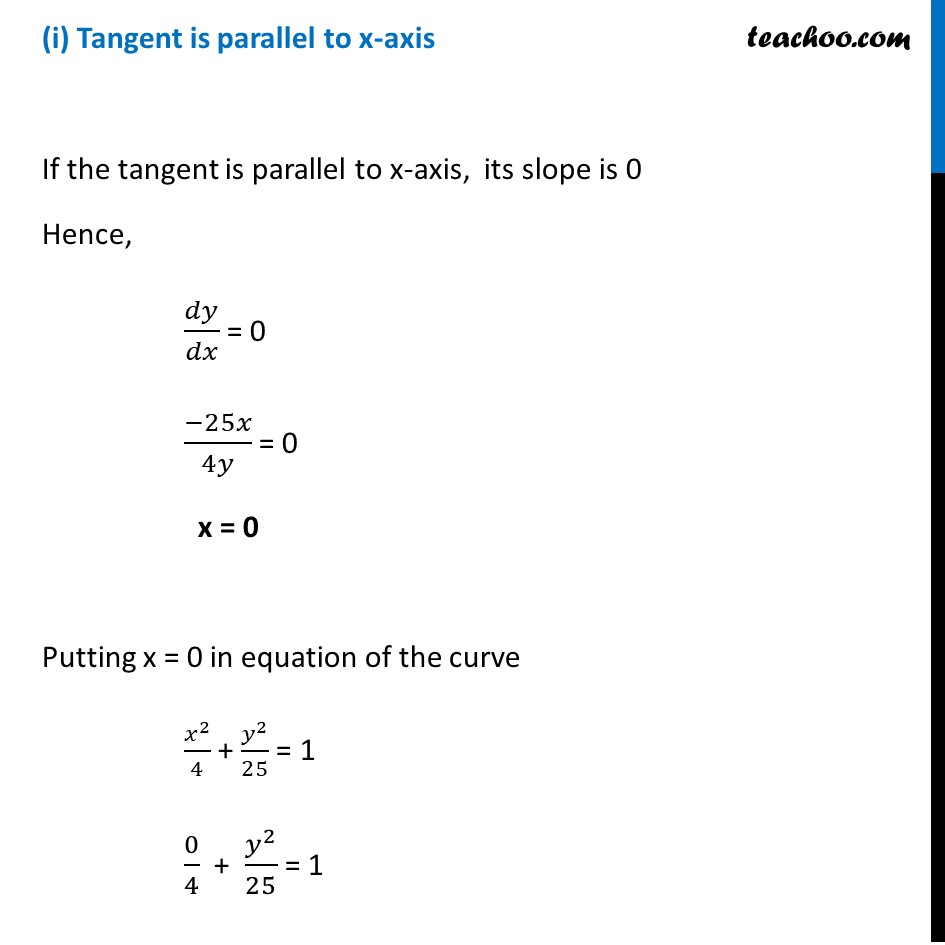
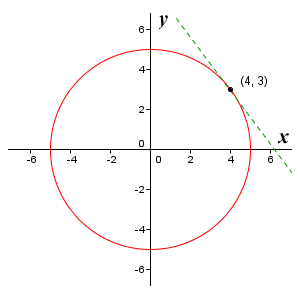
X2+y225 Second Derivative At 4 3
Using the X and Y values below, write a MATLAB function SECOND_DERIV in MATLAB The output of the function should be the approximate value for the second derivative of the data at x, the input variable of the function Use the forward difference method and.

X2+y225 second derivative at 4 3. Derivative (Chain Rule) y ’ =½(r 2 − x 2) y = −3/4 x 25/4 Another Example Sometimes the implicit way works where the explicit way is hard or impossible Example 10x 4 − 18xy 2 10y 3 = 48 How do we solve for y?. Find the second derivative of y by implicit differentiation from the equation 4x^28y^2=36 A 64x^2 B (– 9/4y^3). Now the lefthand side gets the second derivative of y with respect to to x, is going to be equal to, well, we just use the power rule again, negative three times negative 12 is positive 36, times x to the, well, negative three minus one is negative four power, which we could also write as 36 over x to the fourth power And we're done.
The procedure to use the second derivative calculator is as follows Step 1 Enter the function in the respective input field Step 2 Now click the button “Submit” to get the derivative Step 3 Finally, the second order derivative of a function will be displayed in the output field. d dx (x2) d dx (y2 = 25) Using the power rule, d dx (x2) becomes 2x, and if we treat y2 as a constant, the derivative of that and 25 becomes 0 We're just left with 2x d dx = 2x Finding the Second Derivative d dx (2x) = 2 Through finding the second derivative, we arrive at 2 Please excuse me if my answer is misleading or incorrect, as I. 472 Apply a second derivative test to identify a critical point as a local maximum, local minimum, or saddle point for a function of two variables;.
X^2y^2=25 2x 2y\frac{dy}{dx}=0 \displaystyle\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{x}{y. The Derivative Calculator supports solving first, second, fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots You can also get a better visual and understanding of the function by using our graphing tool Chain Rule d d x f (g (x)) = f ' (g (x)) g ' (x) Step 2 Click the blue arrow to submit. Finding the first derivative of the function x 2 y 2 = 4 gives you y ′ = − x y Then to find the 2nd derivative you apply the quotient rule, which looks like this y ″ = y ( − 1) − ( − x) y ′ y 2 which gives you − y x y ′ y 2 But after looking in the back of the book I realized my answer was wrong calculus implicit.
X^2y^2=25 second derivativeIf the second derivative is greater than zero, the stationary point is a minimum If the second derivative equals zero, the stationary point could be a point of inflection The derivative of a curve is found to be g ′ (x) = 4 x 2 − 7 2 x g'(x) = 4x^2 \frac{7}{2}x g ′ (x) = 4 x 2 − 2 7 xWe have to evaluate the. We don't have to!. 1) is a critical point The second derivative test f xx = 2;f yy = 2;f xy = 0 shows this a local minimum with.
First, differentiate with respect to x (use the Product Rule for the xy 2 term). Free derivative calculator differentiate functions with all the steps Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. The Derivative Calculator supports computing first, second, , fifth derivatives as well as differentiating functions with many variables (partial derivatives), implicit differentiation and calculating roots/zeros You can also check your answers!.
Second Derivative A derivative basically gives you the slope of a function at any point The derivative of 2x is 2 Read more about derivatives if you don't already know what they are!. Use the diff function to approximate partial derivatives with the syntax Y = diff (f)/h, where f is a vector of function values evaluated over some domain, X, and h is an appropriate step size For example, the first derivative of sin (x) with respect to x is cos (x), and the second derivative with respect to x is sin (x). H2 Key Point 12 Second Derivative Approximation A central difference approximation to the second derivative f00(a) is f00(a) ≈ f(ah)−2f(a)f(a−h) h2 Example 21 The distance x of a runner from a fixed point is measured (in metres) at intervals of half a second The data obtained are t 00 05 10 15 x 000 365 680 990 1215.
If 2x2 y2 = 17 then evaluate the second derivative of y with respect to x when x = 2 and y = 3 Round your answer to 2 decimal places Use the hyphen symbol, , for negative values. y = x3 2 Apply the power rule y' = 3 2x1 2 And again for the 2nd derivative y'' = 3 4x− 1 2 y'' = 3 4 1 x1 2 y'' = 3 4√x Either way gets you there Answer link. Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ If x^2y^2=25, what is the value of d^2y/dx^2 at the point (4,3)?.
Find dy/dx x^2y^2=25 Differentiate both sides of the equation Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate Since is constant with respect to , the derivative of with respect to is Reform the equation by setting the left side equal to the right side Solve for Tap for more steps. And the second derivative of g(x) at x = 5 is g00(5) = 6 ¢5¡18 = 30¡18 = 12 Therefore the second derivative test tells us that g(x) has a local maximum at x = 1 and a local minimum at x = 5 Inflection Points Finally, we want to discuss inflection points in the context of the second derivative. Answer (1 of 4) First derivative is 2^x ln2 and derivative of 2^x ln2 is ln2 2^x ln2 That is (ln2)^2 * 2^x.
Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. Now we use the second derivative test for x = 2 y''(2) = 6(2) = 12 < 0 Hence the graph has a relative maximum at x = 2 Plugging into the original equation yields (2) 3 12(2) = 16 Now we use the second derivative test for x = 2 y''(2) = 6(2) = 12 > 0 Hence the graph has a relative minimum at x = 2 Plugging into the original. 1 Find the derivative f0(x) of the function f(x) = 5x2 2 Find the derivative dy/dx of the constant function y = 4 3 Find the tangent line to the graph y = √ x at the point (4,2) 4 Find all points on the graph of f(x) = 3x21 where the tangent line has slope 1 5 Find the derivative of the function y = f(x) = x − 2 at the point x.
Textbook Exercise 65 Determine the equation of the tangent to the curve defined by F ( x) = x 3 2 x 2 − 7 x 1 at x = 2 Gradient of tangent = F ′ ( x) F ′ ( x) = 3 x 2 4 x − 7 F ′ ( 2) = 3 ( 2) 2 ( 4) ( 2) − 7 = 13 ∴ Tangent y = 13 x c where c is the y intercept Tangent meets F ( x) at ( 2;. 473 Examine critical points and boundary points to find absolute maximum and minimum values for a function of two variables. The "Second Derivative" is the derivative of the derivative of a function So Find the derivative of a function Then find the derivative of that.
Subject to the constraint 2x2 (y 1)2 18 Solution We check for the critical points in the interior f x = 2x;f y = 2(y1) =)(0;. Second Order Derivative Examples Let us see an example to get acquainted with secondorder derivatives Example 1 Find d2y dx2 d 2 y d x 2 if y = e(x3)–3x4 e ( x 3) – 3 x 4 Solution 1 Given that y = e(x3)–3x4 e ( x 3) – 3 x 4 , then differentiating this equation wrt x we get, dy dx = e(x3)×3x2–12x3 d y d x = e ( x 3) × 3 x 2. P 3 (3/23/08) Section 144, Chain Rules with two variables Example 5 What is the tderivative of z = f (x(t),y(t)) at t = 1 if x(1) = 2,y(1) = 3,.
Learning Objectives 471 Use partial derivatives to locate critical points for a function of two variables;. Answer to x^2y^2 = 25 Find the first and the second derivative By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework. Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp Conic.
Interactive graphs/plots help visualize and better understand the functions. SOLUTION 1 Begin with x 3 y 3 = 4 Differentiate both sides of the equation, getting D ( x 3 y 3) = D ( 4 ) , D ( x 3) D ( y 3) = D ( 4 ) , (Remember to use the chain rule on D ( y 3) ) 3x 2 3y 2 y' = 0 , so that (Now solve for y' ) 3y 2 y' = 3x 2, and Click HERE to return to the list of problems SOLUTION 2 Begin with (xy) 2 = x y 1 Differentiate both sides. Derivative calculator This calculator evaluates derivatives using analytical differentiation It will also find local minimum and maximum, of the given function The calculator will try to simplify result as much as possible.
65 Second derivative (EMCH9) The second derivative of a function is the derivative of the first derivative and it indicates the change in gradient of the original function The sign of the second derivative tells us if the gradient of the original function. Eg Write input x 2 as x^2 2 Use ^(1/2) for square root ,'*' for multiplication, '/' for division, '' for addition, '' for subtraction Eg1 Write input √x as x^(1/2) 2 Write 5x as 5*x 3 Write x5 as x5 4 Write x 25x as x^25*x 3 Use paranthesis() while performing arithmetic operations Eg1 Write sinxcosxtanx as sin(x)cos(x. A function that is decreasing on the intervals \(3 \lt x \lt 2\) and \(0 \lt x \lt 2\) and increasing on \(2 \lt x \lt 0\) and \(2 \lt x \lt 3\text{}\) Subsection 162 The Second Derivative We are now accustomed to investigating the behavior of a function by examining its derivative.
The test has three outcomes If the second derivative is less than zero, the stationary point is a maximum If the second derivative is greater than zero, the stationary point is a minimum If the second derivative equals zero, the stationary point could be a point of inflection The derivative of a curve is found to be g ′ ( x) = 4 x 2 −. 1) Find the second derivative of x^2 y ^ 2 = 25 I can only find the first derivative i can't find the second 2) Find the second derivative of y = x^2 y^3 xy I actually have no clue how to find the second derviative This sort of question is going to be on a test, but my teacher didn't cover it So please explain it step by step. To classify critical points as maximums or minimums, we look at the second derivative The point was called a minimum iff00(x 0) > 0anditwascalledamaximumiff00(x 0) < 0 I like the From (4 ,0) to (0,3), the line that defines it is y = x/22 for 0 x 4 Instead or parametrizing, let’s plug in.
Ex 57, 1 Find the second order derivatives of the function 𝑥^2 3𝑥 2 Let 𝑦 = 𝑥^2 3𝑥 2 Differentiating 𝑤𝑟𝑡𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑(𝑥^2 3𝑥 2))/(𝑑𝑥 ) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑(𝑥^2))/𝑑𝑥 (𝑑(3𝑥) )/𝑑𝑥 (𝑑(2) )/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = 2𝑥30 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒙 = 𝟐𝒙 𝟑 Again Differentiating 𝑤𝑟. Given a function , there are many ways to denote the derivative of with respect to The most common ways are and When a derivative is taken times, the notation or is used These are called higherorder derivatives Note for secondorder derivatives, the notation is often used At a point , the derivative is defined to be. Again, let z = f(x;y) be a function of x and y † @ 2z @x2 means the second derivative with respect to x holding y constant † @ 2z @y2 means the second derivative with respect to y holding x constant † @ 2z @x@y means difierentiate flrst with respect to y and then with respect to x The \mixed" partial derivative @ 2z @x@y is as.
F ( 2)) F ( 2) = ( 2) 3. So the second derivative of g(x) at x = 1 is g00(1) = 6¢1¡18 = 6¡18 = ¡12;. When x = t3 −t and y = 4− t2 x = t3 − t y = 4−t2 dx dt = 3t2 −1 dy dt = −2t From the chain rule we have dy dx = dy dt dx dt We can apply the chain rule a second time in order to find the second derivative, d2y dx2 d2y dx2 = d dx dy dx = d dt dy x dx dt = 3 2 2t = 3 4t wwwmathcentreacuk 6 c mathcentre 09 Key Point if x.
Answer (1 of 2) If x^2y^2=25, what is the value of \frac{d^2y}{dx^2} at the point (4,3)?. 1 For Windows or Linux Press CtrlD 2 For MacOS Press CmdD 3 For iPhone (Safari) Touch and hold, then tap Add Bookmark 4 For Google Chrome Press 3 dots on top right, then press the star sign. 新しいコレクション x^2 y^2=25 second derivative 7562X^2y^2=25 second derivative Example 17 Find Points On X2 4 Y2 25 1 At Which Tangents X^2y^2=25 second derivative X^2y^2=25 second derivativeSecond Derivative D 2 Er W Dw 2 Of The Real Part Of E For Cuin5se8 Download Scientific Diagram.
If x^2 y^2 = 25, what is the value of d^2y/dx^2 at point (4,3)?. F ( x) = e − 2 x − x (a) Use calculus to determine the correct value of the derivative at x = 2 (b) To evaluate the centered finitedifference approximations, start with x = 05 Thus, for the first evaluation, the x values for the centered difference approximation will be. In this chapter, we solve secondorder ordinary differential equations of the form − (E12) Approximating the derivative 2 2 dx d y at node i by the central divided difference approximation, q y L x T T (25) 2 3 3 7 3 6 2 4 3 2 y x x y y y.
Chapter 4 Taylor Series 17 same derivative at that point a and also the same second derivative there We do both at once and define the second degree Taylor Polynomial for f (x) near the point x = a f (x) ≈ P 2(x) = f (a) f (a)(x −a) f (a) 2 (x −a)2 Check that P 2(x) has the same first and second derivative that f (x) does at the point x = a 43 Higher Order Taylor Polynomials. It is best to apply implicit differentiation Differentiating y with respect to x yields.
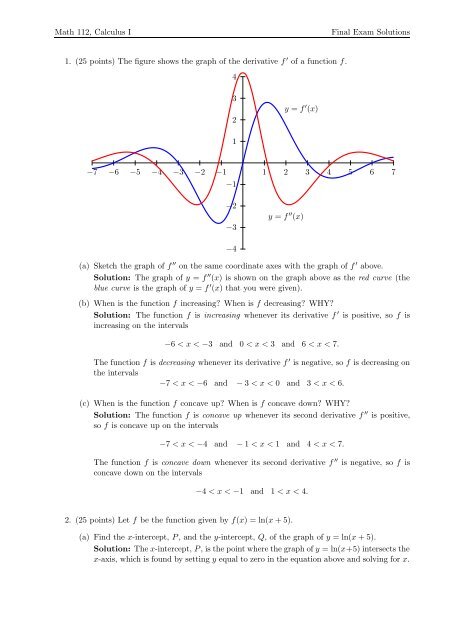
Math 112 Calculus I Final Exam Solutions 1 25 Points The Figure
1

Objectives 1 Be Able To Determine If An Equation Is In Explicit Form Or Implicit Form 2 Be Able To Find The Slope Of Graph Using Implicit Differentiation Ppt Download
X2+y225 Second Derivative At 4 3 のギャラリー

Solved C Calculate The Second Derivative Of F Find Where F Is Concave Up Concave Down And Has Inflection Points F C 0 3x 21 25v 6x 2 4 3 Union Of The Intervals Where F R E Is Concave Up Inf 2 2inf
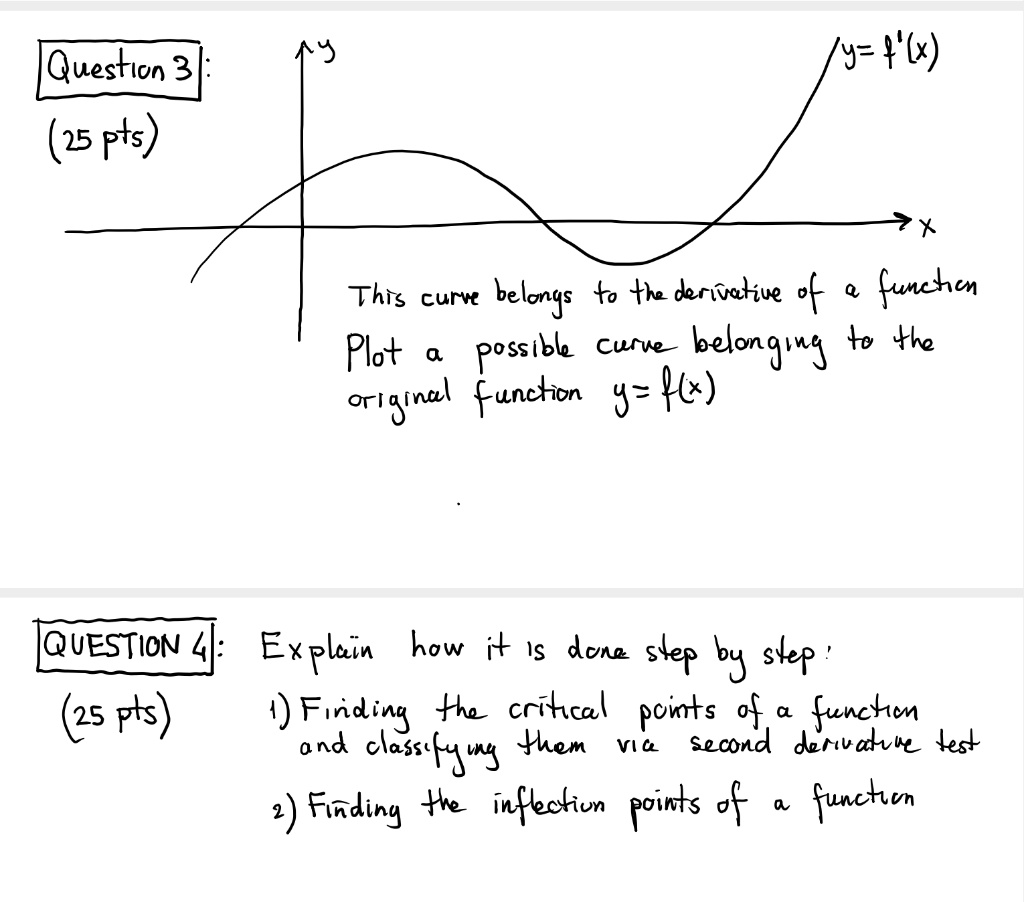
Solved Uestlon 3 Y X 25 Pts This Curvt Belongs To Th Deriveliue F Funhon Plot A Possibl Curve Belongi 3 Te 4he Or 3inel Functon 4 Hc Iquestion Explain How I Is
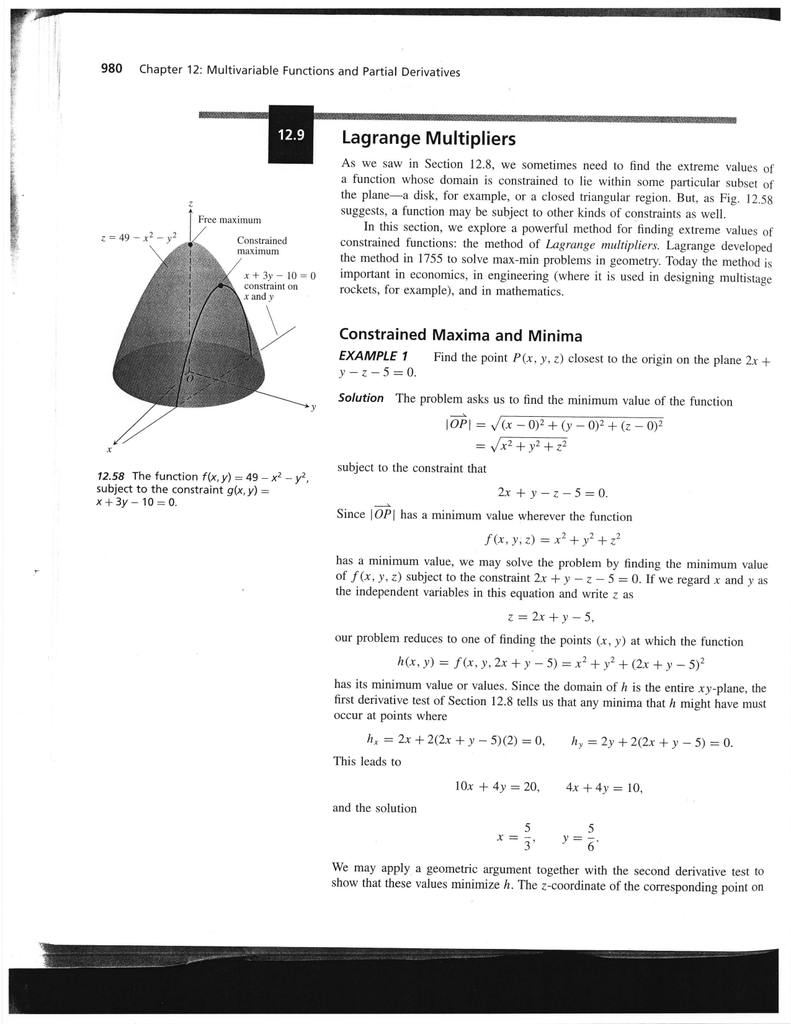
Lagrange Multipliers

Solved Y V1 X2 1 31 2 X Y 2 25 X Y 3 1 Chegg Com
Cocalc Implicit Differentiation Notes Sagews
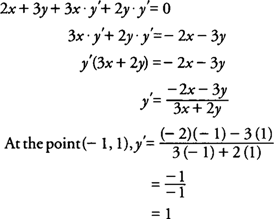
Implicit Differentiation
2
2
Booksubjectcalculu High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
What Is The Minimum Value Of A Positive Real Number Y Such That Y Sqrt X 6 2 25 Sqrt X 6 2 121 Quora

Solved Second Derivative P X F X 2 16fx 1 30x Chegg Com
3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1

Solved Questin 2 25 Marks Find For Y 2x 7x Marks Find The Second Order Derivative For F X In X Sx 1 Matks Suppose The Demand For Certain Item Is P

Example 17 Find Points On X2 4 Y2 25 1 At Which Tangents
Cocalc Implicit Differentiation Notes Sagews

3 Derivatives Derivatives The Functions That We Have
Equation Of A Circle
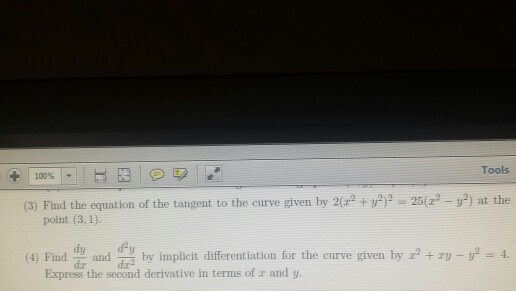
Solved Find The Equation Of The Tangent To The Curve Given Chegg Com
2
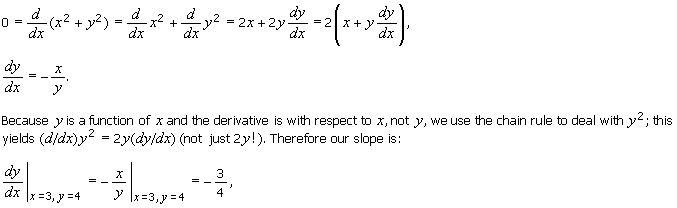
4 2 Implicit Differentiation
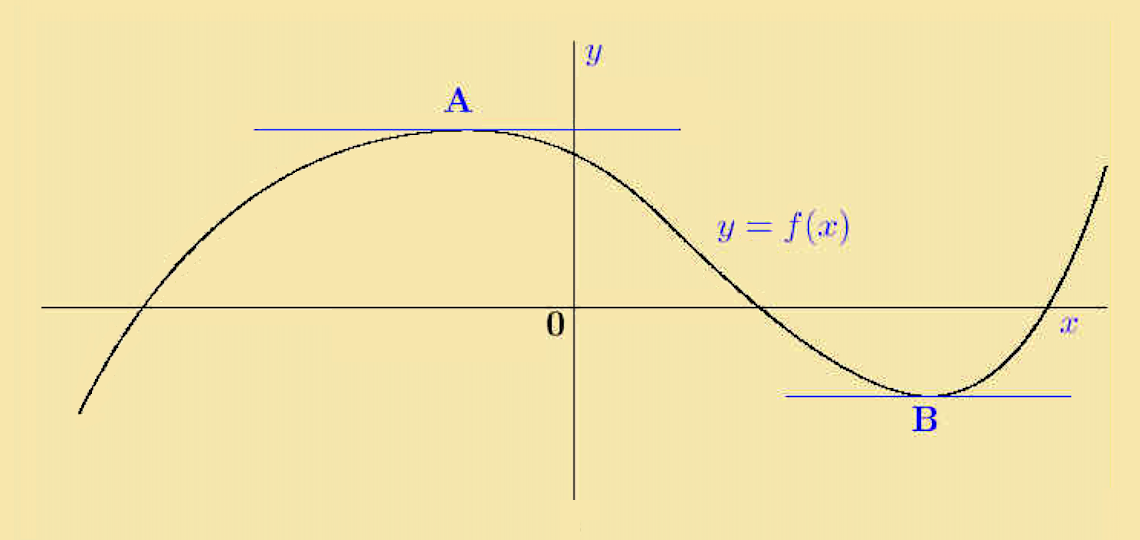
Pplato Basic Mathematics Maxima And Minima

Solved 1 Find The Second Derivative D 2y Dx 2 As A Function Chegg Com
Business Calculus
How To Find Tangents To Circle X 2 Y 2 10 At The Points Whose Abscissae Are 1 Quora

Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
2

Problem Of The Day If X 2 Y 2 25 What Is The Value Of D 2 Y At The Point 4 3 Dx 2 A 25 27 C 7 27 E 25 27 B 7 27 D 3 4 Ppt Download

Unit 2 Lesson 9 Implicit Differentiation 1 2 So Far We Have Been Differentiating Expressions Of The Form Y F X Where Y Is Written Explicitly In Ppt Download
2
What Is The Tangent Through 7 1 For Circle X 2 Y 2 25 Quora

Solved Find The First And Second Derivatives Of The Chegg Com

Solved Find The First And Second Derivatives Of The Chegg Com

2 6 Webassign Answers

Warm Up 10 3 13 1 The Graph Of The Derivative Of F F Is Given Which Of The Following Statements Is True About F A F Is Decreasing For 1 X Ppt Download
Example 17 Find Points On X2 4 Y2 25 1 At Which Tangents
Implicit Differentiation Calculator
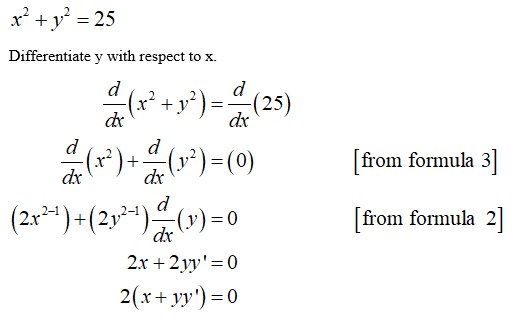
Answered Given X2 Y2 25 Find D2y Dx2 Bartleby

If A X Y X 2 Y 2 25 And B X Y X 2 9y 2 144 Then A B Contains
Can You Find The Point In The First Quadrant On The Lemniscate 2 X 2 Y 2 2 25 X 2 Y 2 Where The Tangent Is Horizon X And The Value Of Y Is Unknown Quora

Curve Sketching
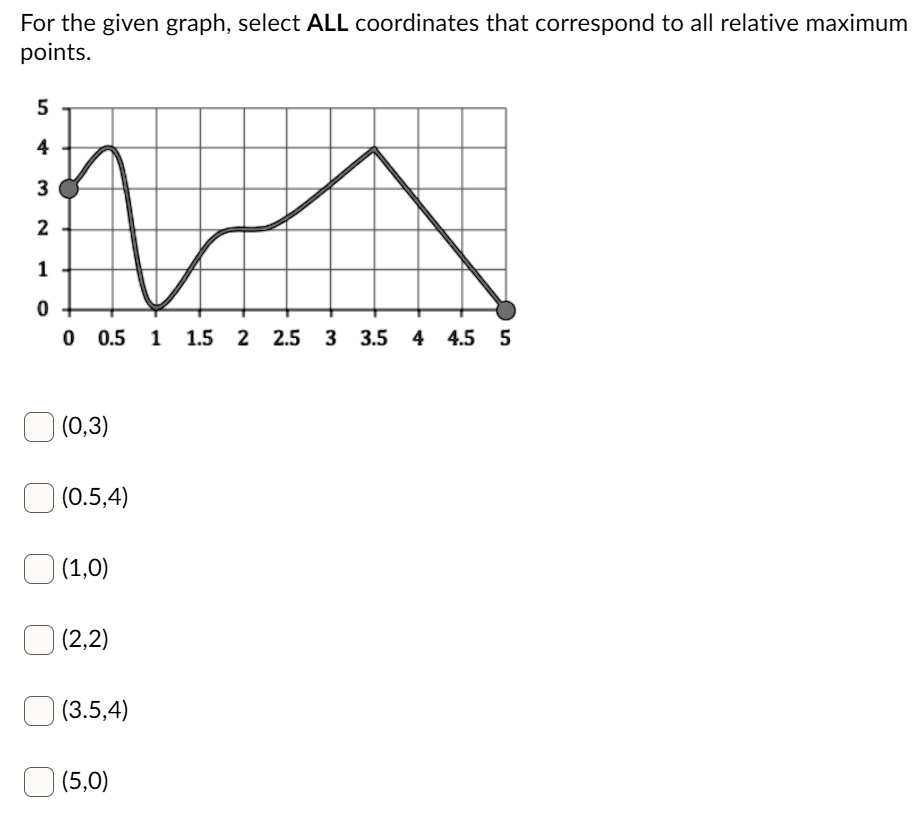
Solved For The Given Graph Select All Coordinates That Correspond To All Relative Maximum Points 5 2 1 0 5 15 2 25 3 3 5 4 45 5 0 3 0 5 4 1 0 2 2 3 5 4 5 0

Solved 2 25 Pts Ordinary Differential Equations Solve The Following Initial Value Problems Ivp Using The Modified Euler Method With A The Average Derivative And B The Derivative At Midpoint Dy 4y

14 1 Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Libretexts

Oneclass 1 Use Implicit Differentiation To Find Dy Dx If Xy Sin X Sin Y 2 Suppose 6x2 3xy
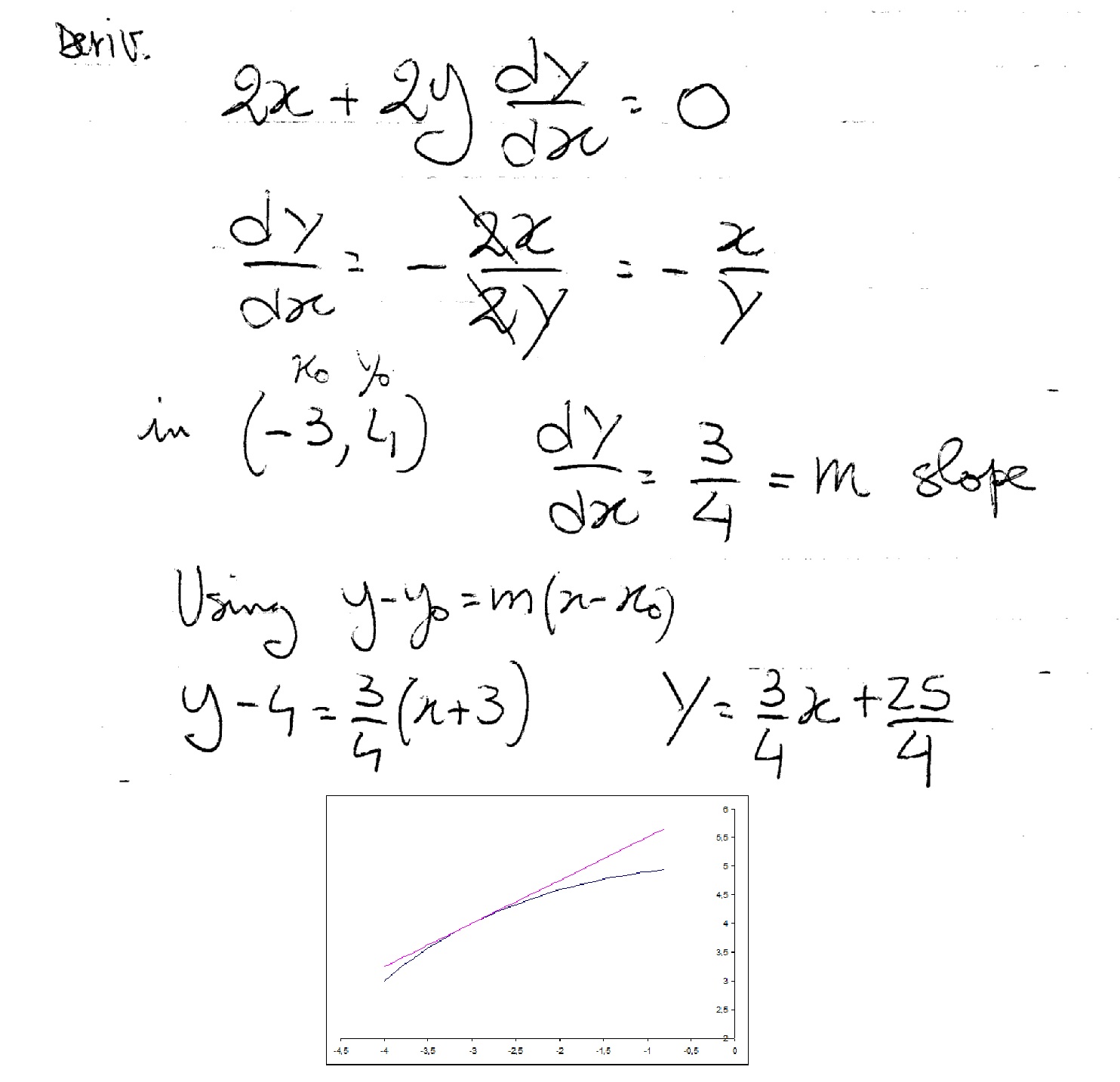
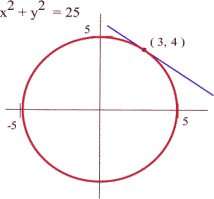
How Do You Find Equation Of Tangent To Circle X 2 Y 2 25 At The Point 3 4 Socratic

Solution Find The Second Derivative Of Y By Implicit Differentiation
Implicit Differentiation
If X 2 Y 2 6x 8y 0 What Is The Maximum Value Of X 2 Y 2 Quora

Sofve Eschuahon3 8 1 5 2 25 X Loo J X Lot 6 Itprospt
What Is The Slope Of The Tangent Line To The Circle X Y 25 At The Point 3 4 Quora
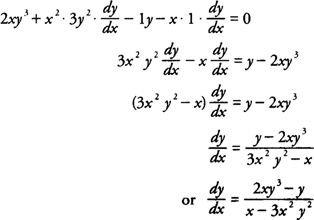
Implicit Differentiation

Solved Derivatives Calculus For Scientists And Engineers Early Transcendental Numerade

Solved A Scalar Function Is Given By F X Y Z Z X 2 Chegg Com

D Use Logarithmic Differentiation To Find Dz 1703 944 22 3 23 4 25 2 Homeworklib

Ap Calculus September 12 Ppt Download
What Is The Slope Of The Tangent Line To The Circle X Y 25 At The Point 3 4 Quora

Implicit Differentiation
2

Implicit Differentiation
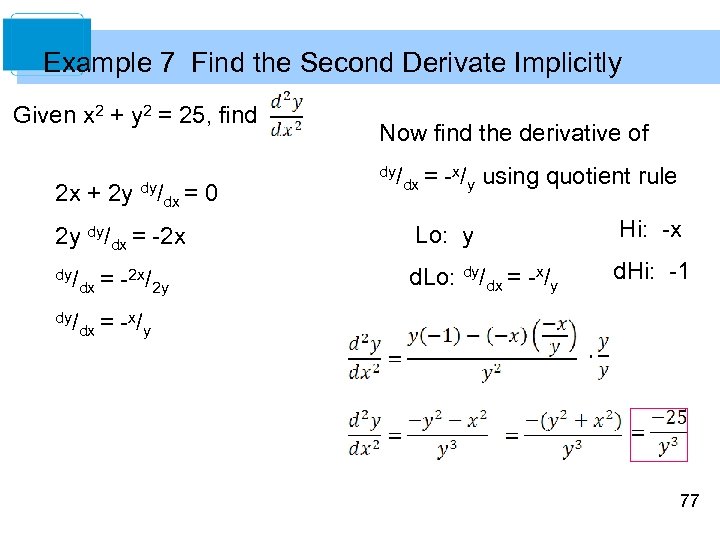
2 Differentiation 2 1 2 2 2 3
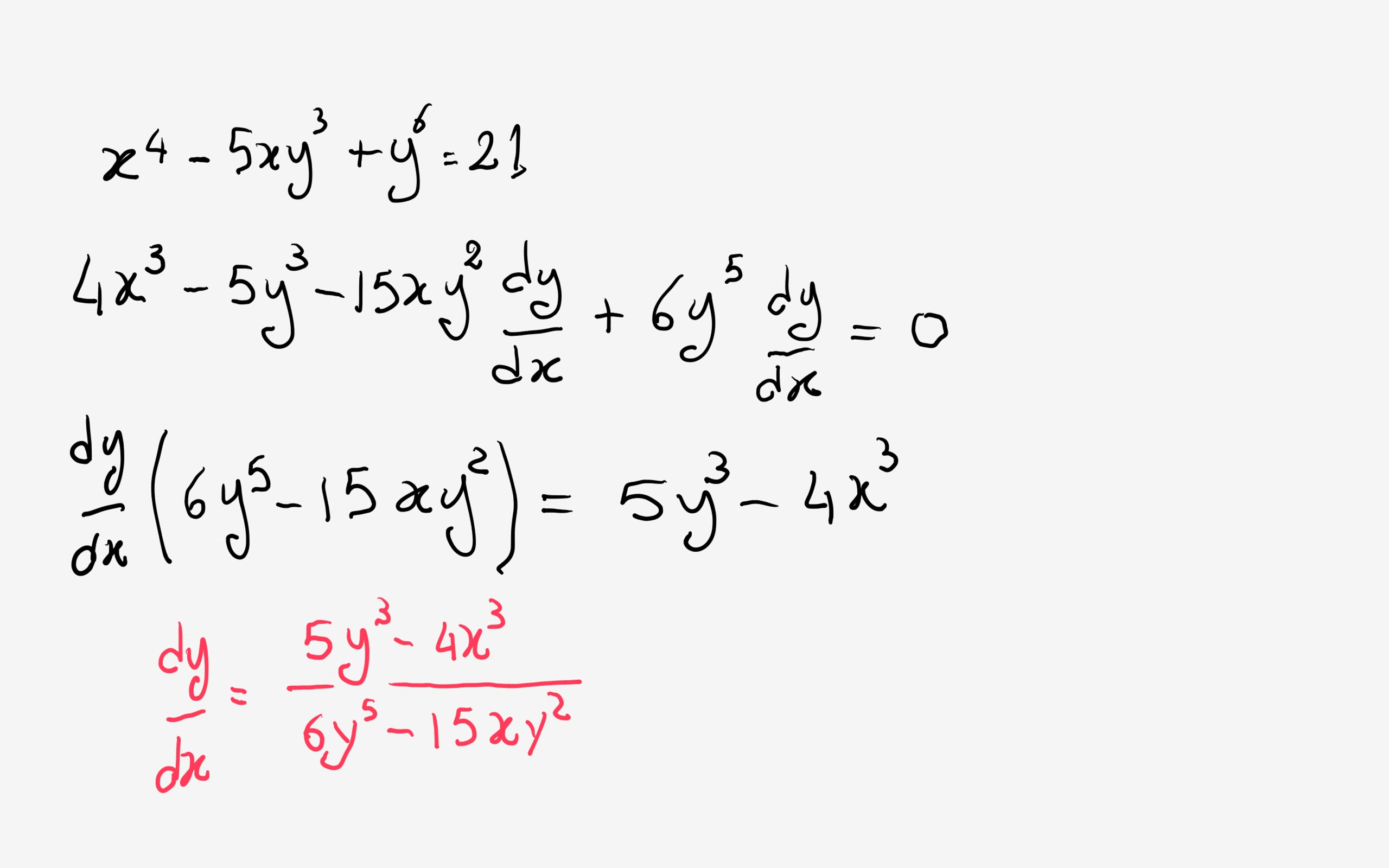
How Do You Find The Implicit Differentiation Of X 4 5xy 3 Y 6 21 Socratic
Implicit Differentiation
Solved Y V1 X2 1 31 2 X Y 2 25 X Y 3 1 Chegg Com
2

2 6 Webassign Answers
How Do You Use The First And Second Derivatives To Sketch Y X 2 25 X 2 Socratic

Unit 2 Lesson 9 Implicit Differentiation 1 2 So Far We Have Been Differentiating Expressions Of The Form Y F X Where Y Is Written Explicitly In Ppt Download

Problem Of The Day If X 2 Y 2 25 What Is The Value Of D 2 Y At The Point 4 3 Dx 2 A 25 27 C 7 27 E 25 27 B 7 27 D 3 4 Ppt Download
Solution Find The Second Derivative Of X 3 5x 2 X 0
Related Rates

Implicit Differentiation

Solved 1 Find The Second Derivative D 2y Dx 2 As A Function Chegg Com
3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1

Solved Question 4 Inflection Points A Function F Z Is Twice Differentiable Everywhere And Has The Following Second Derivative Zx 2 X 3 42 2 25 F C e16 State Each X Coordinate
3 Differentiation

However Some Functions Are Defined Implicitly Some Examples Of Implicit Functions Are X 2 Y 2 25 X 3 Y 3 6xy Ppt Download

Motion Along A Curve Finding Rate Of Change Video Khan Academy

Implicit Differentiation
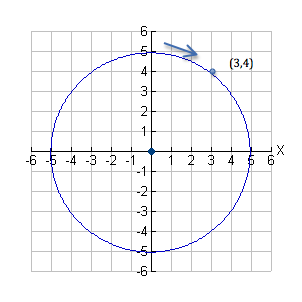
How Do You Use Implicit Differentiation To Find An Equation Of The Tangent Line To The Curve X 2 2xy Y 2 X 39 At The Given Point 5 9 Socratic
2
The Equation Of A Circle Is X 3 2 Y 2 2 25 How Do You Show That The Point A 6 6 Lies On The Circle And Find The Equation Of The Tangent
Solved Find The Absolute Maximum And Minimum On 1 5 F X X 4 Find All Local Extrema Use The First Derivative Test To Classify Them As Ma Course Hero
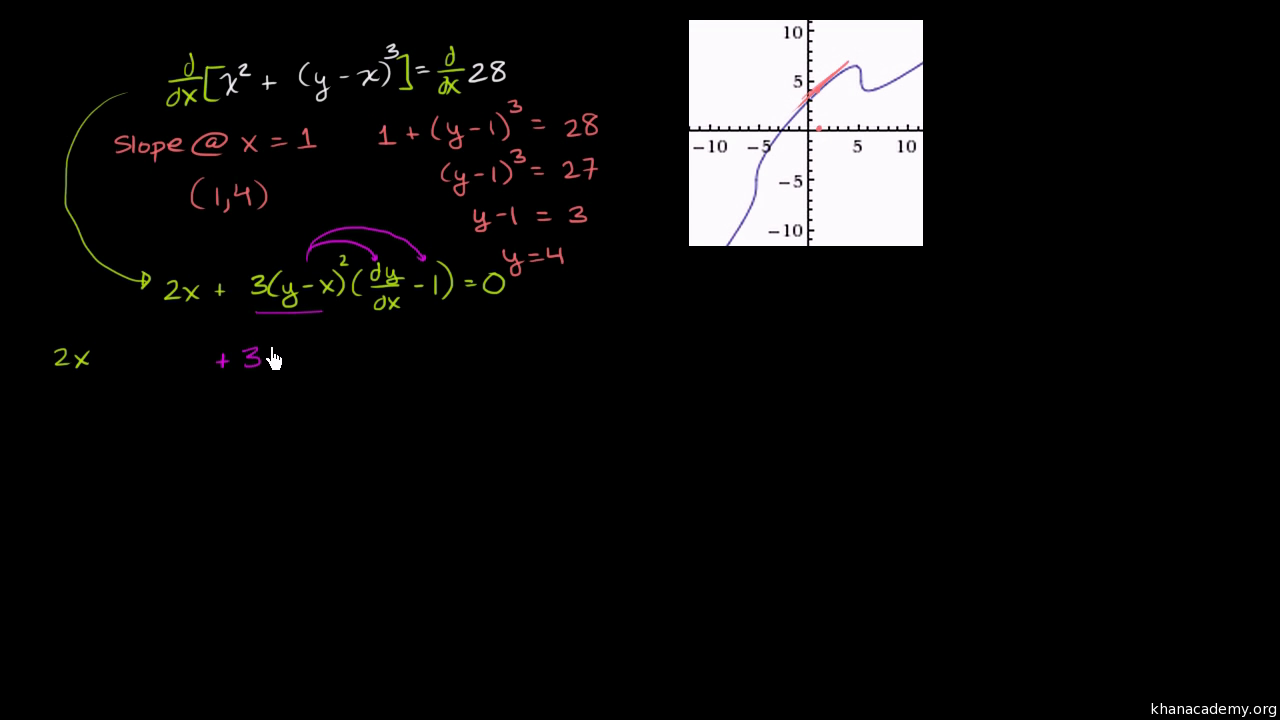
Worked Example Evaluating Derivative With Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy
2

Implicit Differentiation Mastery For Chain Rule U Substitution And Implicit Differentiation Quiz And The Chapter 3 Test Abby S Calc Blog
3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1
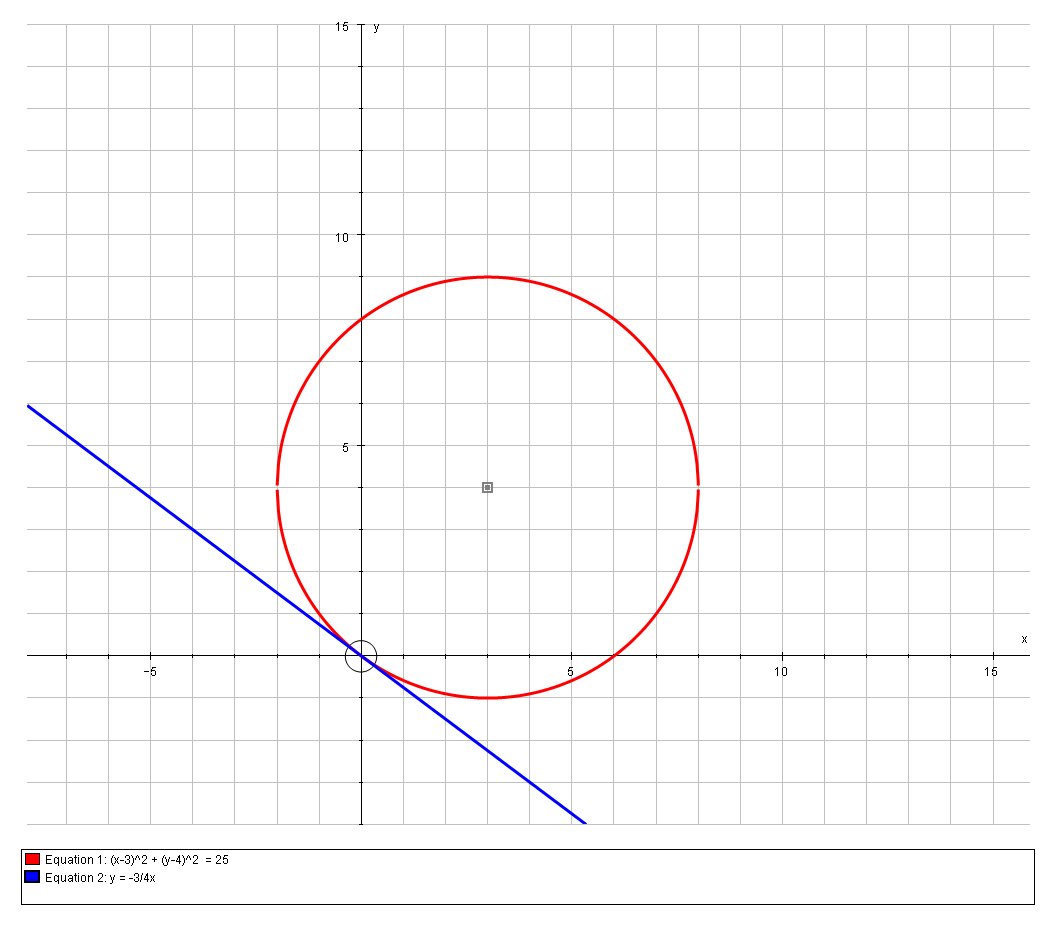
How Do You Write An Equation Of The Line Tangent To X 2 Y 2 6x 8y 0 At The Point 0 0 Socratic
2

4 2 Implicit Differentiation

The Functions That We Have Met So Far Can Be Described By Expressing One Variable Explicitly In Terms Of Another Variable For Example Or Y X Sin Ppt Download
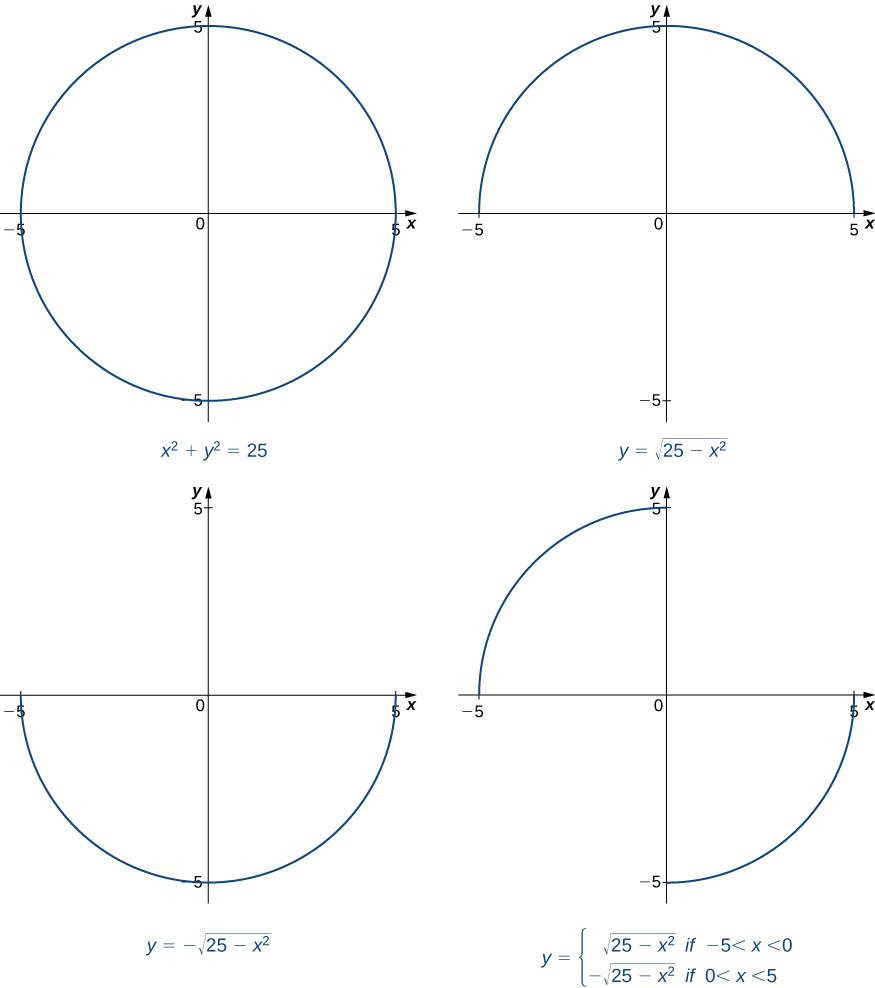
3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1

Problem Of The Day If X 2 Y 2 25 What Is The Value Of D 2 Y At The Point 4 3 Dx 2 A 25 27 C 7 27 E 25 27 B 7 27 D 3 4 Ppt Download
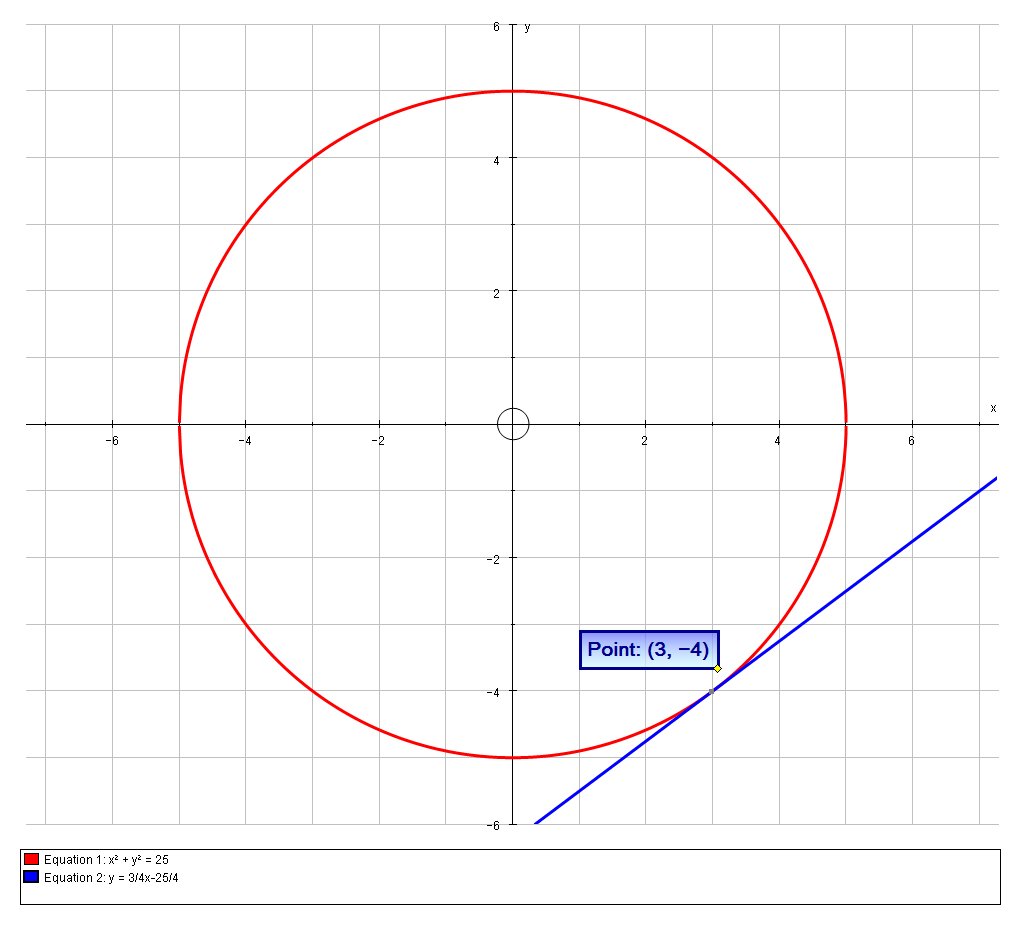
How Do You Find An Equation For The Line Tangent To The Circle X 2 Y 2 25 At The Point 3 4 Socratic

1 Implicit Differentiation 2 Introduction Consider An Equation Involving Both X And Y This Equation Implicitly Defines A Function In X It Could Be Defined Ppt Download
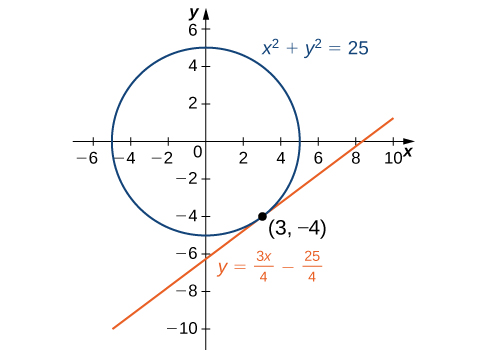
3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1
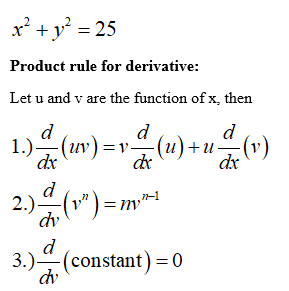
Answered Given X2 Y2 25 Find D2y Dx2 Bartleby

Implicit Differentiation

The Lemniscate 25 R Y Has The Following Graph Determine The Four Points Where This Lemniscate Has A Homeworklib

Solved 3 Find The Equation Of The Tangent To The Curve Chegg Com
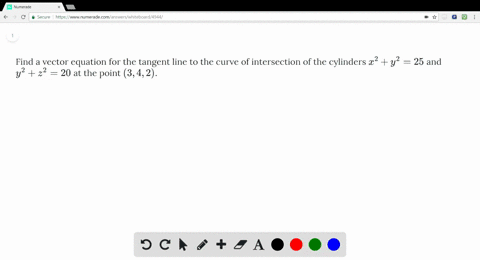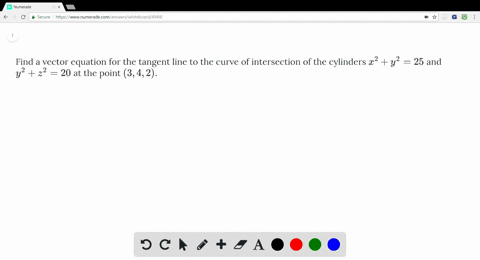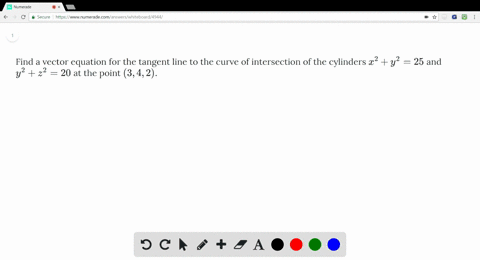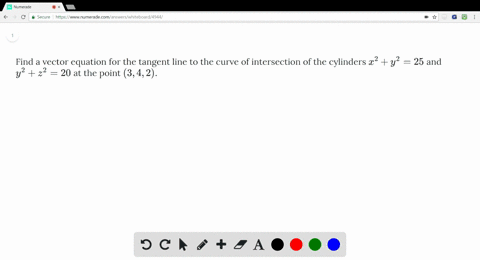
Solved Find A Vector Equation For The Tangent Line To The Curve Of Intersection Of The Cylinders X 2 Y 2 25 And Y 2 Z 2 At The Point 3 4 2

Nonlinear Dynamics Of The Intensity Profile Of A Gaussian Beam Governed Download Scientific Diagram




