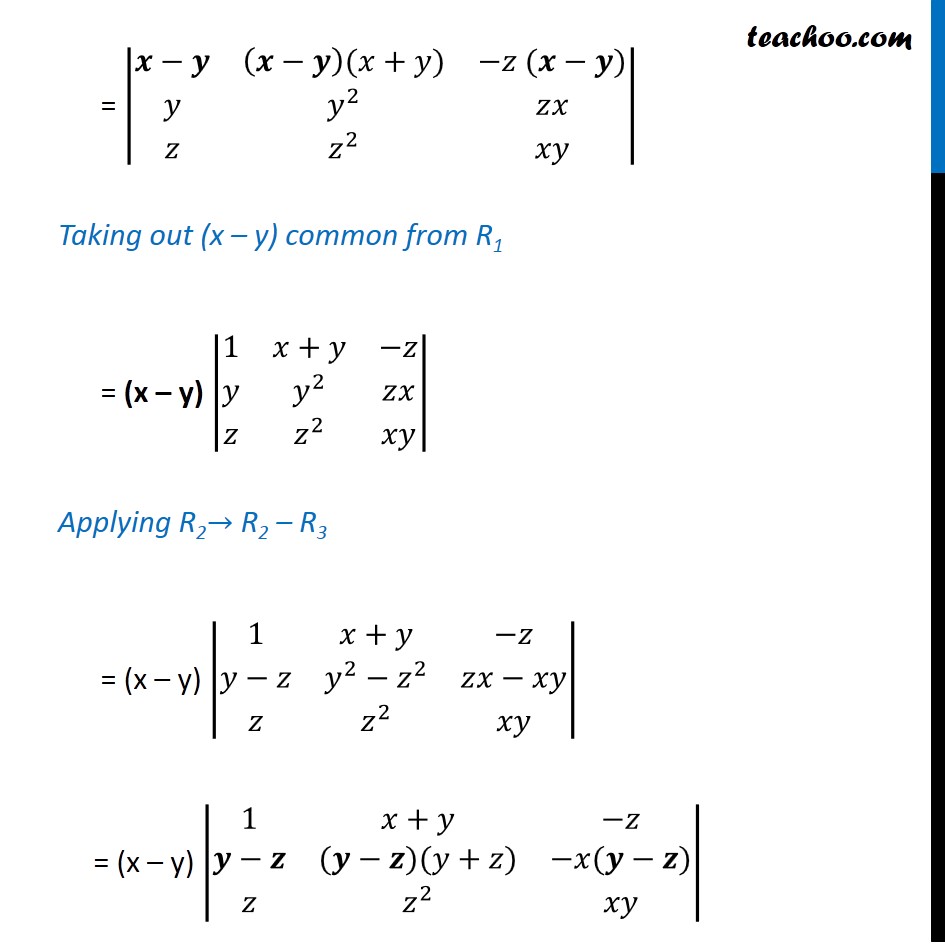
Ex 4 2 9 Show That X X2 Yz Y Y2 Zx Z Z2 Xy X Y Y Z
Solved 1 Consider F X Y Z Xy Xz Subject To The Constraint X Y 2 32 Find The Absolute Minimum And Absolute Maximum Value Of F 2 Course Hero
Web Viu Ca

Z 0 0 2 1 1 2 2 And 1 3 3 Find The Volume Of The Solid That Is Homeworklib

Solved C Find Wxy And Wyx W In 2r 3y W 9 Ry Ry 7 Differentiating Implicitly Find The Value Of Az Ar At The Point 1 D If The Equation 7 L7 0 8
Curl Of A Vector Field Web Formulas

X Y Z Belong To R X Y Z 4 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 6 Find Maximum Possible Value Of Z Mathematics Topperlearning Com 2j1z7sww
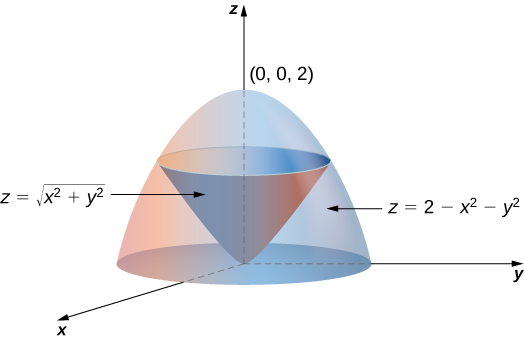
Triple Integrals In Cylindrical And Spherical Coordinates Calculus Volume 3

Using Nabla With Partial Derivatives And The Laplace Operation Partial X 2 Partial Y 2 Partial Z 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
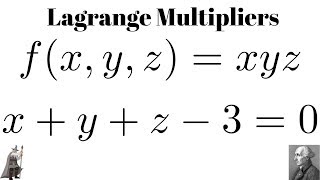
Lagrange Multipliers Maximum Of F X Y Z Xyz Subject To X Y Z 3 0 Youtube
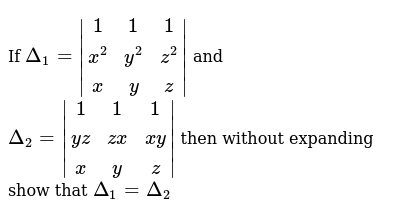
If Delta 1 1 1 1 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 X Y Z And Delta 2 1 1 1 Yz Zx Xy X Y Z Then Without Expanding Show That Delta 1 Delta 2

Math 21a Midterm I Review
What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora

Solved Tutorial Exercise Find The Extreme Values Of F Chegg Com

Find Max And Min With Lagrange Multipliers F X Y Z Xyz 2 G X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Ex 4 2 9 Show That X X2 Yz Y Y2 Zx Z Z2 Xy X Y Y Z

Integrate F X Y Z xz Over The Region In The First Octant X Y Z 0 Above The Parabolic Cylinder Brainly Com
Lagrange Method Formula
Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers

X 2 Y 2 1 0 Chaimmy
Cluster28 Files Instructure Com

Dltn0biiupdqmm

Evaluatef X Y Z Ds F X Y Z X2 Y2 Z2 Homeworklib
Solved Let F X Y Z Xyz 2 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 A If X Y Z Chegg Com

16 2 Vector Fields And Line Integrals Work Circulation And Flux
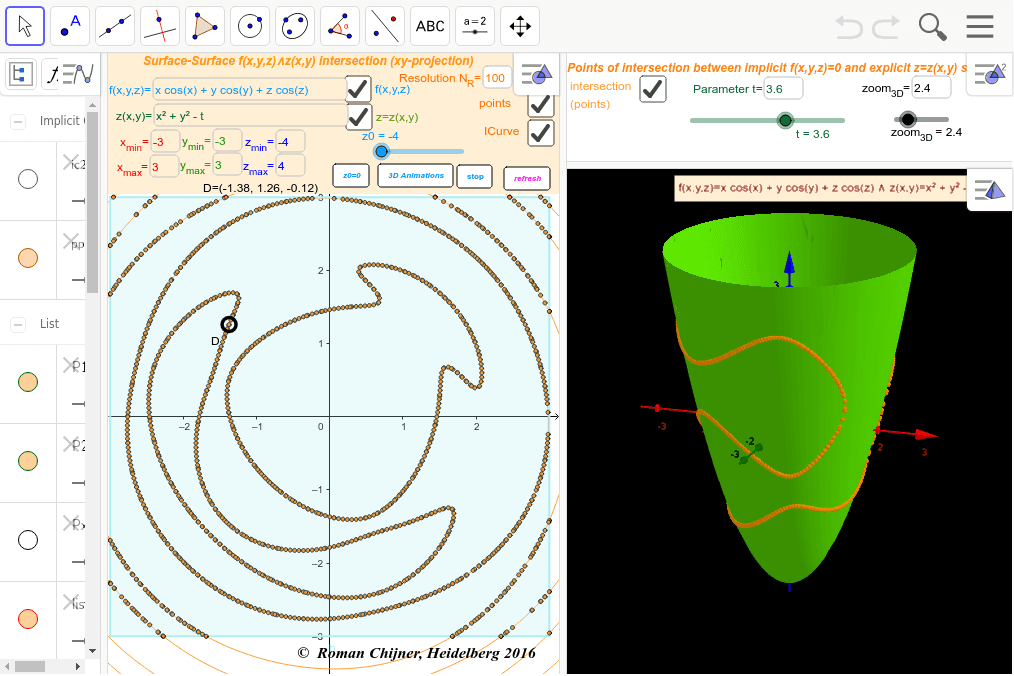
Points Of Intersection Between Implicit F X Y Z 0 And Explicit Z Z X Y Surfaces Geogebra
1

Solved Find The Average Value Of F X Y Z Xyz Over X2 Chegg Com
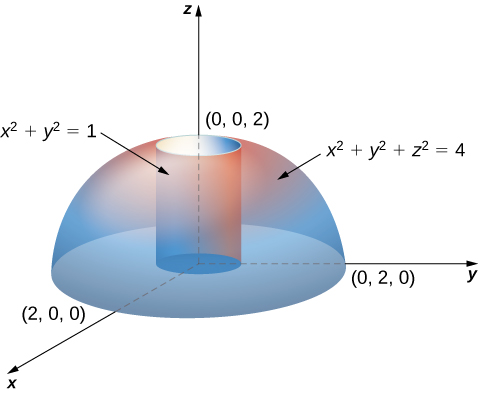
Triple Integrals In Cylindrical And Spherical Coordinates Calculus Volume 3

Matlab Tutorial
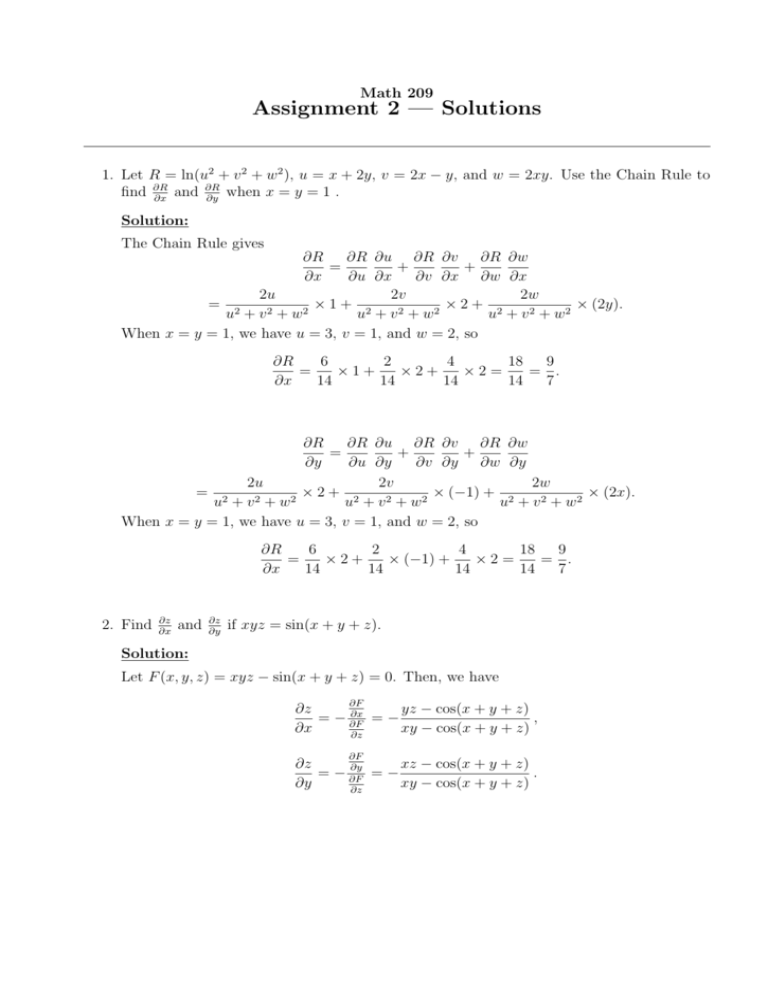
Assignment 2 Solutions
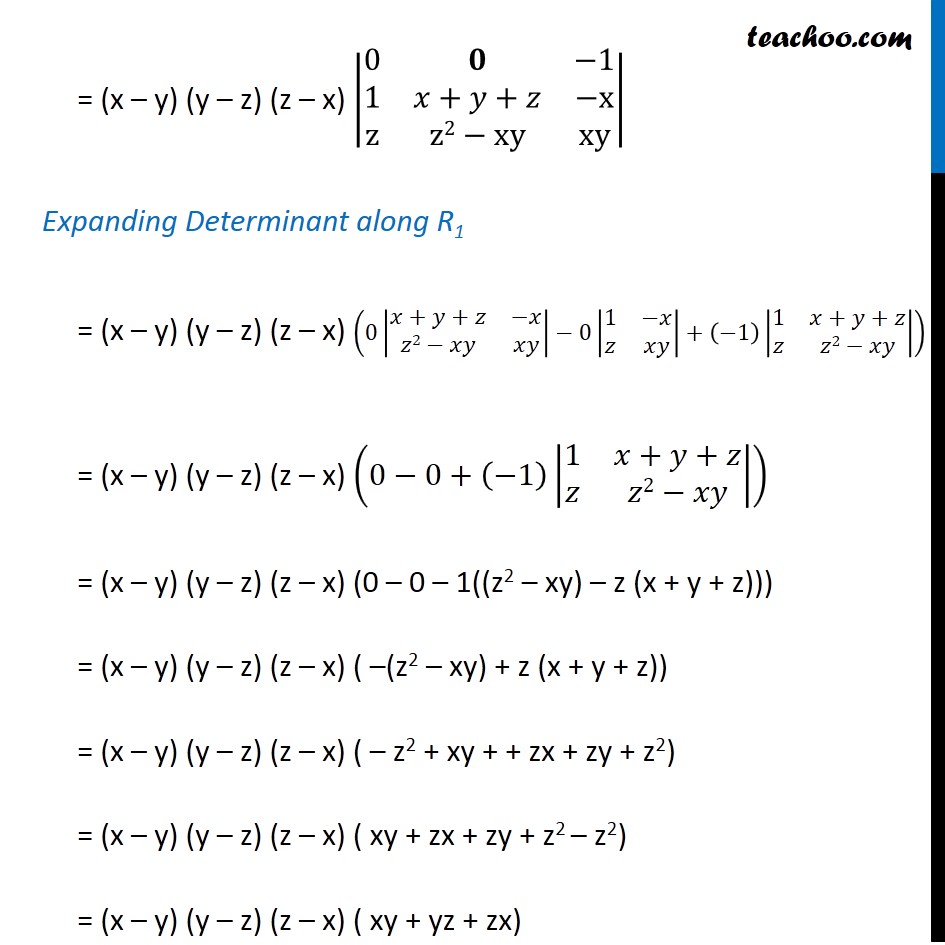
Ex 4 2 9 Show That X X2 Yz Y Y2 Zx Z Z2 Xy X Y Y Z

Solved Find The Extreme Value Of The Function Subject To The Chegg Com
How To Solve Using The Gauss Elimination Method Y Z 2 2x 3z 5 X Y Z 3 Quora
Level Surfaces

Quadratic Function Wikipedia

Solve The Following Problems By Using Lagrange Multipliers A Find The Maximum And Minimum Values Of F X Y Z X 2 Homeworklib
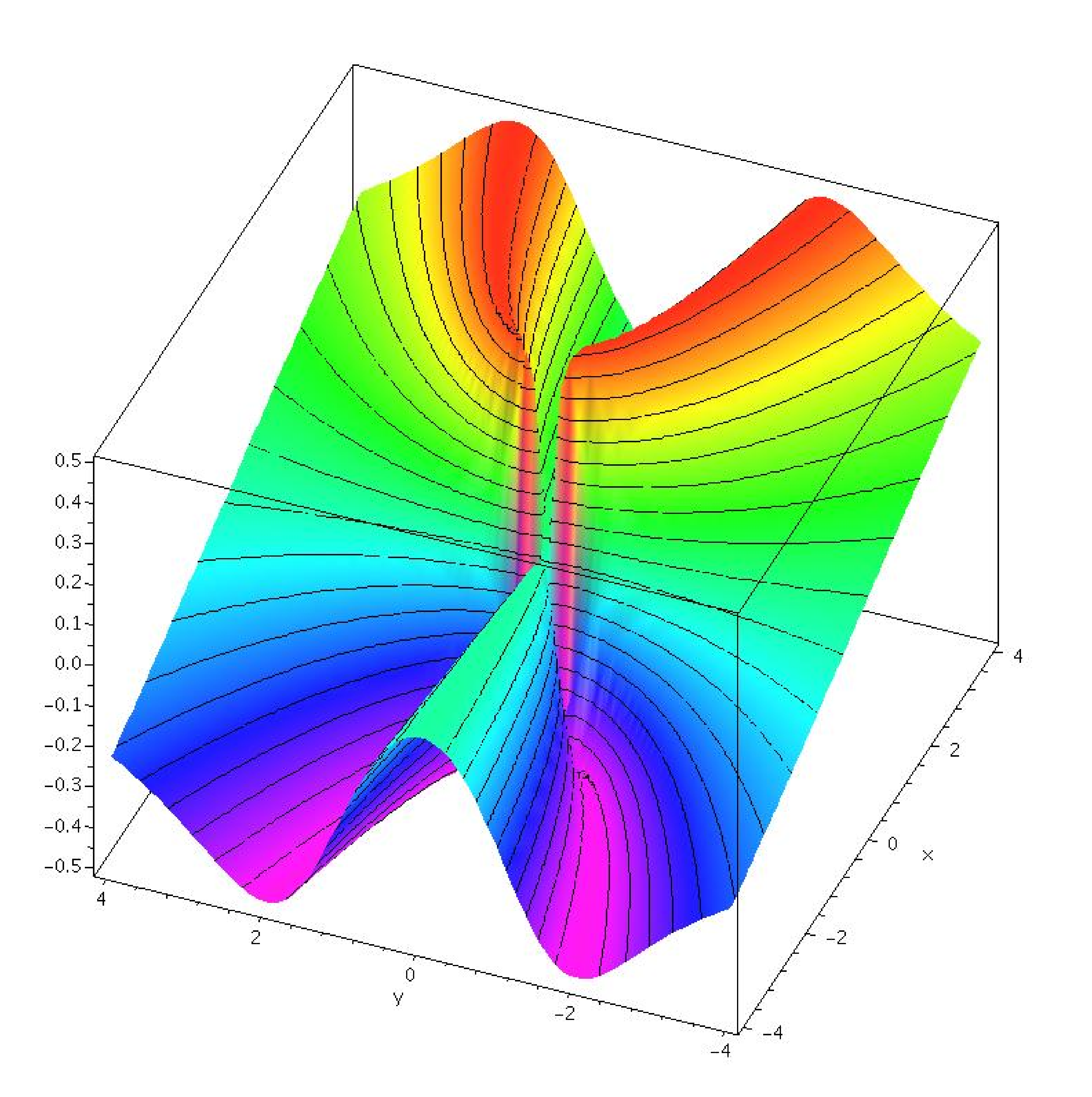
14 2 Limits And Continuity

Answered 9 M A Y Z Xyz Xyz P 2 1 1 U Bartleby
Math Ntu Edu Tw
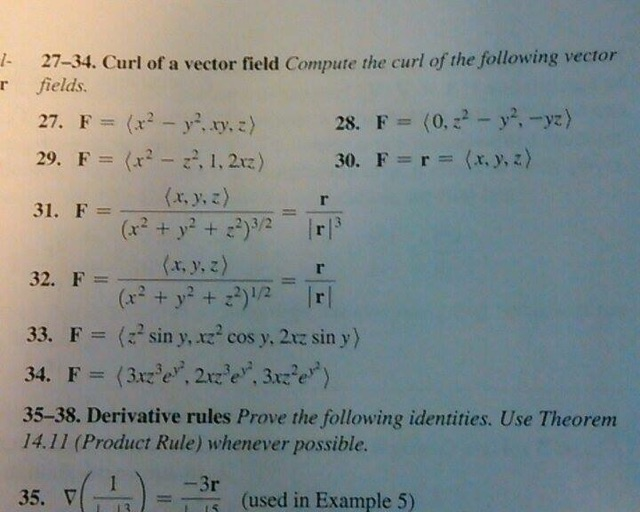
Solved Curl Of A Vector Field Compute The Curl Of The Chegg Com

1 9 3 We Would Like To Make The Length 6 The Only Vectors In The Same Direction As V Are Those Pdf Free Download
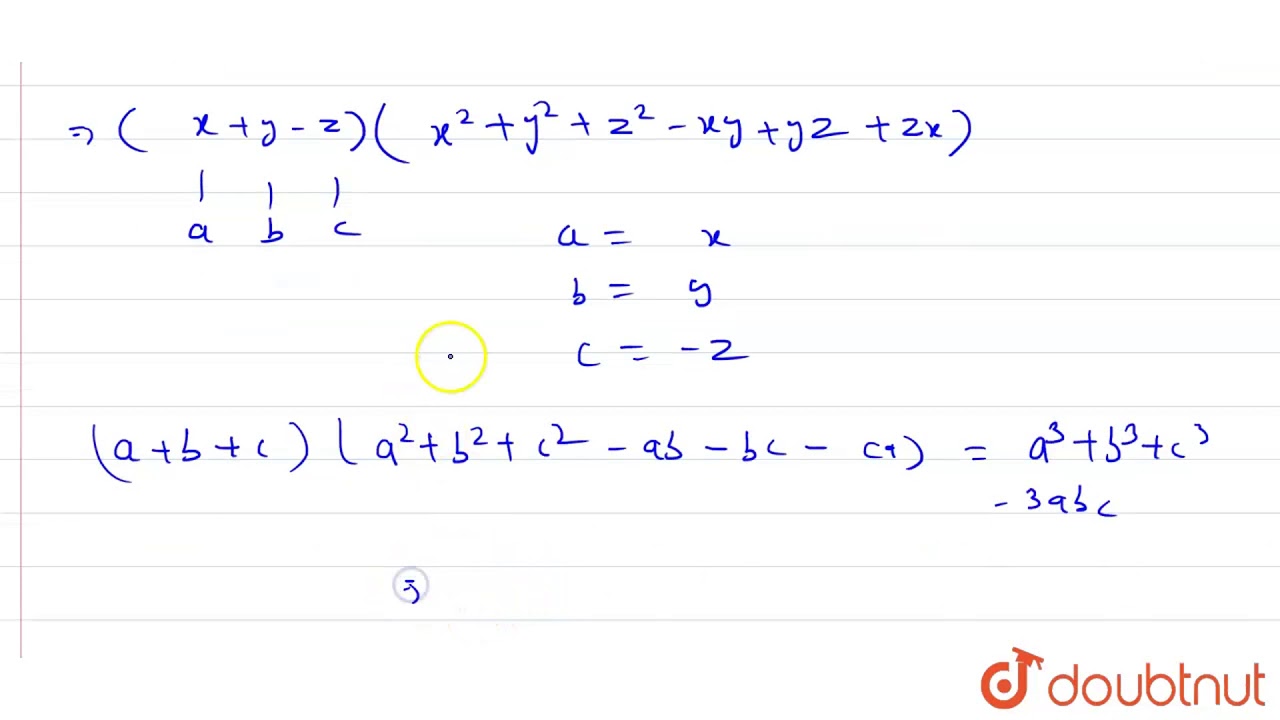
Find The Product X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Xy Yz Zx Youtube
Mathweb Math Ncu Edu Tw
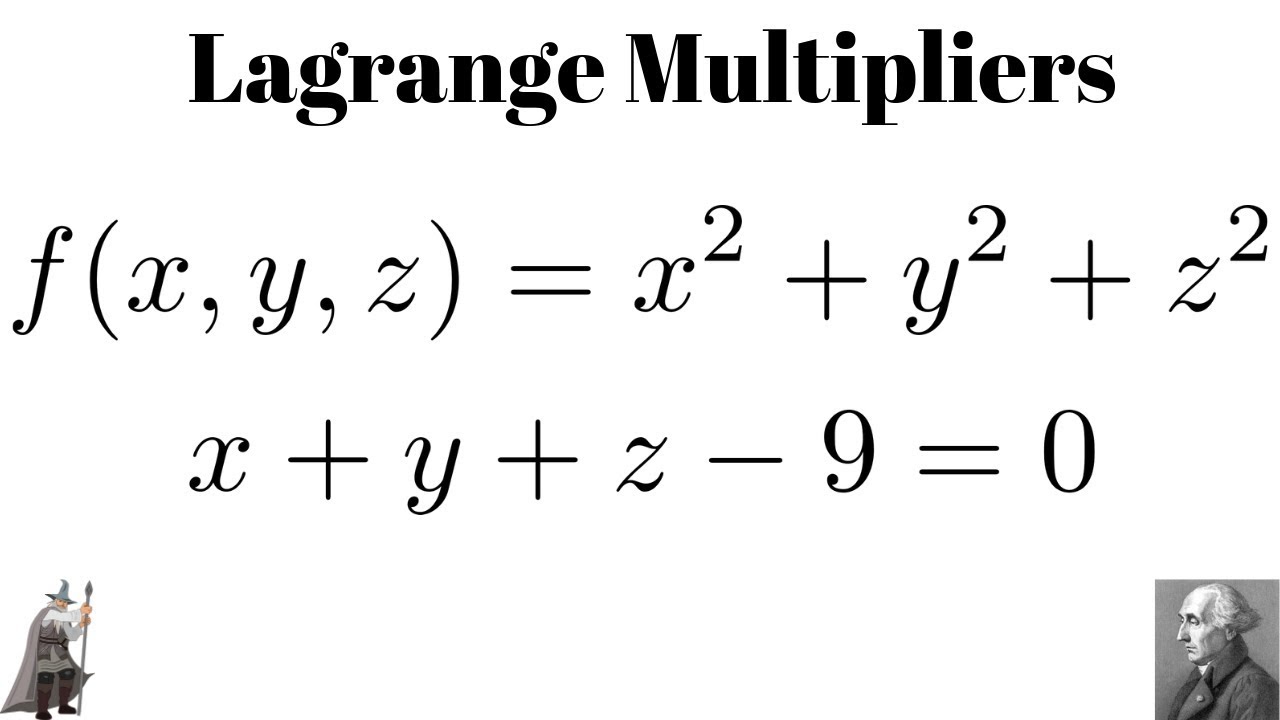
Lagrange Multipliers Minimum Of F X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Subject To X Y Z 9 0 Youtube

Functions Of Several Variables 13 Copyright C Cengage Learning All Rights Reserved Ppt Download
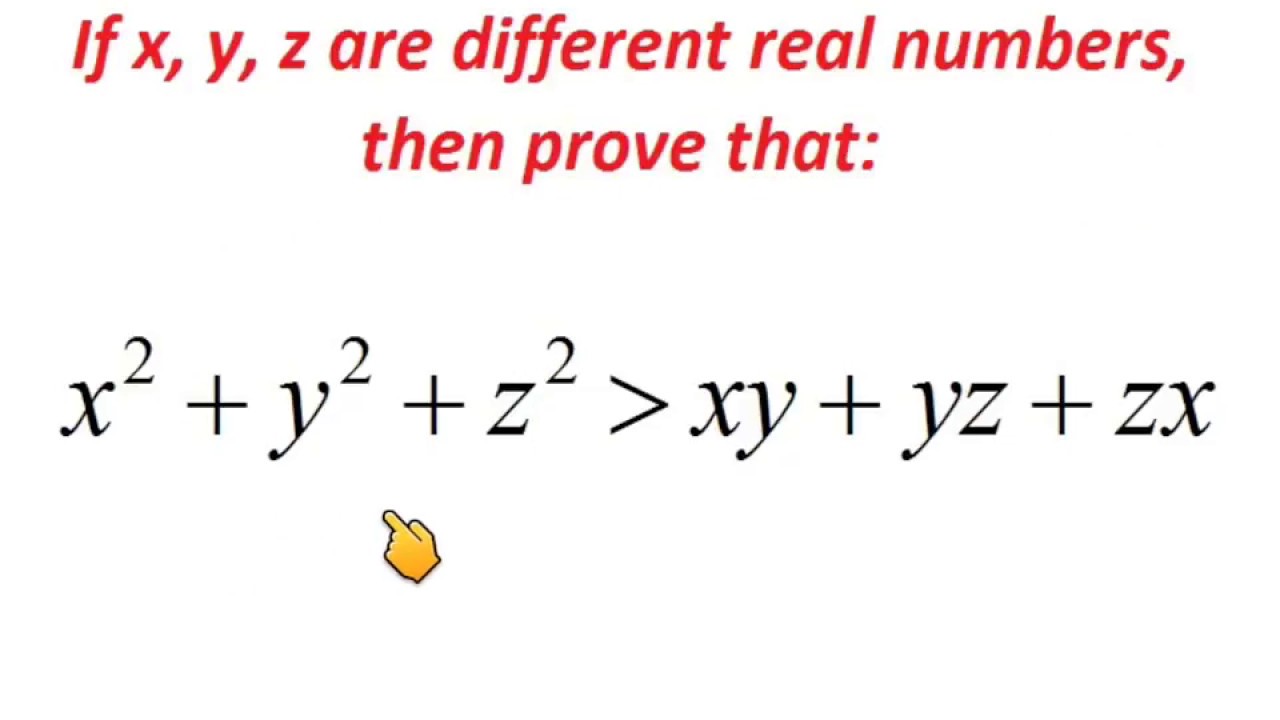
X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Greater Than Xy Yz Xz Proof Important For Iit Jee Nda Scra Sat Competitive Exams Youtube

Solved In Exercises 5 16 Use The Divergence Theorem To Chegg Com

Matlab Tutorial

32 Approximation Of Eg6 Shrek F X Y Z X 4 Y 4 Z 4 4 X 2 Download Scientific Diagram

2 3 Tangent Plane To A Surface Mathematics Libretexts
270 F X Y Z 1 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 B X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 9 Y 0 Z 0 Bartleby
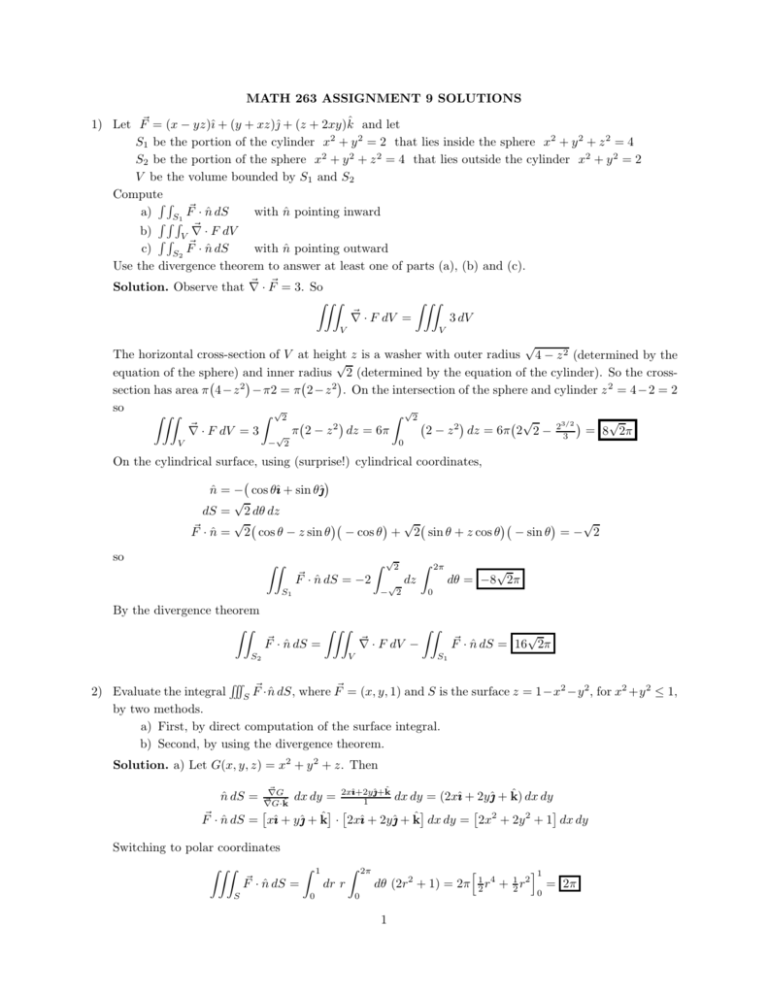
Math 263 Assignment 9 Solutions 1 Let F X Yz I Y Xz
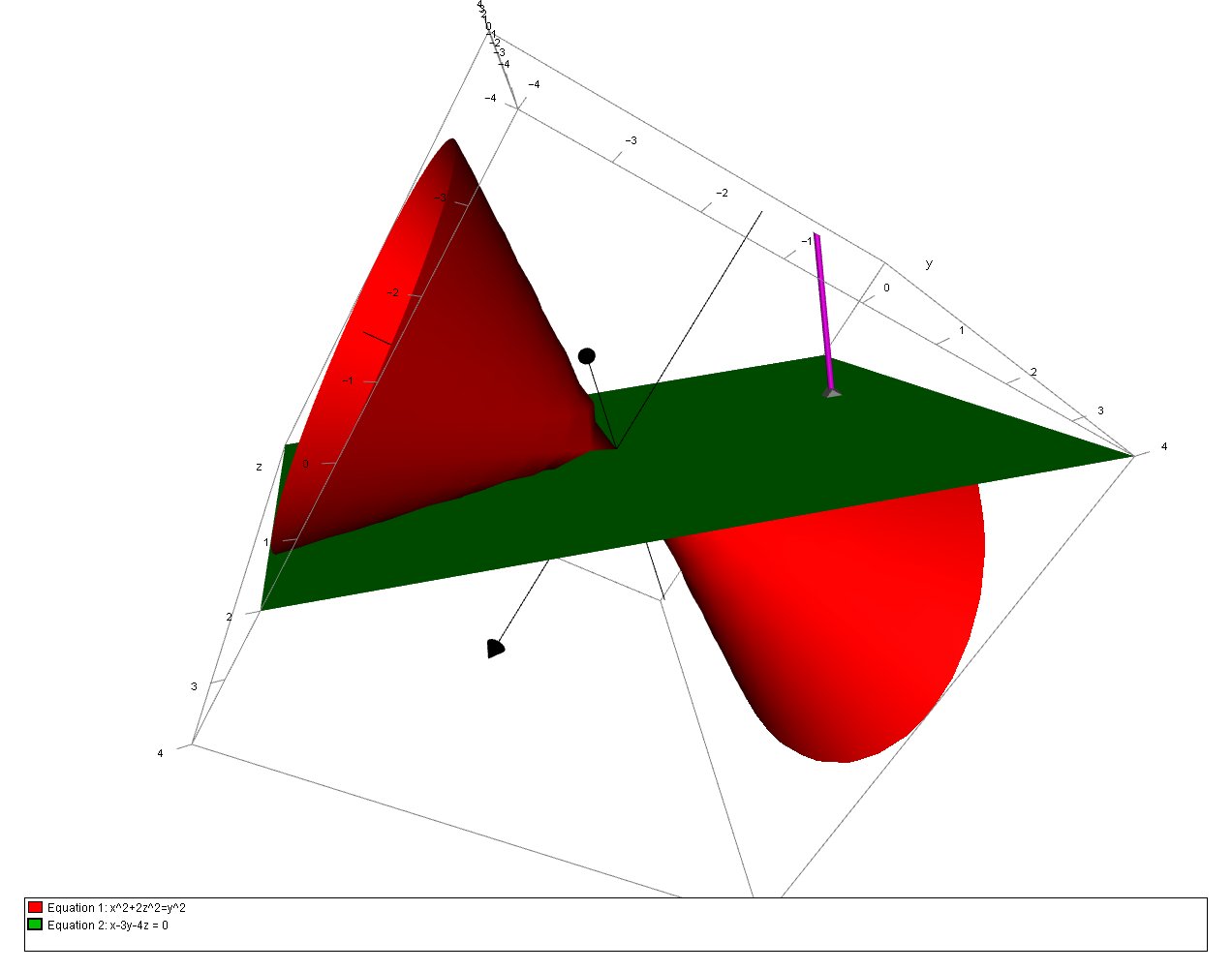
How Do You Find The Equations For The Tangent Plane To The Surface X 2 2z 2 Y 2 Through 1 3 2 Socratic
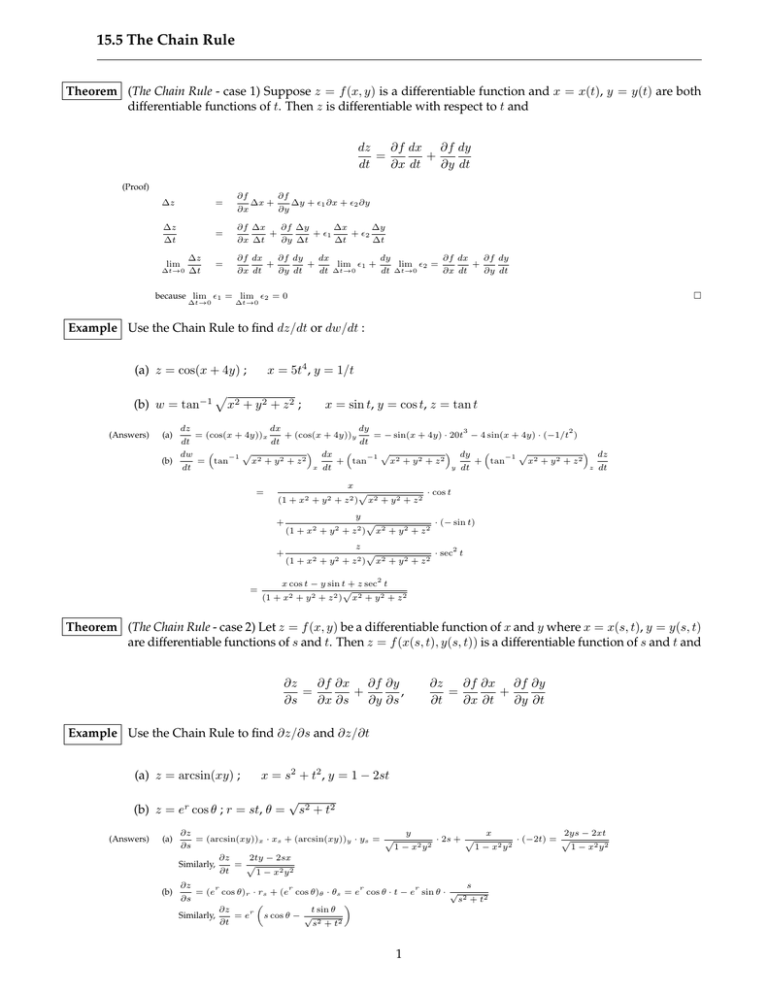
15 5 The Chain Rule
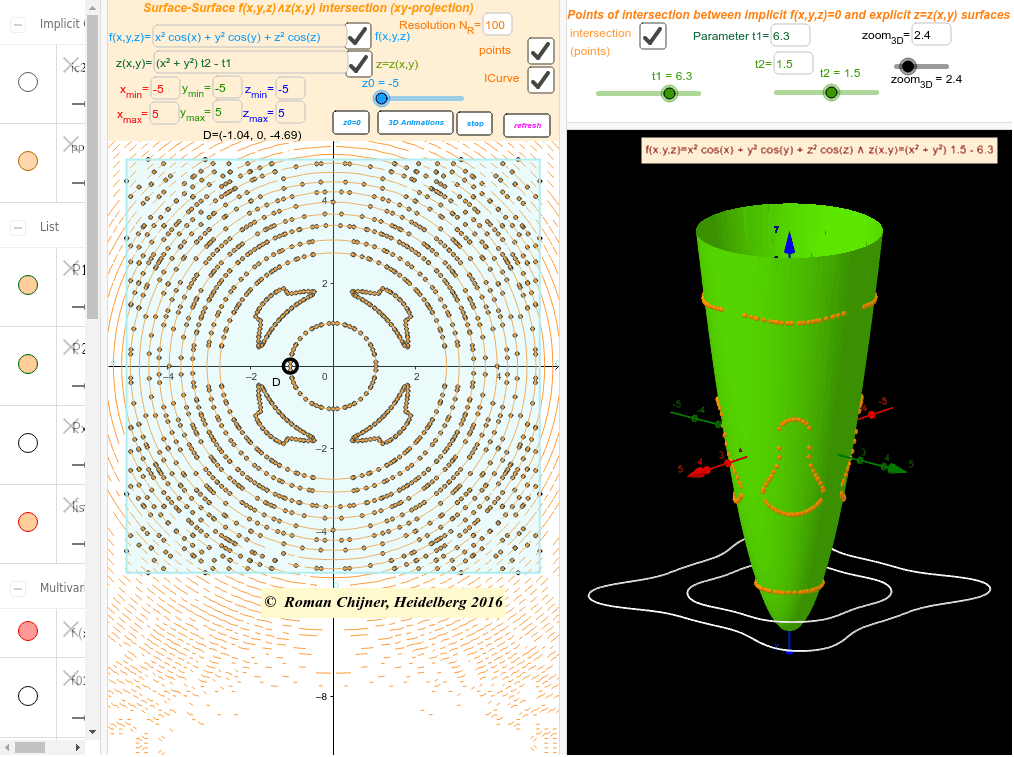
Points Of Intersection Between Implicit F X Y Z 0 And Explicit Z Z X Y Surfaces Geogebra

Lagrange Multipliers By Rohit Venkat Ppt Video Online Download
Users Math Msu Edu

Solve The Equation X 2p 2 Y 2q 2 Z 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection
Using Properties Of Determinants Prove That Y X 2 Xy Zx Xy X Z 2 Yz Xz Yz X Y 2 2xyz X Y Z 3 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Solving Lagrange Multiplier Equations Using Mavdisk
Ocw Mit Edu
Ualberta Ca

Examples Wednesday Feb 19

Given The Boolean Function Fx Y Z 0 2 4 5 6 Reduce It Using Karnaughs Knowledgeboat

Solved Find The Extreme Values Of F X Y Z X 2 Y Z 1 On The Intersection Of The Plane Z 1 With The Sphere X 2 Y 2 Z 2 10
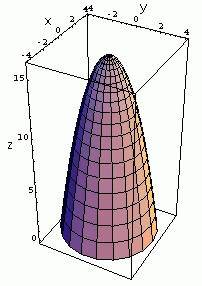
Surface Area
Math Ualberta Ca

Thomas Calculus 11e 8 1262 Pages 351 381 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
Solved Form Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function F Ax By Cz X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Also Find Order And Degree Of The Course Hero

Math 217 Assignment 3 Selected Solutions
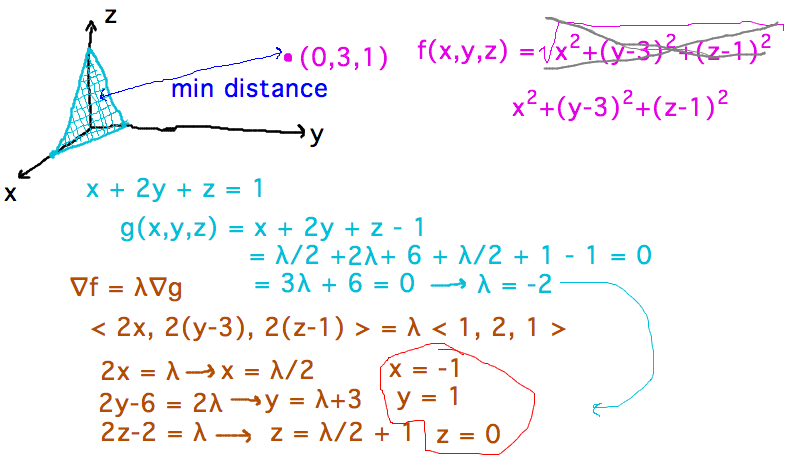
Geneseo Math 223 03 Lagrange Multipliers

Pdf Partial Derivatives Exercise Set 14 1 Luiz De Oliveira Academia Edu
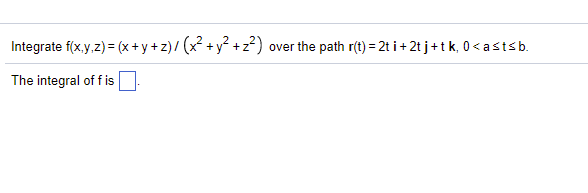
Solved Integrate F X Yz X Y Z X2 Y2 Z2 Over Chegg Com
How To Determine The Extreme Values Of The Function Math F X Y Z X 2y 2z Math For Condition Math X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Math Quora

Ad Eng Math 6 8 15 Pages 1 244 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
Math Odu Edu
What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora

Solved Example 5 Evaluate Jjs When F X Y 2 Yi Xj Zk And Is The Boundary Of The Solid Region Enclosed By The Paraboloid 9 X2 Y2 And The Plane

Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube

Solved Use The Divergence Theorem To Find The Outward Flux Of The Field F 21 Y K 2zk Across The Boundary Of The Solid E A Y 2 Er 22 Y 2 0
Lagrange Multipliers Minimize F X Y X 2 Y 2 Subject To X 2y 5 0 Topic Play
Users Math Msu Edu

F 3 2 Y 2 2 Z Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Xz 2 Xyz 2 0 729 729 Download Scientific Diagram




